Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is often associated with childhood, but it also affects many adults. Contrary to popular belief, ADHD does not necessarily disappear in adulthood. On the contrary, it can evolve and manifest differently, creating unique challenges in daily life. In this article, we will explore what it means to live with ADHD in adulthood and how to support adults with this disorder so they can lead fulfilling lives.
What is ADHD?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurological disorder. It is characterized by symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. In adults, ADHD can manifest in various ways, ranging from difficulties concentrating at work or in daily tasks to uncontrollable impulses that can harm interpersonal relationships. It is essential to understand that ADHD often persists into adulthood and can have a significant impact on daily life.
There are three types of ADHD:
Combined: this is the most common case. In combined ADHD, all signs (inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity) are present.
Inattentive: in this case, there is only inattention, while impulsivity and hyperactivity are not present. This type of ADHD is more challenging to detect.
Hyperactive: this is the least common case. It is characterized by hyperactivity and impulsivity.
Signs in Adults
The signs of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults can be subtle yet disruptive.
Inattention: persistent inattention, with difficulties concentrating on long or boring tasks, as well as frequent forgetfulness of appointments or important responsibilities, marked difficulties regarding concentration and the ability to stay organized. They tend to be constantly distracted, have trouble finishing tasks, and frequently lose essential items.
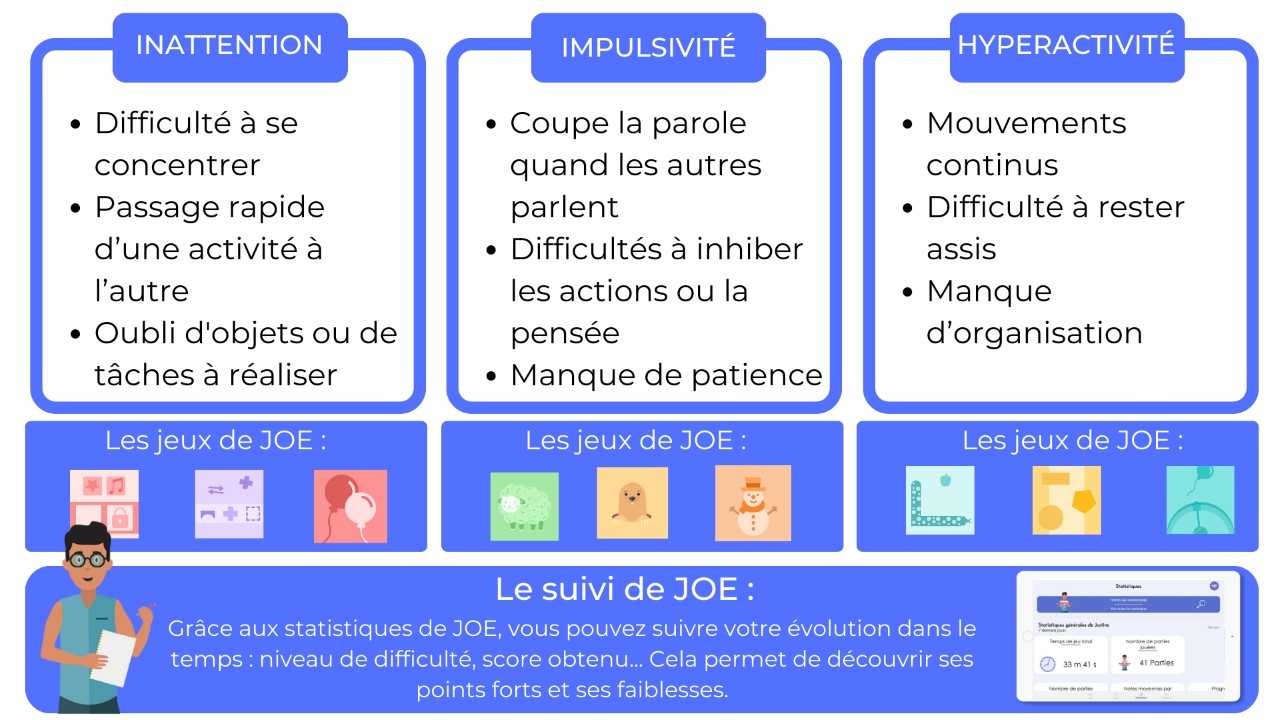
Impulsivity: hasty decision-making or inappropriate comments in conversations, impulsive decisions, and exaggerated emotional reactions.
Hyperactivity (often less obvious in adults than in children): constant inner restlessness, difficulty staying seated for long periods, or a tendency to frequently move their legs, constant mental agitation, difficulties relaxing, and a need for constant stimulation.
These signs can vary in intensity from person to person, and it is essential to recognize them to obtain an accurate diagnosis and seek ways to manage ADHD effectively in adulthood. The symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults encompass a range of manifestations that can significantly influence daily life. When identified and managed appropriately, these symptoms allow adults with ADHD to better understand their own needs and implement strategies to improve their quality of life.
WORK AND ADHD
Balancing work and ADHD can be challenging, but it is entirely achievable. Adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) often encounter difficulties at work due to symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. However, with appropriate strategies, such as establishing a structured routine, time management, prioritizing tasks, and open communication with colleagues and supervisors, it is possible to minimize the negative impacts of ADHD on professional life. Moreover, many adults with ADHD possess traits like creativity, spontaneity, and nonlinear thinking, which can be assets in certain professions. Recognizing ADHD, seeking adequate support, and leveraging strengths associated with the disorder can enable individuals to thrive in their careers despite the challenges they face.

SOCIAL RELATIONS
Social relationships play a crucial role in the lives of adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
Symptoms such as impulsivity, difficulty listening attentively, and a tendency to fidget can sometimes complicate interactions with friends, family, and colleagues. However, awareness and open communication about ADHD can help strengthen relationships. Educating loved ones about the disorder and exploring strategies to manage symptoms, such as medication or therapy, can help improve mutual understanding. Additionally, some characteristics of ADHD, such as spontaneity and creativity, can be assets in social relationships. By adopting effective management strategies and focusing on their strengths, adults with ADHD can maintain positive and fulfilling social connections.
COGNITIVE TRAINING
Cognitive training has garnered increasing interest as an approach to help adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) better manage their symptoms. These programs aim to strengthen cognitive skills such as attention, working memory, and mental flexibility, which are often deficient in individuals with ADHD. By relying on exercises, games, and feedback techniques, cognitive training can help improve concentration, planning, and emotional regulation. While these approaches may be promising, they are not a miracle solution and should not replace other forms of treatment, such as behavioral therapy or medication. The effectiveness of cognitive training can vary from person to person, but they offer an additional tool in the arsenal of ADHD management strategies for adults.
Brain Training Programs
There are many ways to exercise memory and cognitive functions. Daily practice of brain exercises reduces the risks of neurological disorders, as some programs target all cognitive functions.
The brain training program CLINT has been specifically designed for adults to keep the brain healthy through fun and stimulating brain exercises. It includes over 30 cognitive games and targets concentration, focus, reflexes, languages, and many other cognitive functions.
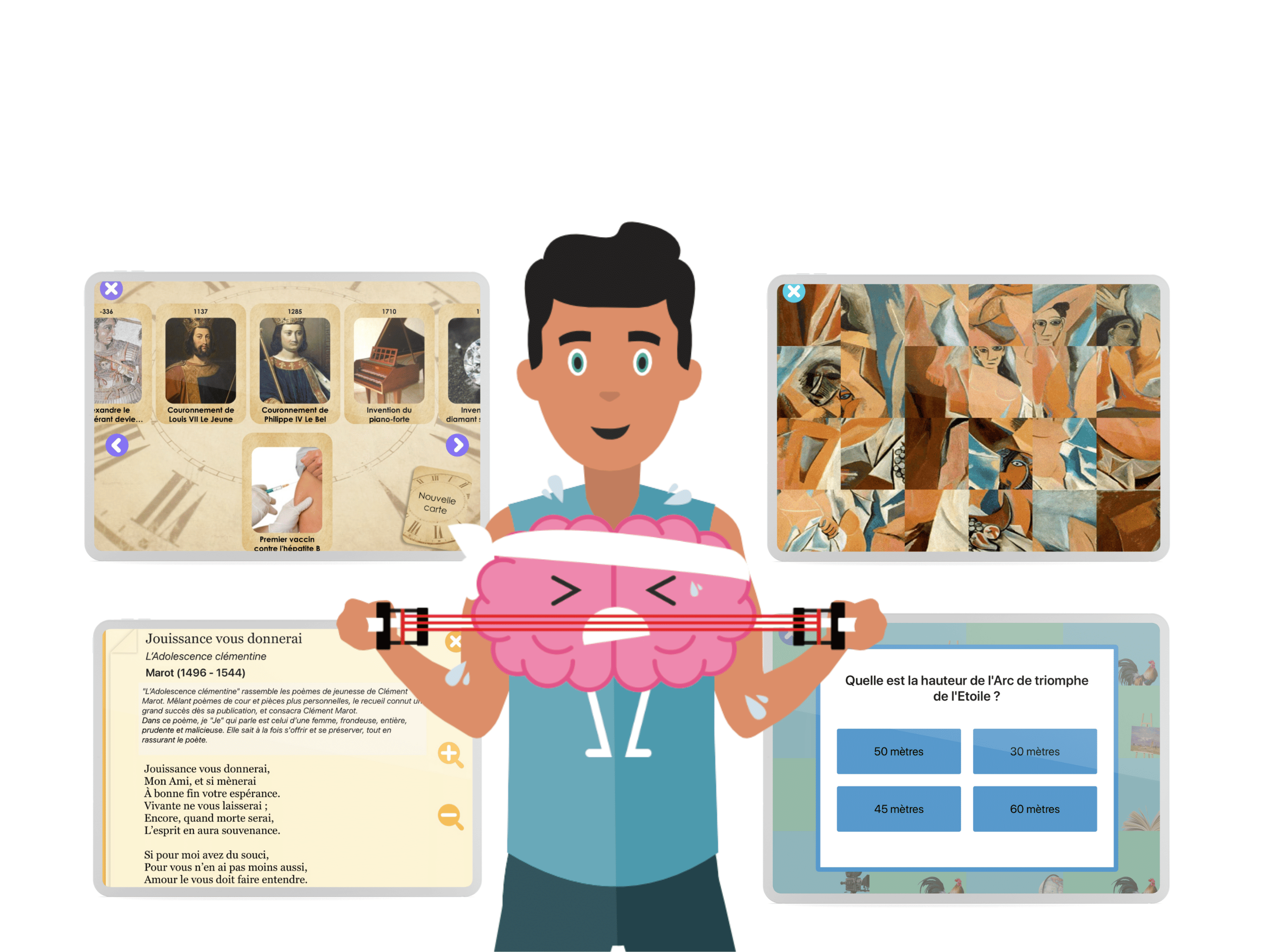
Through games that work on reaction time, activation and inhibition of action, and reflection, CLINT supports adults with ADHD in their lives by stimulating the more fragile cognitive functions.
You can also track your progress over time in the “statistics” tab and thus customize your training! Here are some games offered by Clint:
The Mole Invasion
In this game, the person must click on the moles that appear on the screen.
This game allows for working on inhibition since there are three types of moles: normal moles to click once, moles with helmets to click twice, and moles with glasses not to click. Beyond inhibition, it also works on the ability to adapt the response according to the present stimulus.
Depending on the difficulty level, you can choose the types of moles present in the game.

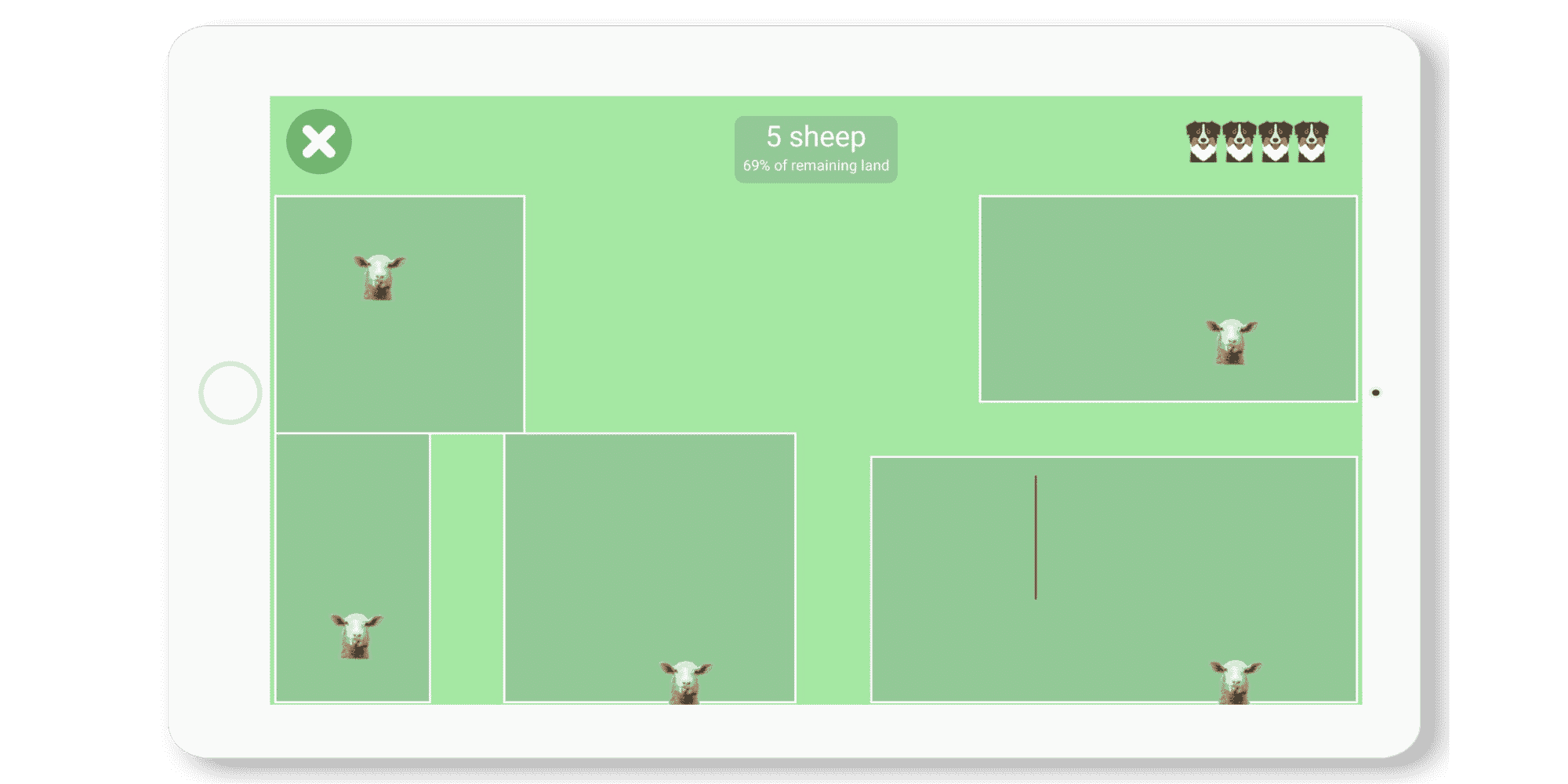
Panurge
In this game, the person must draw lines to reduce the enclosures.
Here, we work on waiting since one must wait for the right moment to draw the line without touching the sheep. The person must also have good anticipation skills to foresee the movements of the sheep and thus know when and where to act.
This activity also allows for working on planning because the person must plan their movements to achieve the goal.
The Crazy Cards
In this game, the person must memorize the order of the cards and reproduce it.
This activity works on attention since the person must closely observe the proposed cards to remember the correct order. In the difficult level, there are also cards that are added after the presentation of the model to memorize (there are thus intruders that the person should not use). You can ask the person to look at the images and, when the time comes to find the correct order, ask them to verbally state the correct order of the images without looking at the screen. This allows for working on associations and thus transitioning from a visual stimulus to an auditory response.

ADHD MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
Managing ADHD in adulthood requires tailored strategies that take into account the specifics of each individual. Here are some effective approaches:
- Establish a daily routine: Creating a structured schedule can help reduce anxiety and improve productivity.
- Use time management tools: Apps or planners can facilitate the organization of tasks and appointments.
- Practice mindfulness: Meditation or breathing techniques can help improve concentration and reduce stress.
- Set priorities: Identifying the most important tasks and addressing them first can help better manage time and efforts.
IMPACT OF ADHD ON MENTAL HEALTH
ADHD can have significant consequences on the mental health of adults. Individuals with ADHD are more likely to suffer from:
- Depression: Difficulties managing daily tasks can lead to feelings of failure and sadness.
- Anxiety: Worry related to organization and performance can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
- Relationship problems: Difficulties in communication and listening can harm personal and professional relationships.
It is crucial to recognize these impacts and seek psychological support, whether through therapy, support groups, or consultations with mental health professionals.
RESOURCES AND SUPPORT FOR ADULTS WITH ADHD
There are many resources available to help adults manage ADHD. Here are some options:
- Support groups: Participating in discussion groups can provide a space to share experiences and advice.
- Books and publications: Many works address ADHD in adults, offering strategies and inspiring testimonials.
- Specialized apps: Time management and productivity apps can help structure tasks and track progress.
- Professional consultations: Working with a specialized coach or therapist can provide personalized support and tailored tools.
NUTRITION AND ADHD
A balanced diet can play a key role in managing ADHD symptoms. Here are some nutritional tips:
- Consume omega-3 fatty acids: These fatty acids, found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, can have a beneficial effect on concentration.
- Avoid added sugars: Excessive sugar intake can worsen symptoms of hyperactivity and inattention.
- Eat regularly: Balanced meals and healthy snacks throughout the day can help maintain stable energy levels.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for optimal brain function and can influence concentration.
By integrating these elements into their diet, adults with ADHD can potentially improve their overall well-being and ability to manage symptoms.









