Social interaction is a fundamental aspect of human development, crucial for building relationships, communication skills, and understanding societal norms. For autistic children, however, navigating these social dynamics can present unique challenges. Understanding the importance of social interaction for their overall well-being is paramount, as it not only shapes their present experiences but also lays the foundation for their future interactions.
Autistic children often encounter obstacles in social settings due to differences in processing sensory information, interpreting social cues, and communicating effectively. These challenges can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration, hindering their ability to form meaningful connections with peers and adults alike. Therefore, it becomes imperative to explore strategies and techniques aimed at facilitating social interactions tailored to the specific needs of autistic children.
By addressing these challenges head-on and providing appropriate support and guidance, we can create environments that foster inclusive social interactions, allowing autistic children to thrive and participate fully in the richness of social experiences.
Understanding Social Communication in Autism
Understanding social communication in autism entails recognizing the differences in social communication skills exhibited by individuals on the spectrum. These differences may manifest in various forms, such as challenges in initiating or maintaining conversations, interpreting nonverbal cues, or understanding social norms.
Common barriers to social interaction for autistic individuals include sensory sensitivities, difficulty with abstract language, and challenges in perspective-taking. It’s essential to acknowledge that each person with autism has their own unique set of strengths and weaknesses in social communication. By recognizing and building upon these individual strengths while addressing areas of difficulty, we can support autistic individuals in developing meaningful social connections and navigating social interactions more effectively.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment for autistic individuals involves several key strategies. Firstly, it’s crucial to establish a safe and comfortable space where they feel secure and at ease. This can be achieved by minimizing sensory overload, such as reducing harsh lighting, loud noises, or overwhelming visual stimuli. Providing sensory-friendly accommodations like noise-canceling headphones or fidget toys can further enhance comfort.
Additionally, clear expectations and guidelines help create predictability and reduce anxiety. This involves straightforwardly communicating rules and routines, using visual supports if needed. By prioritizing the creation of such an environment, we can empower autistic individuals to engage more confidently in social interactions and activities, fostering a sense of belonging and well-being, you can learn more about it here.
Teaching Social Skills
Teaching social skills to autistic individuals involves a systematic approach aimed at breaking down complex social behaviors into manageable steps. This allows for a structured and incremental learning process, which is crucial for comprehension and retention. Visual supports, such as social stories, visual schedules, or picture prompts, provide concrete guidance and reinforcement. Modeling desired behaviors and interactions also plays a significant role in demonstrating social norms and expectations.
Furthermore, practicing social scripts and engaging in role-playing scenarios offer opportunities for hands-on learning and skill development in real-life situations. By employing these strategies consistently and flexibly, educators and caregivers can effectively support autistic individuals in acquiring and mastering essential social skills, enhancing their confidence and competence in social interactions.
Structured Social Activities
Structured social activities tailored to the needs of autistic individuals are instrumental in promoting social engagement and skill development. Planning such activities involves careful consideration of the individual’s preferences and interests, ensuring their active participation and enjoyment. By incorporating activities that align with the child’s passions, whether it’s art, music, sports, or nature exploration, we can enhance their motivation and enthusiasm for social interaction. Group activities, including both peers and siblings, provide valuable opportunities for practicing social skills in a supportive and inclusive setting. These interactions foster communication, cooperation, and the development of friendships, promoting a sense of belonging and camaraderie. Through structured social activities that are both enjoyable and meaningful, autistic individuals can experience positive social experiences and grow in their social abilities.
Peer-Mediated Interventions
Peer-mediated interventions are powerful tools for fostering social interaction and inclusion among autistic individuals. By training peers to support social interaction, we empower them to become allies and advocates in the social development of their autistic peers. This training often involves education on autism spectrum disorders, strategies for communication and interaction, and promoting empathy and understanding. Encouraging empathy among peers helps create a supportive environment where differences are embraced and celebrated. Facilitating inclusive play and interaction opportunities further reinforces the acceptance and integration of autistic individuals within peer groups.
Through peer-mediated interventions, not only do autistic individuals benefit from increased social engagement and acceptance, but peers also gain valuable skills in empathy, communication, and building meaningful relationships that extend beyond the immediate context.
Utilizing Technology for Social Interaction
Utilizing technology for social interaction offers innovative avenues for supporting autistic individuals in developing and enhancing their social skills;
-
Social Skills Apps and Games:
- Offer interactive and engaging platforms for practicing various aspects of social interaction;
- Provide a controlled and supportive environment for individuals to develop their social skills.
-
Video Calls and Online Social Groups:
-
- Facilitate connections with peers regardless of geographical boundaries;
- Enable opportunities for conversation, collaboration, and relationship-building in a virtual space.
-
Virtual Reality Experiences:
- Provide immersive simulations for practicing social skills in realistic scenarios;
- Allow for repeated exposure and learning in a safe and controlled setting, enhancing social competence.
By leveraging technology, we can supplement traditional methods of social skills intervention, offering diverse and accessible options for autistic individuals to develop their social competencies and thrive in social settings.
Encouraging Flexibility and Resilience
Encouraging flexibility and resilience in autistic individuals is vital for navigating the complexities of social interaction. Teaching coping strategies tailored to their specific social challenges equips them with tools to manage stress, anxiety, and sensory overload effectively. Emphasizing the importance of flexibility instills adaptability in navigating unpredictable social situations, encouraging openness to new experiences and perspectives.
Additionally, building resilience involves helping individuals develop the ability to bounce back from social setbacks, such as rejections or misunderstandings, by providing support, validation, and guidance. By fostering a mindset of flexibility and resilience, autistic individuals can approach social interactions with confidence, persistence, and a willingness to learn and grow, ultimately enhancing their overall well-being and social competence.
Collaboration with Educators and Therapists
Effective collaboration with educators and therapists is essential for supporting autistic individuals in their social development. Communicating goals and strategies with school personnel ensures that everyone involved in the individual’s education is working towards common objectives. Implementing social skills training within educational settings allows for consistent practice and reinforcement of learned skills in real-life scenarios. Additionally, seeking guidance from therapists enables the development of individualized interventions tailored to the unique needs of each autistic individual.
By fostering open communication and collaboration among educators, therapists, and other stakeholders, we can create comprehensive support systems that address the social challenges faced by autistic individuals effectively, ultimately promoting their social growth and success in various environments.
Family Involvement and Support
Family involvement and support are crucial factors in the social development of autistic individuals. Educating family members about autism and social interaction fosters understanding and empathy, enabling them to provide appropriate support and encouragement. Creating opportunities for socialization within the family, such as engaging in shared activities or outings, allows autistic individuals to practice social skills in a familiar and supportive environment.
Additionally, providing emotional support and encouragement reinforces their self-esteem and resilience in facing social challenges. By actively involving families in the social development process, we create a network of support that extends beyond formal interventions, promoting the holistic well-being and social integration of autistic individuals within their family unit and broader community.
Celebrating Progress and Successes
Recognizing and celebrating small achievements
Acknowledging and celebrating progress and successes are integral components of supporting autistic individuals in their social development journey. By highlighting milestones achieved along the way, we reinforce the importance of continuous growth and improvement. Celebrating progress not only boosts morale but also fosters a sense of accomplishment and motivation to continue striving towards goals.
Whether it’s mastering a new social skill, initiating a conversation with a peer, or participating in a group activity, each achievement deserves recognition and celebration. By creating a culture that values and celebrates progress, we instill a positive mindset and resilience in facing challenges, ultimately contributing to the overall well-being and success of autistic individuals.
Providing positive reinforcement for efforts in social interaction
In the process of social development, every small achievement is a significant step forward. Recognizing and celebrating these incremental successes are essential for boosting confidence and motivation. Whether it’s making eye contact during a conversation, sharing a toy with a peer, or greeting someone independently, each accomplishment deserves acknowledgment and praise. By highlighting these small achievements, we validate the effort and progress made by autistic individuals, reinforcing their sense of self-worth and competence. Celebrating small victories not only builds confidence but also encourages perseverance and resilience in the face of challenges, fostering a positive and supportive environment for continued growth and development.
Building confidence through acknowledgment of progress
Positive reinforcement plays a vital role in encouraging and reinforcing desired behaviors, particularly in social interaction for autistic individuals. By providing praise, encouragement, or rewards for efforts made in social situations, we reinforce the importance of engaging with others and attempting new social skills. Whether it’s offering a high-five for initiating a conversation, verbal praise for sharing or taking turns, or a small reward for attending a social event, positive reinforcement reinforces the connection between effort and positive outcomes. This not only strengthens social skills but also builds confidence and self-esteem, motivating autistic individuals to continue making progress and actively participating in social interactions.
Facilitating social interaction involves a multifaceted approach. Firstly, it’s essential to implement strategies such as creating inclusive environments, promoting group activities, and providing opportunities for shared interests to foster social engagement.
Additionally, emphasizing the significance of patience and persistence is crucial, as building social skills takes time and effort. Encouraging ongoing support and intervention in social development ensures individuals receive the necessary assistance and guidance as they navigate social interactions. By combining these strategies and emphasizing patience and ongoing support, we can effectively facilitate social interaction and enhance social development for individuals across various contexts.
AND FOR FURTHER INFORMATION

COCO, FOR AUTISTIC CHILDREN
COCO is a program adapted for autistic children that offers a collection of educational and cognitive games. Increasing level of difficulties let the children progress at its own pace. Also a mandatory sports break every 15 minutes of screen time to avoid addiction.

CARING FOR AN AUTISTIC CHILD
In this guide, we’ll give you practicals advice on how to support a child suffering from Autism and how to stimulate and bond with them. Useful day-to-day tips to make life easier for family and professional caregivers.

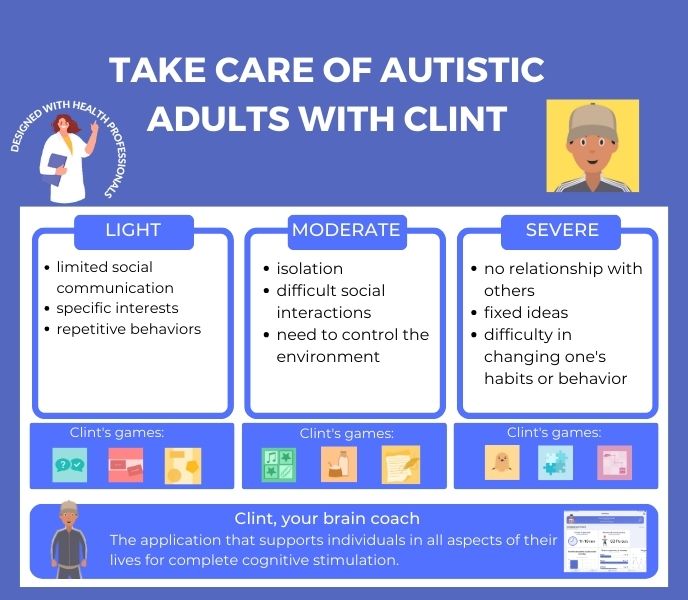
CLINT, FOR AUTISTIC ADULTS
Adapted for adults affected by autism , the CLINT program offers different games in order to develop the knowledge, improve concentration and strengthen mental capacities. CLINT has been designed to be accessible for everyone, and keep a close-eye to the mental health.
Other articles that might interest you:
How Parents Can Contribute to Teacher Training
As we delve into the realm of education, it becomes increasingly clear that teacher training is not merely a...
Differentiated Instruction Approaches: Training and Practical Application
Differentiated instruction is a pedagogical approach that recognizes the diverse needs of students in a classroom. It...
Key Skills Teachers Need to Support Students with Special Needs
As we embark on our journey to support children with special needs, it is essential for us to cultivate a deep...