Parkinson’s Disease, a neurodegenerative disorder affecting millions worldwide, manifests through a spectrum of symptoms, among which fine motor skill challenges stand prominent. Individuals with Parkinson’s often struggle with tasks requiring precision and coordination due to the progressive deterioration of dopaminergic neurons in the brain. These fine motor skill deficits not only impact daily activities but also diminish overall quality of life. However, amidst these challenges, technology emerges as a beacon of hope. Leveraging advancements in assistive technology, individuals with Parkinson’s can regain a sense of independence and functionality.
From specialized computer peripherals to smartphone applications and wearable devices, technology offers innovative solutions tailored to address specific motor impairments. Its significance in Parkinson’s management extends beyond mere assistance; it fosters autonomy and empowerment, enabling individuals to navigate their daily lives with greater ease and confidence. In this context, exploring the intersection of technology and Parkinson’s disease unveils a realm of possibilities poised to redefine the landscape of care and support for those affected by this condition.
Understanding Fine Motor Skill Challenges in Parkinson’s
Definition and Characteristics
Fine motor skill challenges in Parkinson’s Disease encompass difficulties in executing precise movements, stemming from the disruption of neural pathways involved in motor control. These challenges often manifest as tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and difficulties with dexterity and coordination. Individuals with Parkinson’s may experience a progressive decline in their ability to perform tasks requiring delicate manipulation and coordination, such as writing, buttoning clothes, or handling utensils.
Impact on Daily Life Activities
The impact of fine motor skill challenges in Parkinson’s Disease reverberates throughout various aspects of daily life, impeding independence and diminishing quality of life. Simple tasks like dressing oneself, preparing meals, or engaging in hobbies become arduous undertakings fraught with frustration and difficulty. Moreover, fine motor limitations can compromise safety, leading to challenges in tasks such as handling medications or navigating environments. The cumulative effect of these challenges often results in decreased confidence and increased reliance on external support.
Common Strategies for Coping
Individuals with Parkinson’s employ various strategies to cope with fine motor skill challenges and maintain functional independence. These may include breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps, utilizing adaptive aids and assistive devices such as weighted utensils or specialized grips, and practicing relaxation techniques to alleviate muscle rigidity and tremors. Occupational therapy plays a pivotal role in developing personalized strategies to optimize motor function and adapt to evolving limitations. Additionally, leveraging technology, such as voice-activated assistants or electronic organizers, can mitigate the impact of fine motor difficulties and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s.
Introduction to Technological Interventions
Technological interventions in the context of addressing fine motor skill challenges in Parkinson’s Disease encompass a wide array of innovative solutions aimed at enhancing functionality and improving quality of life. This domain encompasses the development and application of assistive devices, software applications, and wearable technology tailored to meet the specific needs of individuals with Parkinson’s. The importance of tailored solutions cannot be overstated, as each person’s experience with Parkinson’s is unique, requiring personalized approaches to effectively address their motor limitations. From specialized computer peripherals designed to accommodate tremors and limited dexterity to smartphone applications facilitating medication management and movement tracking, the landscape of available technologies continues to evolve, offering unprecedented opportunities to empower individuals with Parkinson’s and promote independence in daily activities.
Overview of Parkinson’s Disease and Technology
Parkinson’s Disease has a rich historical context, dating back to its initial clinical description by James Parkinson in 1817. Over the centuries, our understanding of this neurodegenerative disorder has deepened, leading to significant advancements in its management and treatment. One of the most notable evolutions in Parkinson’s care is the integration of technological solutions aimed at ameliorating its symptoms and improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
From the early development of basic assistive devices to the emergence of sophisticated wearable technology and smartphone applications, the landscape of technological interventions in Parkinson’s has expanded exponentially. Today, a diverse array of assistive devices such as smartwatches for monitoring symptoms, specialized utensils for meal preparation, and motion-sensing devices for physi
Assessing Fine Motor Skill Challenges
Assessing fine motor skill challenges in individuals with Parkinson’s Disease requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates various diagnostic methods, including clinical evaluations, neurological examinations, and standardized assessments of motor function. These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals identify the specific nature and severity of fine motor deficits, enabling the formulation of targeted intervention plans. Understanding the unique needs and limitations of each individual is paramount in this process, as it allows for the customization of therapeutic strategies and the selection of appropriate assistive devices or adaptive techniques.
Occupational therapists play a pivotal role in this regard, utilizing their expertise to assess fine motor abilities, identify barriers to independence, and collaborate with individuals to develop personalized interventions aimed at optimizing functional performance and enhancing overall quality of life despite the challenges posed by Parkinson’s Disease.
Technological Solutions for Fine Motor Skill Challenges
Technological solutions offer promising avenues for addressing fine motor skill challenges in individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches equipped with sensors, enable continuous monitoring of movement patterns and symptom fluctuations, providing valuable insights for both patients and healthcare providers. Adaptive tools and equipment designed with ergonomics and ease of use in mind offer practical solutions for everyday tasks, including specialized utensils with larger handles and grip aids to facilitate better manipulation and control.
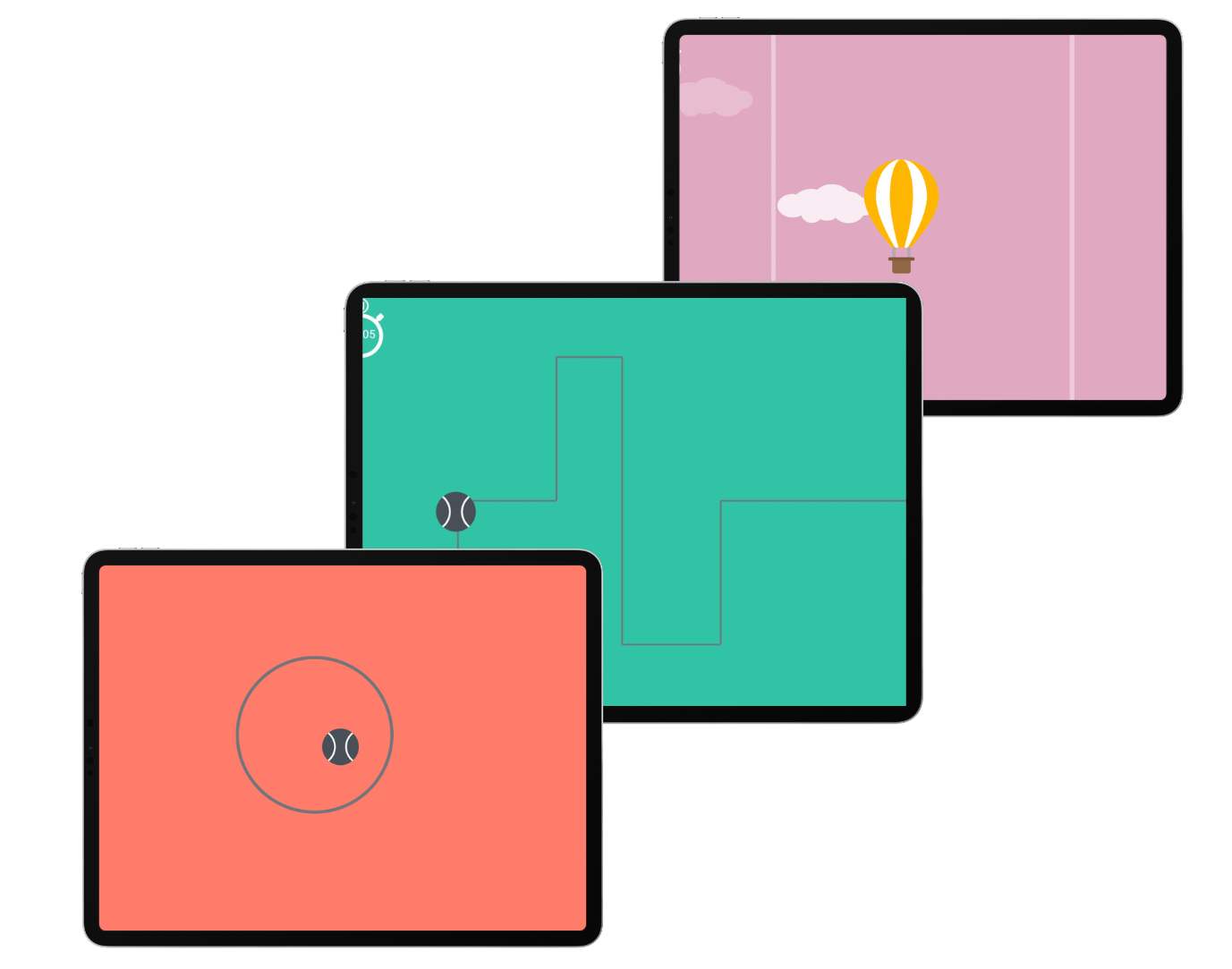
Virtual reality (VR) and gamification present innovative approaches to motor rehabilitation, engaging individuals in interactive and enjoyable activities designed to improve coordination, dexterity, and cognitive function. These technologies not only enhance motor skills but also promote neuroplasticity and functional independence, underscoring their potential to revolutionize the management of fine motor challenges in Parkinson’s Disease. The Rolling Ball app is a great app for that.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the promising potential of technological solutions for addressing fine motor skill challenges in Parkinson’s Disease, several challenges and limitations hinder widespread adoption and effectiveness. Accessibility remains a critical issue, with many individuals facing barriers related to physical access, digital literacy, and cognitive impairments that may limit their ability to utilize technology effectively. Affordability concerns also pose significant obstacles, as specialized devices and software solutions can be prohibitively expensive for many patients and healthcare systems.
Moreover, user acceptance and adoption rates vary widely, influenced by factors such as comfort with technology, perceived usefulness, and ease of integration into daily routines. Overcoming these challenges requires a concerted effort from developers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to prioritize inclusivity, affordability, and user-centered design in the development and implementation of technological interventions for Parkinson’s Disease.
Future Directions and Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of addressing fine motor skill challenges in Parkinson’s Disease is marked by a landscape of emerging technologies, driven by ongoing research and development trends. From advancements in wearable sensors and neurostimulation devices to the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms for personalized intervention strategies, the possibilities for innovation are vast. Research efforts are increasingly focused on understanding the underlying mechanisms of motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s, paving the way for targeted interventions and novel therapeutic approaches.
Collaborative efforts among multidisciplinary teams, including clinicians, engineers, and individuals living with Parkinson’s, foster synergistic innovation and ensure that technological solutions are grounded in real-world needs and experiences. By embracing collaboration, harnessing cutting-edge technologies, and remaining committed to patient-centered care, the future holds tremendous promise for transforming the management and quality of life for individuals with Pa
Ethical Considerations and Privacy Issues
Ethical considerations and privacy issues loom large in the realm of technological interventions for fine motor skill challenges in Parkinson’s Disease. Data security concerns arise as wearable devices and digital platforms collect sensitive health information, raising questions about the protection of personal data from breaches and unauthorized access. Informed consent becomes paramount in technology use, necessitating transparent communication regarding data collection, storage, and usage practices to empower individuals with Parkinson’s to make informed decisions about their privacy.
Moreover, ensuring equitable access to technological solutions requires addressing disparities in digital literacy, socioeconomic status, and healthcare access, to prevent exacerbating existing inequalities. Balancing innovation with ethical principles requires a concerted effort from stakeholders to uphold privacy rights, promote autonomy, and mitigate potential risks associated with the integration of technology into Parkinson’s care.
Integrating Technology into Parkinson’s Care Plans
Integrating technology into Parkinson’s care plans necessitates a comprehensive strategy that encompasses a multidisciplinary approach, training and education for healthcare providers, and empowering patients and caregivers. By adopting a multidisciplinary approach, healthcare teams can leverage diverse expertise to tailor treatment plans effectively. Training and education programs equip healthcare providers with the skills and knowledge required to utilize technology-driven solutions adeptly, ensuring optimal patient care.
Furthermore, empowering patients and caregivers with technological tools fosters active participation in disease management, enhancing their understanding and control over Parkinson’s symptoms and treatment regimens. Together, these components form a cohesive framework that not only enhances the quality of care but also promotes autonomy and improves outcomes for individuals living with Parkinson’s disease.
The integration of technology into Parkinson’s care plans relies on a multifaceted approach, including multidisciplinary collaboration, training for healthcare providers, and empowering patients and caregivers. By recapitulating these key points, we underscore the importance of a holistic strategy in addressing the complex needs of Parkinson’s patients. Moreover, there is a pressing call to action for further exploration and innovation in leveraging technology to advance Parkinson’s care.
Through continued research and development, we can aspire to enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by Parkinson’s disease. Ultimately, there is hope that by embracing technology, we can unlock new possibilities and pathways towards improved management and treatment outcomes for those living with this condition.
AND FOR FURTHER INFORMATION
SCARLETT, EASY MEMORY GAMES FOR PARKINSON
SCARLETT is a user-friendly memory game program that offers a collection of simple yet engaging exercises, specifically designed to gently enhance memory skills. No timer, no score and no failure. Just the pleasure of playing. Try it for free for one week.

CLINT, A CHALLENGING BRAIN GAMES APP
For individuals seeking a more challenging experience, the CLINT program serves as a more demanding version, offering complex memory games that require greater cognitive effort, making it suitable for those in need of a more strenuous mental workout.

THE ROLLING BALL TO WORK ON FINE MOTOR SKILLS
The Rolling Ball app is an innovative tool designed to enhance fine motor skills through engaging and interactive challenges. By guiding a virtual ball through intricate mazes and obstacles, users can improve their precision, control, and hand-eye coordination.
Other articles that might interest you:
How Parents Can Contribute to Teacher Training
As we delve into the realm of education, it becomes increasingly clear that teacher training is not merely a...
Differentiated Instruction Approaches: Training and Practical Application
Differentiated instruction is a pedagogical approach that recognizes the diverse needs of students in a classroom. It...
Key Skills Teachers Need to Support Students with Special Needs
As we embark on our journey to support children with special needs, it is essential for us to cultivate a deep...








