Through thorough analysis and careful consideration, this evaluation aims to provide insights into the diverse array of adapted games, offering guidance to caregivers, families, and healthcare professionals seeking to integrate these resources into their care routines. By highlighting the strengths, weaknesses, and distinctive features of each game, this initiative endeavors to empower individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions in selecting the most suitable games for their loved ones or patients battling Alzheimer’s disease.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by the gradual decline in cognitive function, memory loss, and impairment in daily activities. Individuals with Alzheimer’s face a myriad of challenges, ranging from difficulties in communication and comprehension to issues with problem-solving and spatial awareness. As the disease advances, patients often experience heightened confusion, disorientation, and mood fluctuations, impacting their overall quality of life.
In this challenging landscape, adapted games play a crucial role in Alzheimer’s care, offering therapeutic benefits such as cognitive stimulation, memory retention, and emotional engagement. These games are tailored to suit the specific needs and abilities of individuals with Alzheimer’s, providing a source of enjoyment, social interaction, and mental agility amidst the cognitive decline associated with the disease.
Criteria for Evaluation
Cognitive engagement and stimulation
One of the primary criteria for evaluating adapted games for individuals with Alzheimer’s is their ability to provide cognitive engagement and stimulation. These games should offer activities that challenge various cognitive functions such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and language skills. The effectiveness of the game in promoting mental agility and cognitive enhancement is crucial for maintaining and potentially improving cognitive abilities in Alzheimer’s patients.
Ease of use and accessibility
Ensuring that adapted games are easy to use and accessible is essential for their practical application in Alzheimer’s care. These games should have intuitive interfaces, simple instructions, and user-friendly designs to accommodate individuals with varying degrees of cognitive impairment. Additionally, accessibility features such as adjustable difficulty levels, clear visuals, and audio cues can enhance the overall usability of the games, making them more inclusive and enjoyable for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Emotional engagement and enjoyment
The emotional engagement and enjoyment offered by adapted games play a significant role in their effectiveness as therapeutic tools for Alzheimer’s patients. These games should elicit positive emotions, such as happiness, relaxation, and a sense of accomplishment, to enhance the overall well-being of individuals with Alzheimer’s. Engaging gameplay, captivating visuals, and meaningful content can contribute to creating enjoyable experiences that foster emotional connections and promote a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction.
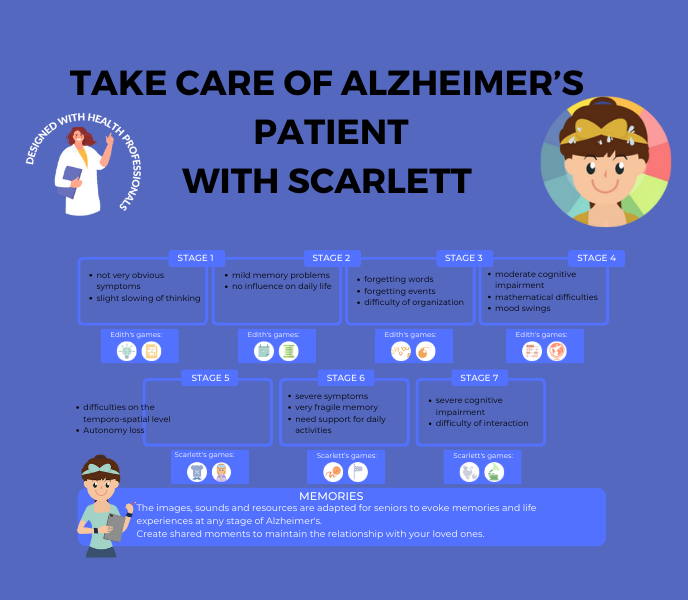
Adaptability to different stages of Alzheimer’s
Adapted games must be adaptable to accommodate the evolving needs and abilities of individuals with Alzheimer’s across different stages of the disease. They should offer flexibility in gameplay options, progression pathways, and customization features to cater to varying levels of cognitive functioning and motor skills. The ability to adjust the game’s complexity, pacing, and content ensures that it remains engaging and beneficial for individuals at different stages of Alzheimer’s, from early to advanced stages.
Safety considerations
Safety considerations are paramount when evaluating adapted games for individuals with Alzheimer’s, as these individuals may be more susceptible to potential risks associated with gaming activities. Games should be designed with built-in safety features to prevent accidental injury, confusion, or frustration. Additionally, monitoring mechanisms and caregiver controls can help ensure that individuals with Alzheimer’s engage with the games safely and without adverse consequences to their physical or emotional well-being. Prioritizing safety measures enhances the overall usability and effectiveness of adapted games in Alzheimer’s care.
Review Methodology
The review methodology encompasses a structured approach to assessing games tailored for individuals with Alzheimer’s. The selection process for games involves meticulous research, consultation with experts, and consideration of criteria such as cognitive engagement and adaptability. Testing procedures and methodologies are designed to systematically evaluate the selected games, employing standardized assessments and user feedback to gauge cognitive stimulation, ease of use, and emotional engagement. Data collection involves both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights obtained through interviews and observations. Analysis of the gathered data utilizes statistical techniques and thematic coding to identify trends and inform recommendations.
This comprehensive methodology ensures a rigorous evaluation process, ultimately providing valuable insights for caregivers and healthcare professionals in selecting appropriate games for Alzheimer’s care.
Recommendations for Different Stages of Alzheimer’s
Guidelines for Caregivers
Expanding on the guidelines for caregivers, with a focus on integrating adapted games into the care routines for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease, can provide a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of how to enhance their quality of life effectively. Caregivers are pivotal in creating a supportive and engaging environment, and by adopting a thoughtful and flexible approach, they can significantly impact the well-being of those they care for. Here’s an expanded version:
Guidelines for Caregivers
Caregivers hold a fundamental role in enriching the lives of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. The introduction and adaptation of games into daily routines offer a unique avenue for cognitive stimulation and enjoyment. To optimize this approach, caregivers might consider the following detailed strategies:
- Personalization of Game Selection:
- Carefully select games that resonate with the individual’s past interests and current cognitive abilities. This might involve simple puzzles for some or more complex strategy games for others, depending on their stage of Alzheimer’s and personal preferences.
- Regularly introduce new games to keep the routine exciting and stimulating, while also revisiting favorites that provide comfort and familiarity.
- Observation and Adjustment:
- Pay close attention to how the individual reacts to different games, looking out for signs of joy, engagement, frustration, or fatigue. This ongoing observation is crucial for tailoring the experience to their needs.
- Be prepared to modify the game’s difficulty or switch activities altogether if it becomes apparent that the current selection is not achieving the desired positive engagement or is leading to stress.
- Creating a Supportive Environment:
- Foster a positive, encouraging atmosphere where the focus is on the process and enjoyment, rather than on winning or achieving specific outcomes. This can help mitigate any stress or frustration associated with the challenges of the game.
- Ensure the gaming area is comfortable, well-lit, and free of distractions to help maintain focus and make the gaming experience as enjoyable as possible.
- Engagement and Interaction:
- Join in on the games whenever possible, as shared activities can strengthen bonds, provide social interaction, and offer emotional support. This can also make adapting the game’s rules or objectives on the fly easier, ensuring they remain suitable for the individual’s abilities.
- Use this time as an opportunity to observe and engage in meaningful conversations, further enhancing the therapeutic benefits of game-playing.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Professionals:
- Maintain open lines of communication with healthcare professionals and therapists involved in the individual’s care. Their insights can be invaluable in choosing and adapting games that complement other therapeutic activities and strategies.
- Seek advice on integrating game-based activities into a broader care plan, especially regarding how these activities can support cognitive and emotional well-being.
Incorporating these guidelines into the caregiving routine can significantly enhance the caregiving experience, providing not just cognitive stimulation for individuals with Alzheimer’s but also opportunities for connection and joy. The thoughtful integration, customization, and monitoring of adapted games underscore the caregiver’s role in fostering a nurturing and stimulating environment, contributing to a higher quality of life for both the caregiver and the individual with Alzheimer’s.
Future Directions and Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of Alzheimer’s care holds promising advancements in adapted gaming technology, offering innovative solutions to support cognitive health and well-being. Researchers are exploring the potential of virtual reality, augmented reality, and gamification techniques to create immersive and engaging experiences tailored to the needs of individuals with Alzheimer’s. This presents numerous research opportunities to investigate the effectiveness of gaming interventions in improving cognitive function, memory retention, and overall quality of life for patients.
Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, game developers, and researchers are crucial for the development and dissemination of these innovations. By fostering interdisciplinary partnerships and sharing knowledge, we can accelerate the translation of research findings into practical applications, ultimately enhancing the care and support available to individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease.
Our exploration of adapted gaming in Alzheimer’s care highlights several key findings. Firstly, these games offer a personalized and engaging approach to cognitive stimulation, tailored to the individual’s abilities and preferences. Secondly, research underscores the significant potential of adapted games in improving cognitive function, memory retention, and overall well-being for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Importantly, the importance of integrating such games into caregiving routines cannot be overstated, as they provide not only mental stimulation but also moments of joy and connection for both patients and caregivers. As we move forward, there is a pressing call to action to promote the widespread use of adapted games in Alzheimer’s care settings. By advocating for their incorporation into care plans and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, we can harness the power of gaming technology to enhance the lives of those affected by Alzheimer’s disease.
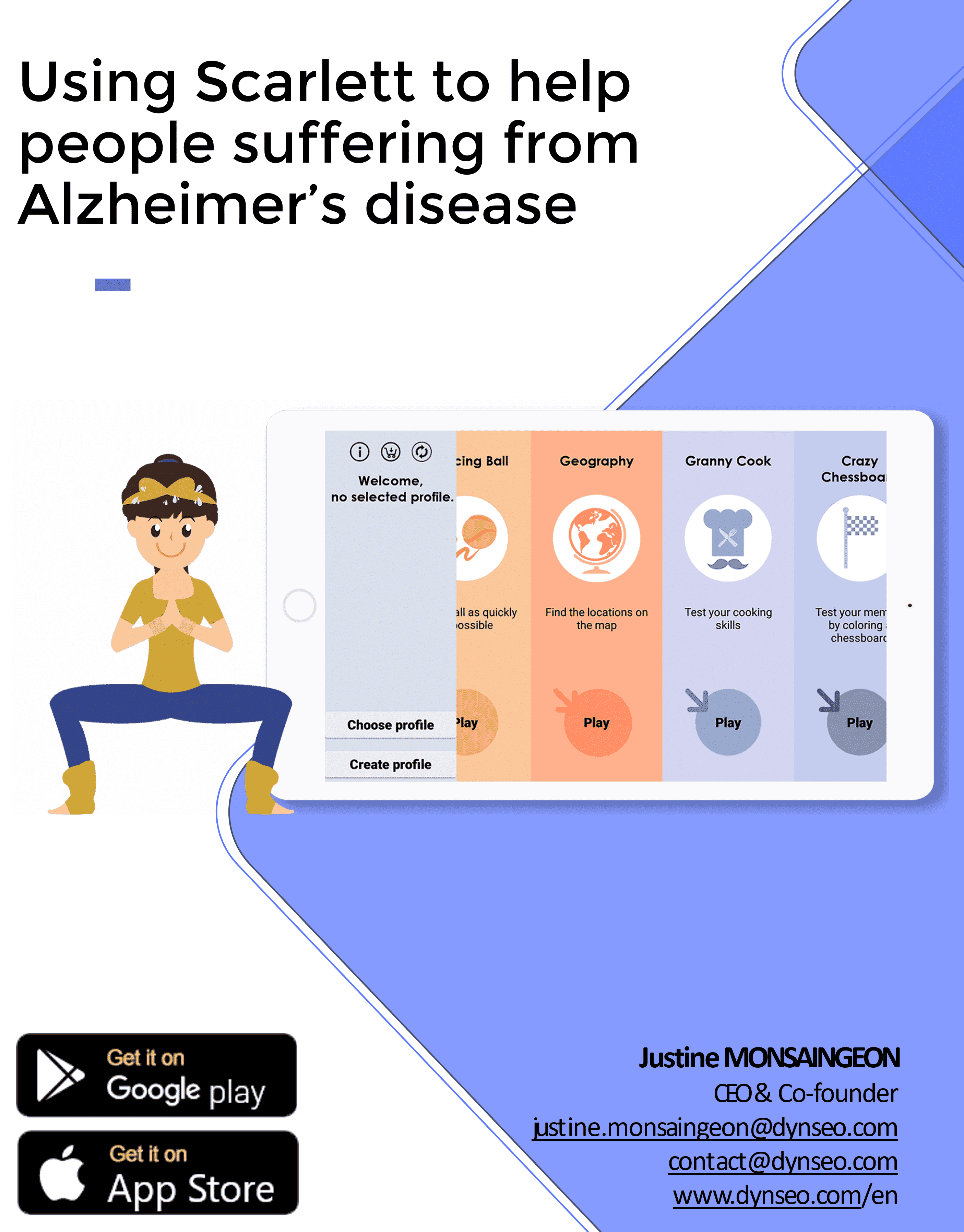
AND FOR FURTHER INFORMATION
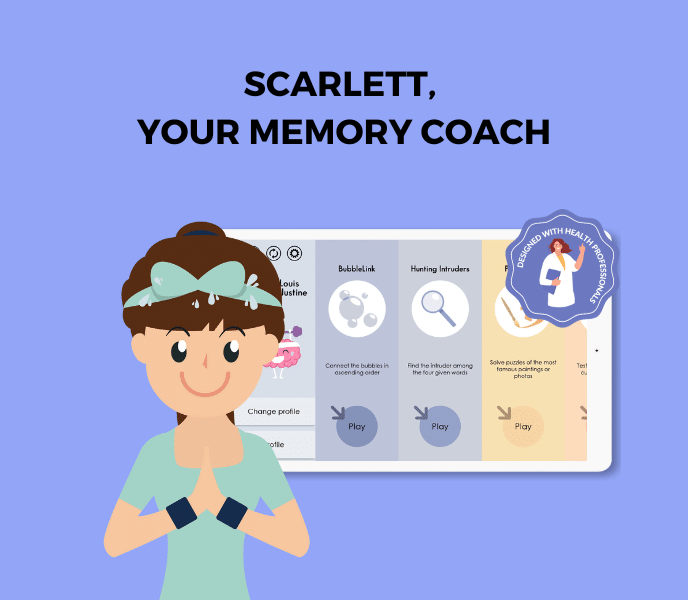
SCARLETT, YOUR MEMORY COACH FOR ALZHEIMER’S
The SCARLETT play program has been specially designed with healthcare professionals for use with Alzheimer’s patients. Non-checking games adapted to their level and prior knowledge. The aim is to focus on the pleasure of playing.
Other articles that might interest you:
The Role of Cognitive Apps in Speech Therapy for Alzheimer’s Patients
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior. As...
Memory Apps for Alzheimer’s: Enhancing Recall in Speech Therapy Sessions
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior. As...
Cognitive Rehabilitation Apps for Speech Therapy with Alzheimer’s Patients
In recent years, the landscape of cognitive rehabilitation has evolved significantly, largely due to the advent of...