As speech therapists, our mission is to provide essential support and care for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease, addressing the communication challenges that accompany this condition. Alzheimer’s progressively impairs cognitive functions, including language and communication abilities, presenting unique obstacles for patients and caregivers alike. In our practice, we recognize the transformative potential of adapted games in augmenting traditional speech therapy approaches. Adapted games encompass a diverse array of activities tailored to the specific needs and abilities of Alzheimer’s patients, offering interactive and engaging opportunities for cognitive stimulation and social interaction.
Integrating games into therapy sessions not only enhances the effectiveness of our interventions but also adds an element of enjoyment and motivation for our patients. By harnessing the therapeutic power of games, we aim to optimize outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals living with Alzheimer’s, fostering meaningful communication and connections amidst the challenges of the disease.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive neurological disorder, is characterized by the gradual deterioration of cognitive functions, primarily affecting memory, thinking, and behavior. As the disease advances, individuals experience significant challenges in communication, ranging from difficulties finding words and forming coherent sentences to impairments in understanding and processing language. These communication deficits not only hinder social interactions but also impact daily activities and quality of life for patients and their caregivers. For speech therapists, addressing the communication impairments associated with Alzheimer’s presents unique challenges.
Developing effective intervention strategies requires a nuanced understanding of the disease progression and its impact on language abilities, as well as the ability to adapt therapy techniques to accommodate individual needs and limitations. Despite these challenges, speech therapists play a crucial role in supporting individuals with Alzheimer’s to maintain their communication skills and enhance their overall well-being.
Role of Speech Therapists
Speech therapists play a pivotal role in Alzheimer’s care, providing essential support to individuals grappling with communication difficulties. Through targeted interventions, speech therapy aims to improve and maintain the communication abilities of Alzheimer’s patients, enhancing their quality of life and fostering meaningful connections with others. The goals of speech therapy encompass a range of objectives, including improving speech clarity and articulation, enhancing language comprehension and expression, and addressing swallowing difficulties that may arise as the disease progresses. To achieve these goals, speech therapists employ a variety of strategies tailored to the individual needs and abilities of their patients.
These strategies may include exercises to strengthen oral muscles, memory and language tasks to stimulate cognitive function, and techniques to facilitate communication, such as augmentative and alternative communication methods. By addressing the unique communication challenges posed by Alzheimer’s disease, speech therapists play a vital role in empowering patients to communicate effectively and maintain their independence for as long as possible.
Introduction to Adapted Games
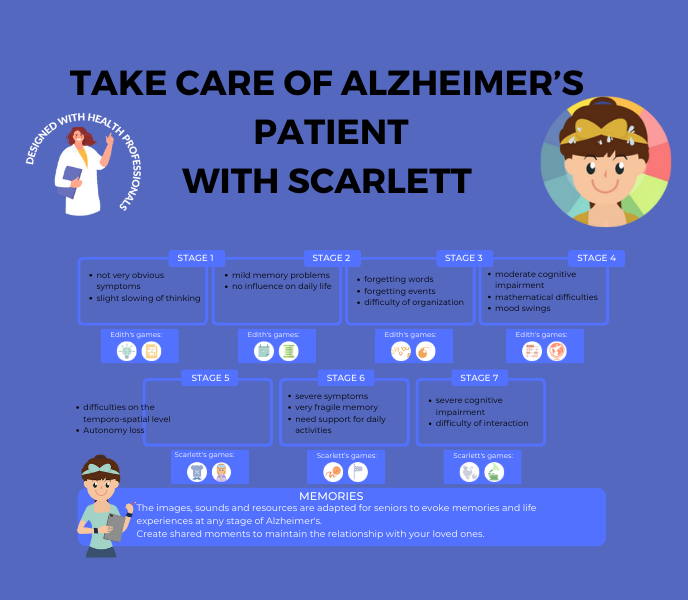
Adapted games refer to modified or specially designed activities tailored to meet the unique needs and abilities of individuals with specific challenges or conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease. These games are carefully crafted to accommodate cognitive, physical, or sensory impairments, providing engaging and accessible opportunities for therapeutic intervention and recreational enjoyment. For Alzheimer’s patients, adapted games may include simplified versions of traditional board games, memory-matching activities, or interactive digital games designed to stimulate cognitive function and promote social interaction.
The benefits of incorporating adapted games into therapy sessions are manifold, ranging from cognitive stimulation and memory enhancement to fostering social connections and improving overall mood and well-being. By harnessing the therapeutic potential of adapted games, therapists can effectively address the communication and cognitive challenges associated with Alzheimer’s disease, enriching the therapeutic experience and enhancing the quality of life for their patients.
Incorporating Adapted Games in Therapy
Incorporating adapted games into therapy sessions for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease requires a personalized approach tailored to each patient’s abilities and preferences. Firstly, therapists must conduct thorough assessments to understand the cognitive and physical capabilities of their patients, as well as their interests and preferences. Based on this assessment, therapists can then carefully select appropriate games that align with the patient’s abilities and therapeutic goals.
These games may include memory exercises, word games, or sensory activities designed to stimulate cognitive function and promote engagement. Furthermore, therapists must be adept at adapting games to suit individual needs, modifying rules, materials, or instructions as necessary to accommodate cognitive impairments or physical limitations. By incorporating adapted games into therapy sessions in a thoughtful and individualized manner, therapists can effectively address the unique needs of each patient, maximizing therapeutic outcomes and enhancing overall well-being.
How Adapted Games Support Therapy
Adapted games serve as invaluable tools in therapy sessions for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease, offering multifaceted support in addressing various cognitive and communication challenges.
Enhancing cognitive abilities
Adapted games are specifically designed to provide cognitive stimulation, helping individuals with Alzheimer’s exercise their mental faculties and maintain cognitive function. These games often involve tasks such as memory exercises, problem-solving activities, and pattern recognition tasks, which engage different areas of the brain and promote neuroplasticity. By regularly engaging in adapted games, patients can improve memory retention, enhance attention span, and sharpen cognitive skills, ultimately slowing down the progression of cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Improving communication skills
Adapted games are also instrumental in improving communication skills among individuals with Alzheimer’s. These games often incorporate language-based activities, such as word games, storytelling prompts, and conversation starters, which provide opportunities for patients to practice verbal expression and comprehension in a supportive and engaging environment. By participating in adapted games that target communication skills, patients can enhance their ability to articulate thoughts, express emotions, and engage in meaningful interactions with others, thereby enhancing their overall communication abilities and quality of life.
Promoting social interaction and engagement
One of the significant benefits of adapted games is their ability to promote social interaction and engagement among individuals with Alzheimer’s. Many adapted games are designed for group settings, encouraging collaboration, teamwork, and peer support. These games provide opportunities for patients to engage in shared experiences, foster connections with others, and combat feelings of isolation and loneliness commonly experienced in Alzheimer’s patients. Additionally, the enjoyable and interactive nature of adapted games encourages active participation and sustained engagement, promoting a sense of fulfillment and well-being among patients as they connect with others and enjoy meaningful social interactions.
Practical Tips for Speech Therapists
Overcoming Challenges
Overcoming challenges encountered in integrating adapted games into therapy sessions for individuals with Alzheimer’s requires thoughtful strategies and flexibility. Firstly, addressing resistance to participating in games involves understanding the underlying reasons for reluctance, such as fear of failure or discomfort with the unfamiliar. Therapists can employ gentle encouragement, positive reinforcement, and patience to gradually build trust and confidence in engaging with games. Secondly, dealing with the limitations of adapted games necessitates creativity and adaptation. While some games may need modification to better suit individual needs and abilities, therapists can also explore a variety of game options to find those most engaging and beneficial for their patients.
Lastly, managing behavioral issues during game sessions may require preemptive measures such as establishing clear expectations, providing sensory stimulation, and implementing calming techniques to mitigate agitation or frustration. By addressing these challenges proactively and flexibly, therapists can optimize the therapeutic benefits of adapted games for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Ethical Considerations
Incorporating adapted games into therapy sessions for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease necessitates careful attention to ethical considerations to uphold the dignity and well-being of patients. Firstly, ensuring patient consent and autonomy is paramount. Therapists should engage patients in the decision-making process regarding participation in game-based activities, respecting their right to choose and providing opportunities to express preferences. Additionally, therapists must be mindful of cultural sensitivities when selecting games, taking into account diverse cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and values. Respecting cultural differences ensures that game selections are inclusive and culturally appropriate, fostering a sense of respect and understanding among patients.
Furthermore, maintaining confidentiality and privacy is essential to safeguarding patient information shared during therapy sessions. Therapists must adhere to strict confidentiality protocols and ensure that any personal or sensitive information disclosed during game-based activities remains confidential, promoting trust and confidentiality between therapist and patient. By upholding these ethical considerations, therapists can create a therapeutic environment that prioritizes the dignity, autonomy, and well-being of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
The integration of adapted games into therapy sessions for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease offers numerous benefits that enhance both the therapeutic process and the overall well-being of patients. These games provide valuable cognitive stimulation, improve communication skills, promote social interaction, and foster a sense of joy and engagement. Speech therapists are encouraged to embrace the use of adapted games in their practice, recognizing their potential to complement traditional therapeutic approaches and enrich the lives of their patients.
Moving forward, future research and practice in game-based therapy for Alzheimer’s patients should continue to explore innovative ways to tailor games to individual needs, refine therapeutic strategies, and assess the long-term impact of game-based interventions on cognitive function, communication abilities, and quality of life. By continuing to advance our understanding and implementation of game-based therapy, we can further optimize care for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and enhance their overall quality of life.
AND FOR FURTHER INFORMATION
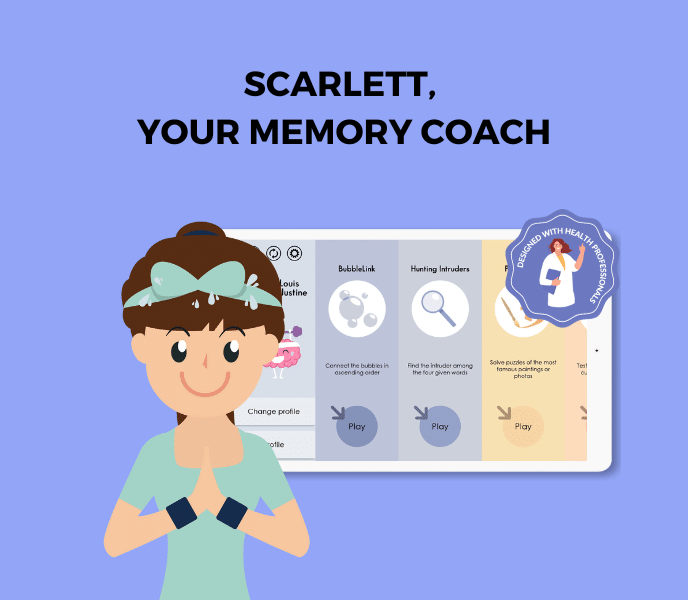
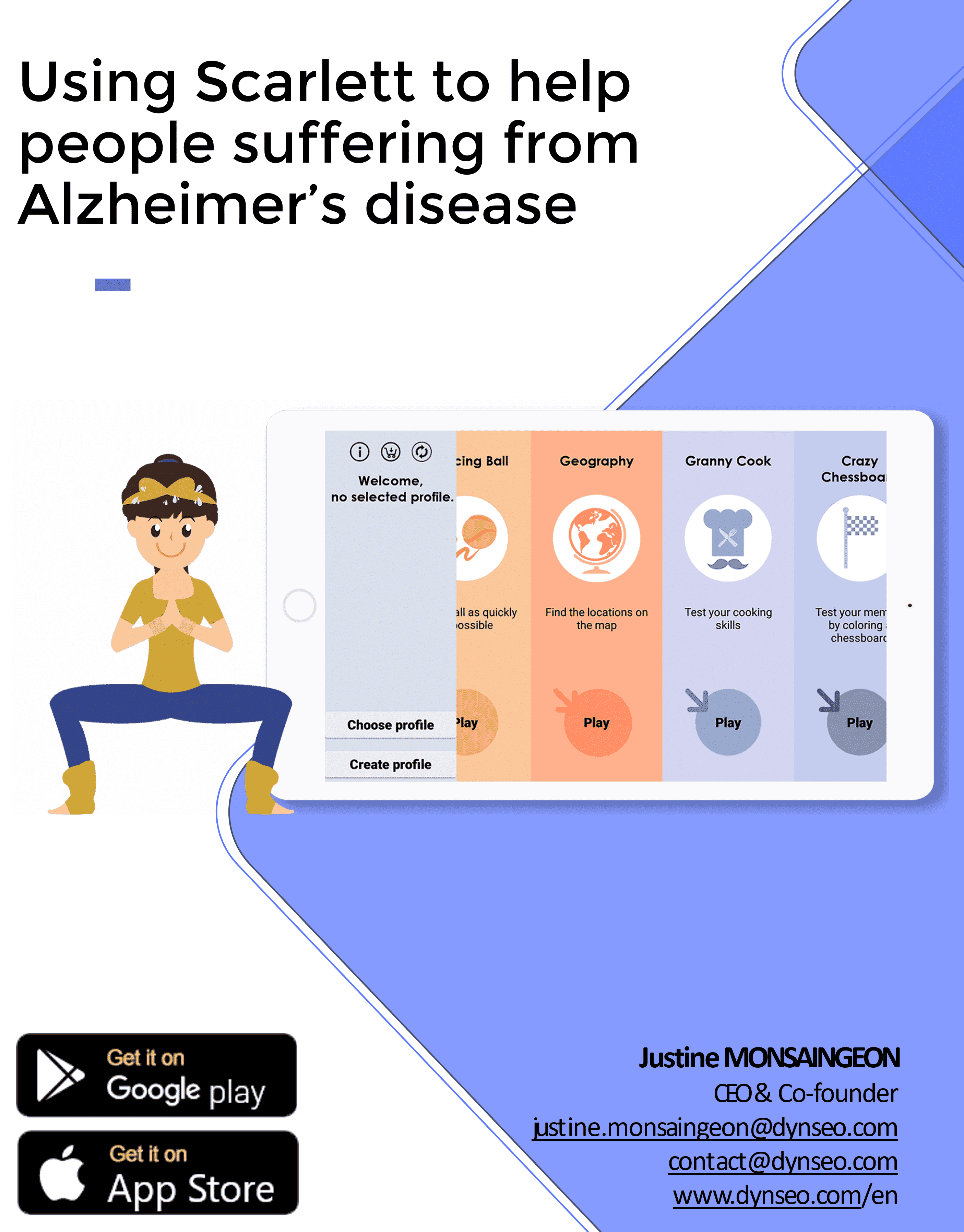
SCARLETT, YOUR MEMORY COACH FOR ALZHEIMER’S
The SCARLETT play program has been specially designed with healthcare professionals for use with Alzheimer’s patients. Non-checking games adapted to their level and prior knowledge. The aim is to focus on the pleasure of playing.
Other articles that might interest you:
The Role of Cognitive Apps in Speech Therapy for Alzheimer’s Patients
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior. As...
Memory Apps for Alzheimer’s: Enhancing Recall in Speech Therapy Sessions
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior. As...
Cognitive Rehabilitation Apps for Speech Therapy with Alzheimer’s Patients
In recent years, the landscape of cognitive rehabilitation has evolved significantly, largely due to the advent of...