The importance of mental clarity in our daily lives cannot be overstated. Two key concepts, attention and concentration, play a crucial role in our ability to function effectively. But what really distinguishes attention from concentration?
Attention is often seen as the ability to consciously direct one’s cognitive resources towards a particular stimulus. It acts as a mental projector, allowing our mind to focus on a specific element among the multitude of information surrounding us.
The different types of attention and concentration
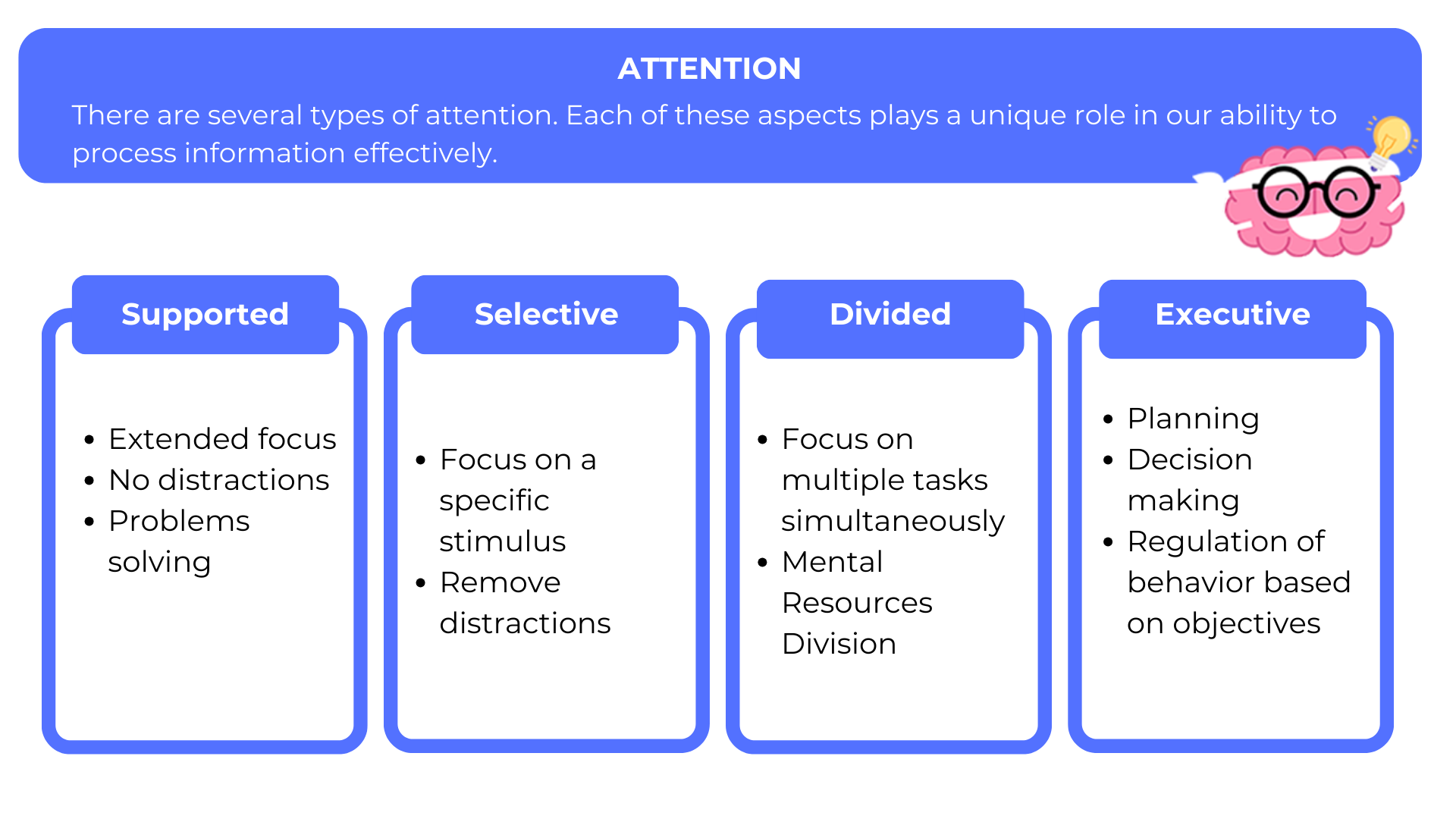
Attention, as a complex cognitive process, comes in a variety of types, each with distinct implications for how we perceive and process the information around us. There are several types of attention, such as selective attention, sustained attention and divided attention. Each of these aspects plays a unique role in our ability to process information efficiently.
Sustained attention
Sustained attention refers to the ability to maintain prolonged concentration on a specific task without distraction. It is crucial in activities such as reading, solving complex problems or carrying out work that requires prolonged focus.
Factors influencing Sustained Attention
Fatigue, motivation and environment can all influence our ability to maintain sustained attention. Understanding these factors is essential to optimizing our performance in demanding tasks.
Selective attention
Selective attention enables us to focus our mental resources on a specific stimulus while ignoring other stimuli in our environment. It’s what enables us to follow a conversation in a noisy environment, or to concentrate on a task despite distractions.
The Cocktail Party
The “Cocktail Party” phenomenon illustrates selective attention, where one person can focus on a particular conversation even in a crowded place with many ongoing discussions.
Divided attention
Divided attention occurs when we try to concentrate on several tasks simultaneously. Unlike selective attention, which focuses on one element at a time, divided attention requires us to divide our mental resources between several activities.
Multitasking and its limits
Although modern society often encourages multitasking, studies suggest that this can lead to a decrease in the quality of attention paid to each individual task. Understanding the limits of divided attention is crucial to optimizing our efficiency.

Executive attention
Executive attention is involved in the management of higher mental processes such as planning, decision-making and problem-solving. It plays an essential role in regulating our behavior according to the objectives we have set.
The role of executive attention in everyday life
Activities such as project planning, complex problem solving and decision making are all dependent on executive attention. Strengthening this form of attention can improve our ability to deal effectively with the challenges of everyday life.
By understanding these different types of attention, we are better equipped to develop strategies to improve our cognitive abilities and optimize our performance in various situations.
Understanding concentration
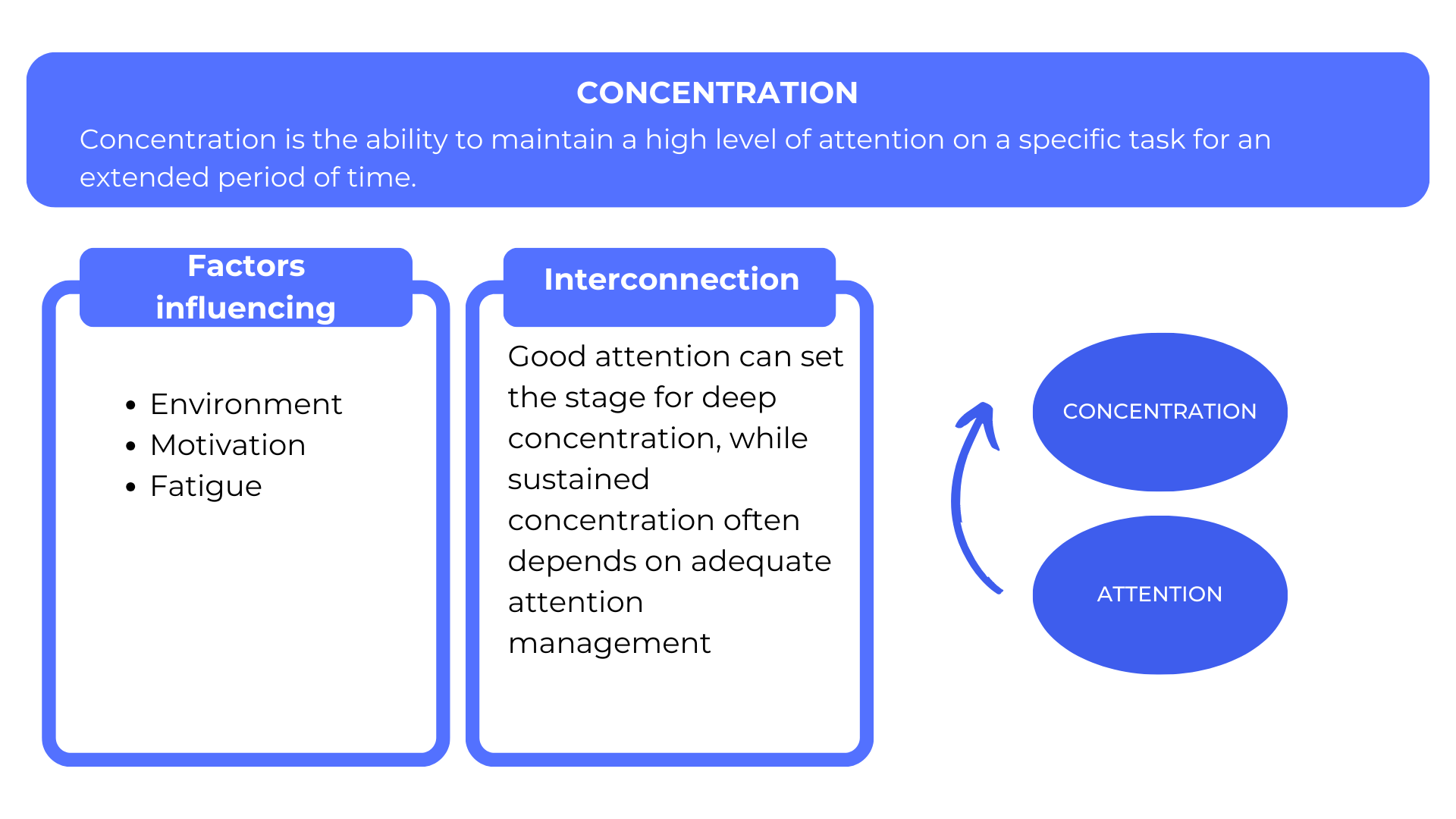
On the other hand, concentration involves the ability to maintain a high level of attention on a specific task for an extended period of time. It’s a mental state where the mind immerses itself deeply in an activity, eliminating distractions.
Factors influencing concentration
Factors such as environment, motivation and fatigue can all influence our ability to maintain optimal concentration. Understanding these variables is essential to improving our cognitive performance.
Interconnections
Although distinct, attention and concentration are closely linked. Good attention can pave the way for deep concentration, while sustained concentration often depends on proper attention management.
Techniques to improve attention and concentration
Practices such as meditation, time management and mindful pausing can help strengthen both attention and concentration.
Attention and concentration: concrete examples illustrating the differences between them
1. Reading a Book (Sustained Attention vs. Concentration)
- Sustained Attention: When you’re reading an exciting book, your ability to maintain sustained attention allows you to stay immersed in the story without being constantly distracted by outside thoughts.
- Concentration: However, concentration comes into play when you immerse yourself deeply in reading, forgetting the passage of time. You’re totally absorbed by the content, eliminating distractions for total immersion.
2. Meeting at work (Selective attention vs. concentration)
- Selective attention: In a noisy meeting, your selective attention enables you to focus on the presenter’s voice despite the ambient hubbub.
- Concentration: Concentration comes into play when, even in the midst of agitation, you manage to immerse yourself deeply in the discussion, analyzing information and making a significant contribution to the meeting.

3. Multitasking (divided attention vs. concentration)
- Divided attention: Answering e-mails while taking part in a virtual meeting allows you to juggle tasks, but can lead to a loss of depth in each activity.
- Concentration: Concentration occurs when you isolate yourself to work on a specific task, eliminating distractions and immersing yourself fully in the work to achieve quality results.
4. Problem solving (executive attention vs. concentration)
- Executive attention: When you’re planning to solve a complex problem, your executive attention is at work, coordinating the different steps and strategies needed to reach your goal.
- Concentration: Once the strategy has been established, concentration comes into play when you tackle the problem, eliminating distractions to immerse yourself fully in the search for solutions.
These examples demonstrate how attention and concentration interact in various everyday contexts, highlighting the complementary nature of these essential mental processes.
Testimony of a Neuropsychologist on Attention and Concentration Work
As a neuropsychologist, I see on a daily basis the significant impact that training attention and concentration can have on mental well-being and cognitive performance. Here’s how I guide my patients to improve these crucial aspects of cognitive function.
Work on attention and concentration in everyday life
1. Practical techniques to improve concentration
Example 1: The Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro method, based on intervals of concentrated work interspersed with short breaks, is an effective approach to training concentration. By dedicating 25 minutes to a specific task, followed by a 5-minute break, you keep your mind fresh and focused.
Example 2: Eliminating Distractions
Identifying and eliminating distractions from your working environment is crucial. Whether it’s putting your phone on silent mode, using app-blocking tools for specific periods, or creating a quiet workspace, these adjustments can dramatically improve concentration.

2. Exercises to develop attention
Example 1: Mindfulness in Daily Activities
Integrating mindfulness into everyday activities, such as eating or walking, is a practical way of developing attention. By paying conscious attention to the details, sensations and experiences of the present moment, you strengthen your ability to stay fully engaged.
Example 2: Cognitive Stimulation Games
Cognitive games, such as puzzles, riddles or specially designed applications, can be fun, attention-grabbing exercises. By incorporating them into your routine, you provide your brain with challenges that encourage the development of concentration.
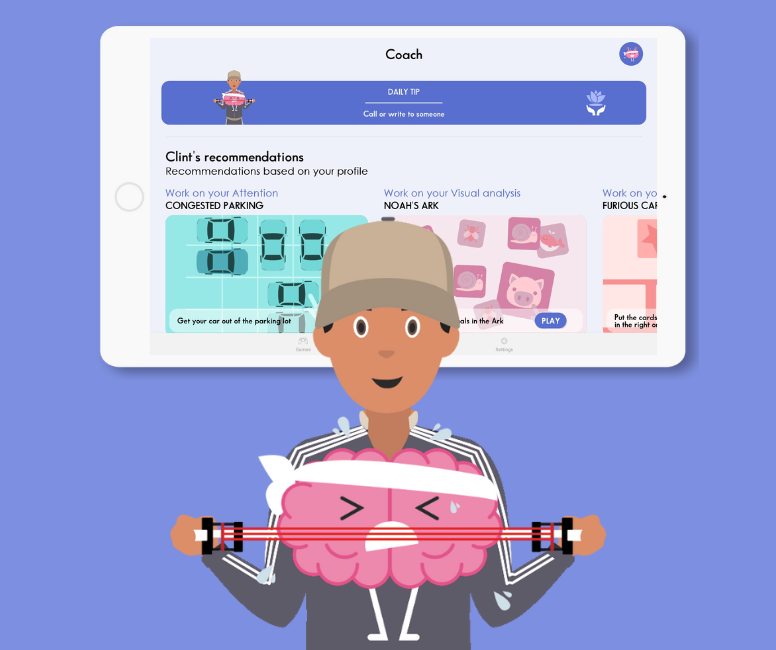
3. Clint, Your brain coach
Clint, your brain coach, is an innovative application designed to optimize your cognitive potential. Combining scientifically validated exercises to strengthen attention and concentration, Clint offers a personalized approach based on individual progress. From quick coffee-break sessions to more in-depth training sessions, Clint adapts to your schedule and specific needs.
With Clint , you can track your performance over time, receive personalized advice and discover a variety of exercises to work specifically on the aspects of attention and concentration that interest you. Turn your daily routine into a constant opportunity for cognitive improvement with the help of Clint, your brain coach.

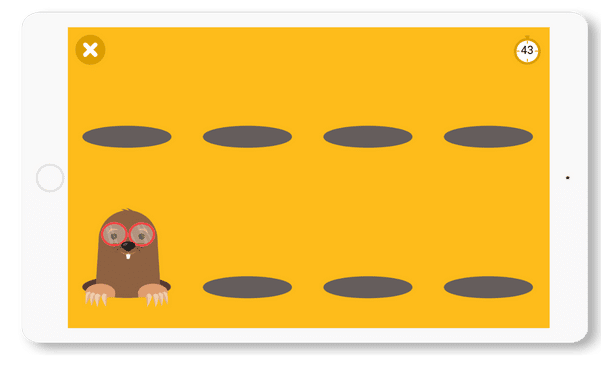
The Mole Invasion
Tap on the 3 mole types according to the instructions on the screen.
With this game, you stimulate attention above all.
You need to use your visual scanning skills to spot moles quickly. She then has to analyze the image to find out which mole appears on the screen. Finally, it must associate the type of mole with the action to be taken.
Crowded Parking Lot
Move the cars in the parking lot to bring out the yellow car.
With this game, you can stimulate all the cognitive functions that are essential for regaining independence.
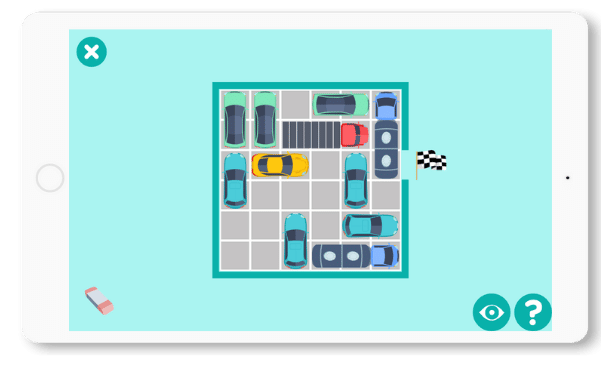
What’s more, to solve this puzzle and find the right sequence of movements to get the yellow car out, you’re also stimulating concentration and planning.
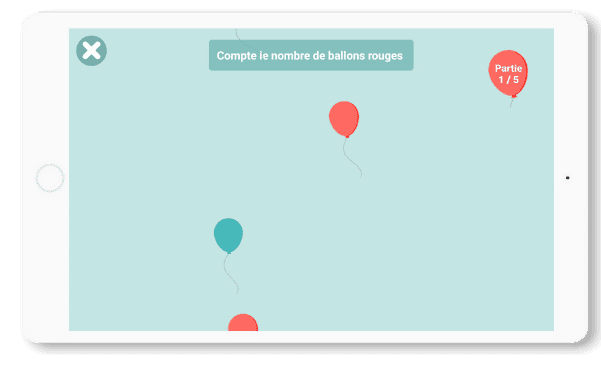
Flying balloons
In this game, the player has to count the balloons passing by on the screen, following the instructions given.
There will be several balloons of different colors, and he’ll have to count the balloons of a single color.
He will therefore have to sort between important stimuli (balloons of the right color) and distracting stimuli (balloons of the wrong color).
CLINT, YOUR BRAIN COACH

TRAINING PROGRAMS

Other articles that might interest you:
How Parents Can Contribute to Teacher Training
As we delve into the realm of education, it becomes increasingly clear that teacher training is not merely a...
Differentiated Instruction Approaches: Training and Practical Application
Differentiated instruction is a pedagogical approach that recognizes the diverse needs of students in a classroom. It...
Key Skills Teachers Need to Support Students with Special Needs
As we embark on our journey to support children with special needs, it is essential for us to cultivate a deep...







