Siblings play an important role in family dynamics. They can be role models, play partners and emotional supports for their brother or sister with ADHD. However, they can also be affected by their sibling’s ADHD in different ways. So we’ll see the ADHD’s impact on siblings in this article.
The siblings of a child with ADHD may feel neglected or forgotten because of the extra attention given to their brother or sister. They may also feel frustrated or angry at their sibling’s impulsive or hyperactive behaviour. What’s more, they may feel responsible for their sibling’s well-being and feel overwhelmed by this responsibility.
The impact of ADHD on siblings: Different aspects to consider
ADHD can have a significant impact on family dynamics. Siblings may experience changes in family dynamics due to the challenges associated with their sibling’s ADHD. For example, parents may be more stressed or less available due to the additional needs of a child with ADHD.
Siblings may also face emotional and behavioral challenges as a result of their sibling’s ADHD. They may feel angry, frustrated or jealous of the extra attention given to their sibling. What’s more, they may have trouble understanding their sibling’s impulsive or hyperactive behavior, which can lead to conflict within the family.
The emotions of brothers and sisters: Anger, frustration and jealousy
The siblings of a child with ADHD may experience a wide range of emotions, including anger, frustration and jealousy. These emotions can manifest themselves in different ways, such as aggressive behavior, tantrums or social withdrawal.
It’s important for parents to recognize and validate siblings’ emotions. They can help manage these emotions by encouraging open communication and offering emotional support. Parents can also help teach siblings strategies for dealing with anger or frustration in a healthy, constructive way.
The impact of ADHD on sibling relationships: Rivalry and distance
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can pose unique challenges not only for the individual affected, but also for siblings, often impacting the entire family dynamic. Rivalry and distance can develop in sibling relationships under the influence of this disorder, but there are strategies to mitigate these effects and strengthen family bonds.
Impact of ADHD on sibling relationships
- Increased rivalry: Children with ADHD often require extra attention and care from parents, which can lead to feelings of neglect among siblings. This perception of an imbalance in parental attention can fuel rivalry between children.
- Sense of distance: Behavioural differences due to ADHD, such as impulsivity or difficulty following rules, can make interactions frustrating for siblings who don’t understand these behaviours. This can lead to a feeling of distance or isolation between children.
Strategies for improving brotherly relations
- Open communication: Encouraging open and honest communication within the family can help dispel misunderstandings and build mutual understanding. It’s crucial that parents facilitate discussions where each child can express his or her feelings without fear of judgment.
- Inclusive family activities: Organizing activities that integrate all children, taking into account their interests and abilities, can strengthen bonds and reduce rivalry. It also helps the child to feel valued within the family.
- ADHD education: Informing siblings about what it is and how it affects behavior can increase empathy and patience between children. Understanding that certain behaviors are the result of a disorder, not a personal choice, can reduce frustration and promote understanding.
- Conflict resolution skills: Teaching children conflict resolution techniques is essential. This includes negotiation skills, emotional management and active listening. These skills are beneficial not only in family dynamics, but also in other aspects of social and educational life.
- Individualized emotional support: Offering emotional support tailored to each child, recognizing their efforts and celebrating their individual successes can help reduce feelings of jealousy or competition.
A concrete example
For example, a family could set up a weekly “family game night” where all the children can take turns choosing games that suit all ages and abilities. During these evenings, parents can actively observe and intervene in conflicts, using these moments as opportunities to teach and practice conflict resolution in a fun and relaxed way.
In short, while it can present challenges in sibling relationships, a proactive and inclusive approach on the part of parents can go a long way to reducing rivalry and distance. By fostering greater understanding and creating opportunities for positive interaction, it’s possible to build stronger, more harmonious fraternal relationships.
Siblings as caregivers: How to involve them in the treatment process
Siblings often play a crucial role as caregivers for a family member with ADHD. Their involvement can significantly improve treatment efficiency and enrich family dynamics, strengthening the bonds between them. It is essential that parents encourage and facilitate this participation in a positive and appropriate way.
The role of siblings in its treatment
- Emotional support: Siblings can provide constant emotional support, which is crucial for a child with ADHD. They can listen to their concerns, share moments of play and relaxation, and provide a comforting presence in difficult times.
- Encouragement and treatment adherence: They can play an active role in encouraging their sibling to adhere to their treatment, whether it’s following a medication schedule, attending therapy sessions, or practicing professionally recommended exercises.
- Managing daily challenges: Siblings can help organize shared living space to minimize distractions, or help set up routines that make time and task management easier for their sibling.
Involving siblings through games
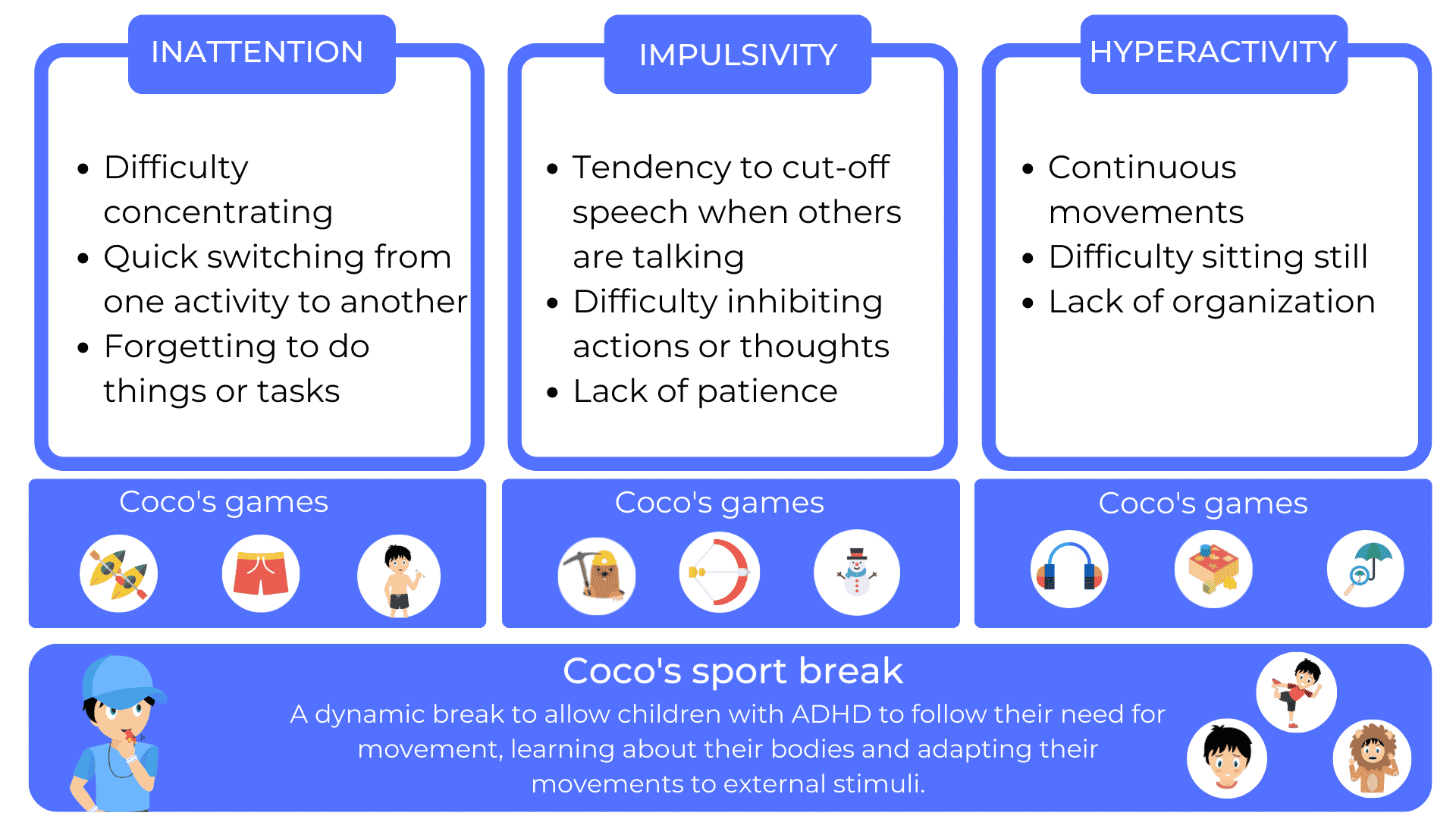
A particularly effective method of strengthening sibling bonds and actively involving siblings in the care process is the use of games designed for children with ADHD, such as Coco Thinks and Coco Moves. These games are specially designed to be played in pairs, with a split screen, making them ideal for sibling duo play.
- Coco Thinks: This game encourages reflection and concentration, where each player can take part in solving puzzles or cognitive challenges adapted to their level. This encourages not only cooperation, but also friendly competition, reinforcing cognitive skills and fraternal bonds.
- Coco Moves: This game encourages children to take part in physical activities that require coordination and balance, while having fun at the same time. The split-screen allows each child to monitor his or her own progress while watching and encouraging his or her sibling. This can be particularly beneficial for the child, as exercise is often recommended as an integral part of treatment.
Benefits of involvement in games
- Developing social and emotional skills: Playing together helps develop skills such as patience, empathy and emotional management, which are essential for interpersonal relationships.
- Reinforced sense of belonging: By taking part in these activities together, siblings strengthen their sense of belonging to the family and their active role in supporting their brother or sister.
- Creating positive memories: The experiences shared during these games create happy, positive memories, which can counterbalance moments of stress or difficulty due to ADHD.
In short, involving siblings in the ADHD treatment process through creative and engaging means like the Coco Pense and Coco Bouge games can turn challenges into opportunities to strengthen bonds and improve family dynamics. This approach not only significantly assists the child with ADHD, but also enriches the life of the whole family.
Brothers and sisters as playmates: How to foster a positive and balanced relationship

It’s important for parents to encourage a positive, balanced relationship between siblings. They can do this by encouraging siblings to play together and share common activities. This can help strengthen the sibling relationship and foster a sense of camaraderie.
Parents can also help resolve conflicts between siblings by teaching problem-solving skills. They can encourage open communication, empathy and mutual respect. This can help siblings develop important social and emotional skills.
Brothers and sisters as role models: How to encourage positive, respectful behavior
Siblings can serve as role models for their brother or sister with ADHD. They can show positive, respectful behavior towards others, which can help their sibling develop appropriate social and behavioral skills.
Parents can encourage positive, respectful behavior by recognizing and rewarding appropriate behavior. They can also teach siblings problem-solving and stress-management skills, which can help them cope with the challenges of their sibling’s ADHD.
Brothers and sisters as beneficiaries: How to offer them emotional and practical support
It’s important for parents to offer emotional and practical support to the siblings of a child with ADHD. Siblings may need a safe space to express their emotions, as well as support in managing the challenges associated with their sibling’s ADHD.
Parents can help siblings manage their emotions by encouraging open communication and offering emotional support. They can also offer practical support by helping siblings find activities or interests of their own, outside of their sibling’s ADHD.
Tips for managing family dynamics and fostering healthy, fulfilling sibling relationships
AND FOR MORE INFORMATION

COCO, EDUCATIONAL GAMES FOR ADHD CHILDREN
Coco thinks and Coco moves is an educational play program for ADHD children aged 5 to 10. A variety of games to work on all cognitive functions. A compulsory sports break every 15 minutes of screen time. Smartphone and tablet.

CLINT, FOR ADHD TEENS AND ADULTS
The CLINT program, your brain coach, will help ADHD teenagers and adults. They can search for games by cognitive function. Joe will also be able to recommend the games best suited to each user’s needs. Smartphone and tablet.
Other articles that might interest you:
Recognizing ADHD in Children: Signs to Look For
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects a significant number of...
Managing ADHD and Anxiety: Tips for Finding Balance
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and anxiety are two distinct yet often overlapping conditions that can...
Managing Combined ADHD: Strategies for Success
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests in various forms, with...