Kindergarten education is rapidly evolving to meet the changing needs of students and society. The integration of tablets in this context has become a crucial topic of discussion. This article will take a deep dive into the opportunities, challenges and best practices for using tablets in children’s early learning.
The benefits of tablets for kindergarten learning
Interactivity and student involvement
Tablets offer an interactive environment that captures the attention of young students. With a touch interface, students can actively participate by using their fingers to interact with educational applications. This interactivity strengthens student commitment and encourages active learning.
Adaptability to different learning styles
One of the major advantages of integrating tablets into kindergarten learning is their ability to adapt to the individual needs of each child. Young students have varied learning styles, with some being visual, others kinesthetic, and still others preferring auditory learning. Tablets make it possible to personalize the learning experience by offering a range of applications and resources adapted to these different styles. For example, a child who learns best by visualizing complex concepts can benefit from interactive educational videos, while another who prefers tactile interaction can solve mathematical problems by manipulating virtual objects. What’s more, educational apps can automatically adjust the difficulty of activities according to each child’s progress, offering targeted support. This adaptability is crucial to meeting the diverse needs of young learners and fostering their holistic development, while creating an inclusive learning environment where every child can thrive.
Developing digital skills from an early age
In today’s digital age, it’s imperative to prepare children for digital skills from an early age. Tablets offer an interactive and intuitive way of introducing basic digital skills to children. By manipulating touch screens, toddlers develop their hand-eye coordination, their ability to follow visual instructions and their understanding of fundamental numerical concepts, such as numbers, letters and shapes. What’s more, educational apps specially designed for young children focus on playful learning, encouraging exploration and discovery. By understanding how to navigate in a digital environment, children acquire essential skills for success in an increasingly technology-driven world. This early exposure to digital tools can also help reduce the digital divide by giving all children, whatever their socio-economic background, the opportunity to become competent users of technology. It’s important to note that the integration of tablets into pre-school education is not limited to academic learning, but also aims to develop digital skills that are essential for everyday life and the future success of every child.
Concerns and counter-arguments
1. Content suitable for young children
One of the main concerns is to ensure that tablet content is age-appropriate. Choosing appropriate, high-quality educational content is essential. Teachers and parents must play an active role in the supervision and selection of this content to ensure it is adapted to children’s needs. When it comes to choosing tablet content for young children, it’s imperative to ensure that it’s both educational and age-appropriate. Teachers and parents must play an active role in selecting and supervising this content to ensure it meets children’s needs. Specific applications such as COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES are excellent examples of educational applications for young children.


3. Teacher training for effective use
To maximize the benefits of tablets in kindergarten, teachers need to be properly trained in their use in the classroom. A
teacher training
is essential to ensure that tablets are effectively integrated into student learning.
Case studies and feedback from kindergarten classes
1. Schools that have successfully integrated tablets
Many schools around the world have successfully integrated tablets into their kindergarten learning programs, demonstrating the benefits of this approach. Here are a few examples of schools that stood out:
- Étoiles Brillantes” school (Paris, France): The“Étoiles Brillantes” school set up a pilot program for the integration of tablets in kindergarten three years ago. Teachers have been trained in the use of tablets and have worked closely with parents to ensure balanced use. The results have been extraordinary, with a significant increase in student engagement and notable improvements in reading and math skills.

- TechKids Academy School (New York, USA): The“TechKids Academy” is a pre-school focused on digital skills and technology. She integrated tablets into her program right from the start. Teachers have designed a curriculum that emphasizes learning through play and exploration using tablets. Students develop not only digital skills, but also problem-solving and creative skills.

.

“I’ve been using tablets in the classroom for a while now, and I have to say it’s amazing. Children are so engaged and enthusiastic when they learn with tablets. I’ve seen significant improvements in their literacy and understanding of numbers. It’s as if tablets make learning more fun for them.”
“I was skeptical at first, but after being trained in the use of tablets in kindergarten, I’m totally convinced. Educational apps are so well designed for young children, and they really adapt to different skill levels. I’ve seen incredible progress in my students, and they’reso proud to show off what they’ve learned on the tablets to their parents.”
“What I love most about using tablets is how versatile they are. I can use them for everything from learning letters and numbers to exploring the world around us. Children are so curious, and tablets allow them to satisfy their thirst for knowledge in an interactive way.”
Strategies for successfully integrating tablets in kindergarten
Selecting the right educational applications
For successful tablet integration, it’s crucial to select high-quality educational applications that match students’ learning objectives. It’s important to consider the age and skill level of the children when making your selection.
Parental guidance and communication with teachers
Parents and teachers need to work closely together to ensure responsible use of tablets. Regular communication between the school and parents is essential to monitor student progress and resolve potential problems.
Integrating tablets into existing educational programs
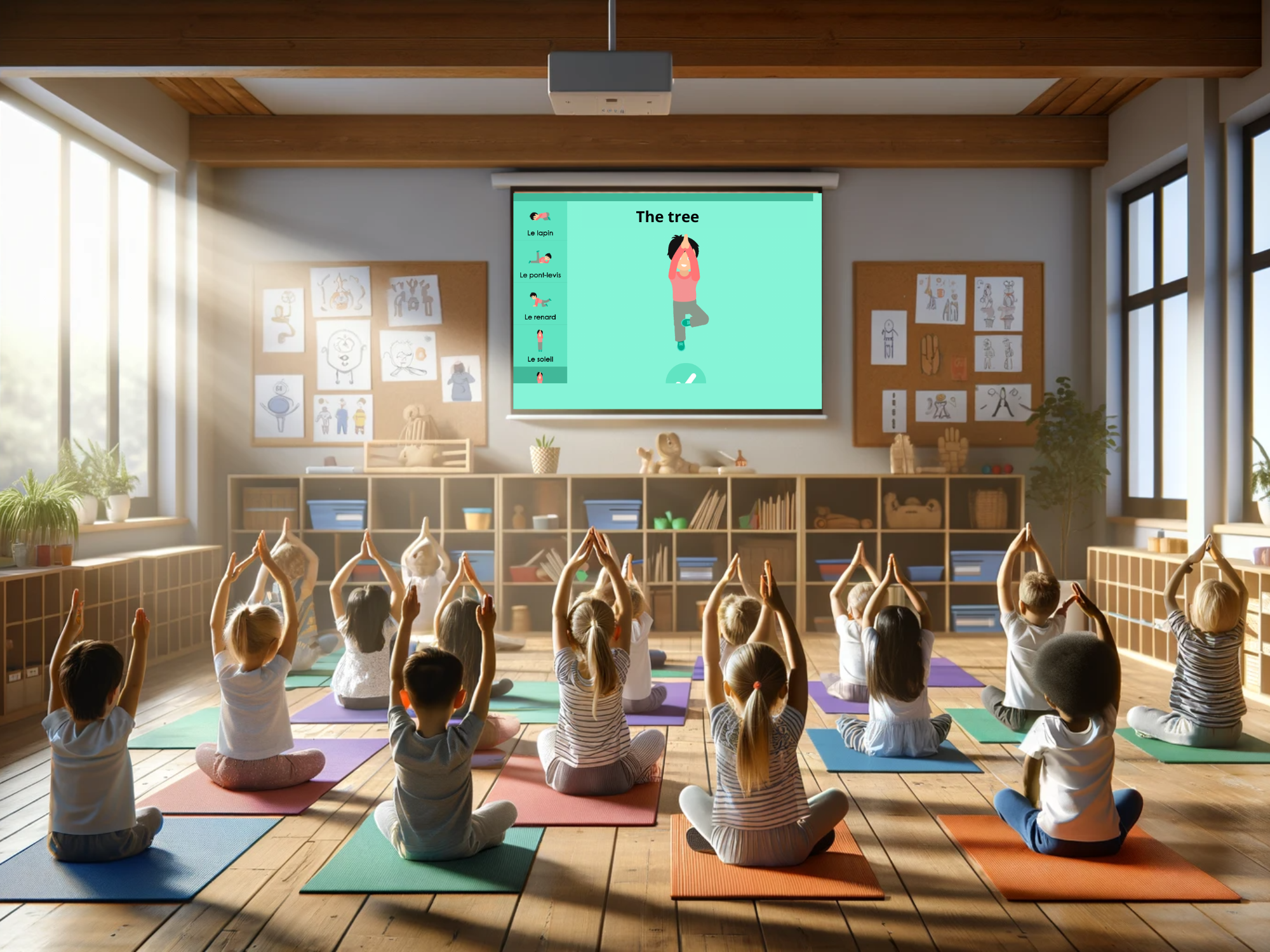
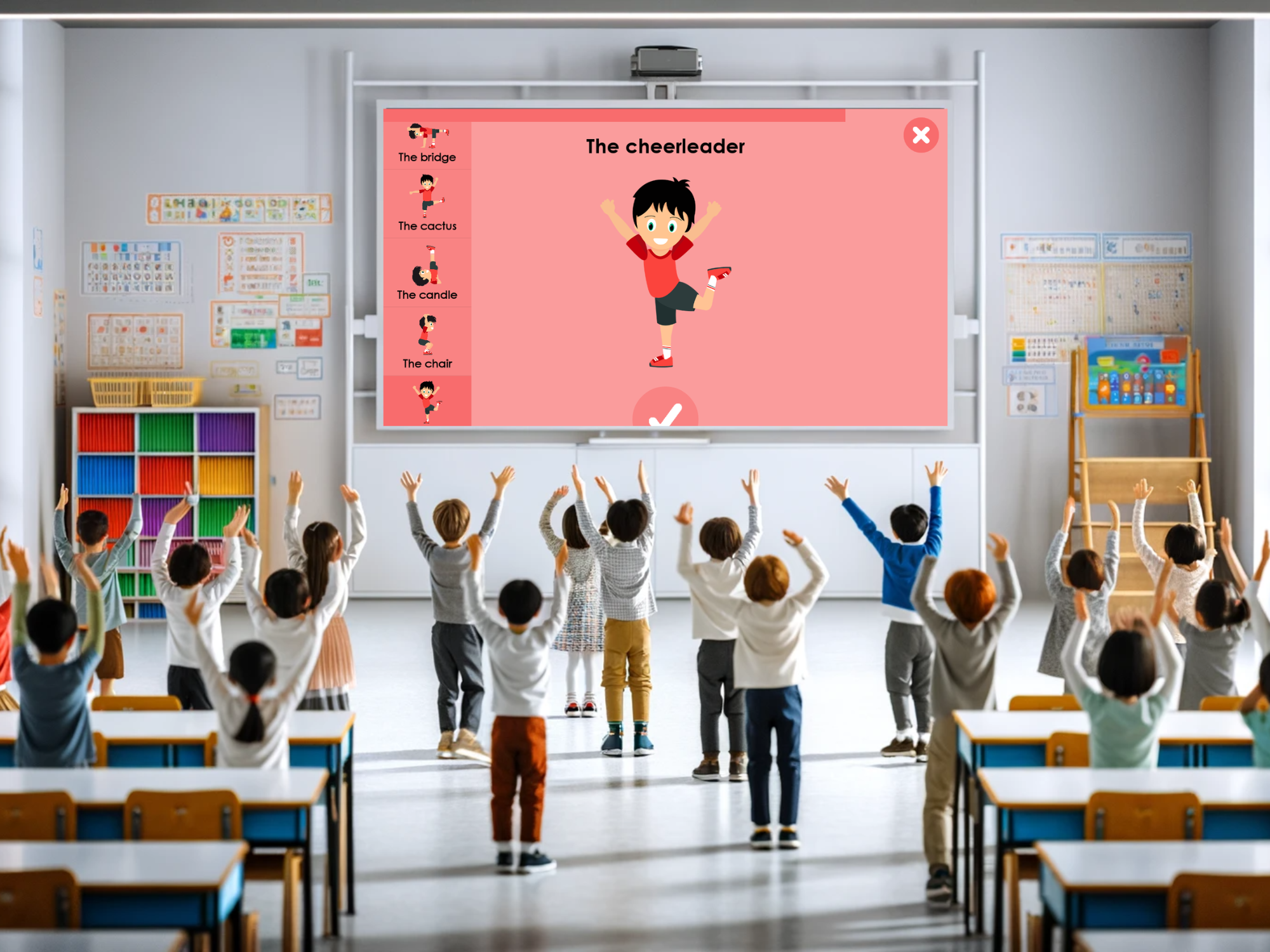
Group games projected on a large screen :

COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES,
a complete app for preschoolers
With more than 30 educational and sports games, you’ll find something that’s just right for your kindergarten, for group or individual use.

Other articles that might interest you:
How Parents Can Contribute to Teacher Training
As we delve into the realm of education, it becomes increasingly clear that teacher training is not merely a...
Differentiated Instruction Approaches: Training and Practical Application
Differentiated instruction is a pedagogical approach that recognizes the diverse needs of students in a classroom. It...
Key Skills Teachers Need to Support Students with Special Needs
As we embark on our journey to support children with special needs, it is essential for us to cultivate a deep...