DYS disorders (dyslexia, dyspraxia, dysphasia, dyscalculia, dysorthographia…) have a significant impact on children’s learning. Faced with these challenges, it is essential that teachers are trained to better understand these disorders and adapt their teaching methods. That’s why DYNSEO offers a comprehensive, immersive training program to help teachers better support their DYS students.
Understanding DYS disorders
DYS disorders are specific cognitive disorders that affect learning functions. They are not linked to a lack of intelligence, but to dysfunction in certain areas of the brain.
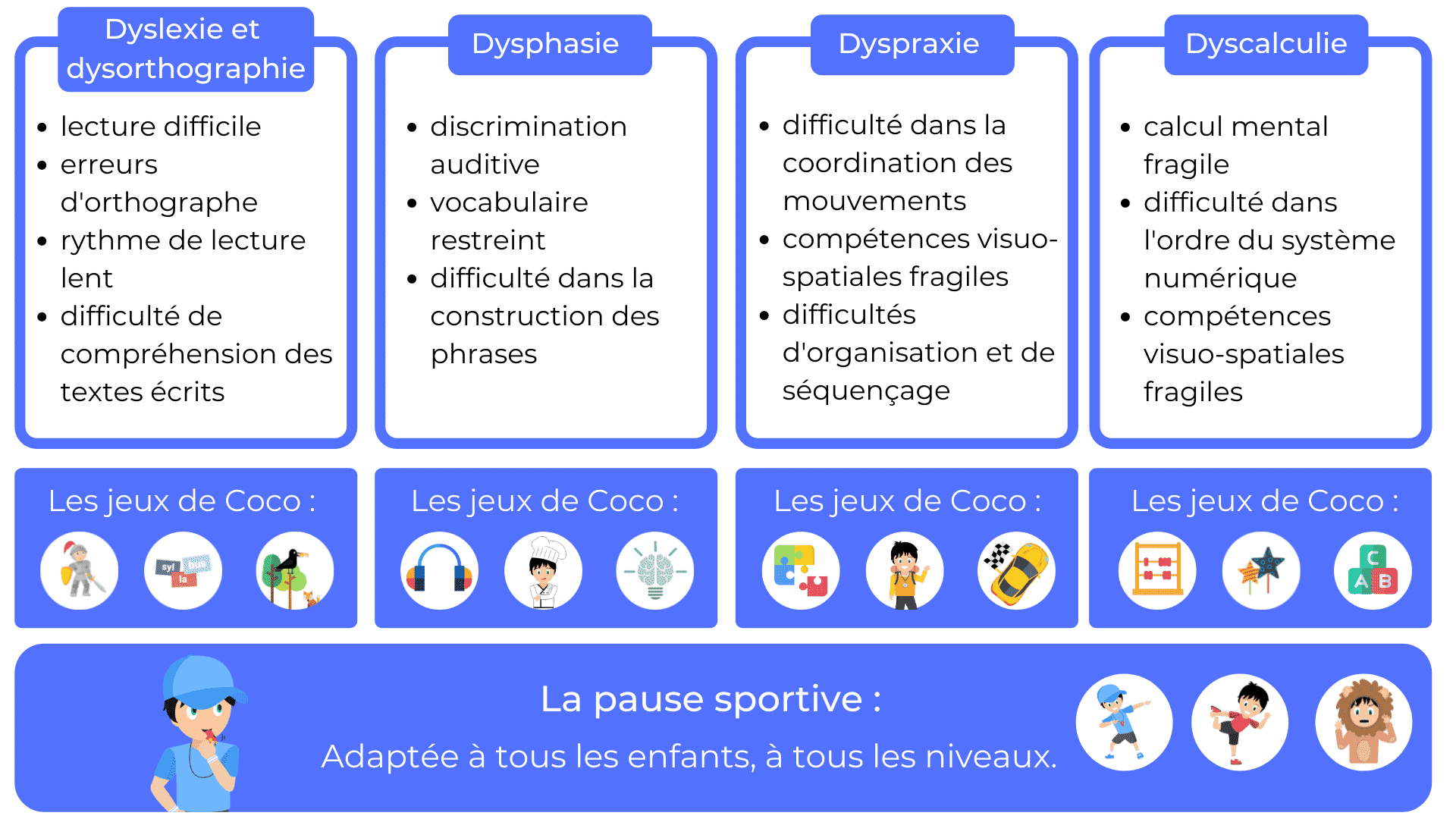
- Dyslexia: Specific reading and spelling disorder.
- Dyspraxia: Disorder affecting motor coordination and gesture organization.
- Dysphasia: Oral language disorder leading to difficulties in understanding and expressing oneself.
- Dyscalculia: Numerical learning disorder affecting understanding of numbers and operations.
- Dysorthography: Disorder affecting spelling and the structuring of writing.
These disorders may occur in isolation or in combination, and require an adapted pedagogical approach.
Training in two parts: Theoretical and Practical
1. Theoretical Training: Understanding DYS Disorders and Adapting Teaching
Duration: 2 hours
Price: €80/hour excluding VAT (€240 excluding VAT, i.e. €288 including VAT)
This first part of the course is designed to provide teachers with a basic understanding of DYS disorders and their implications for the classroom.
Points discussed:
- Description of DYS disorders
- Presentation of the different disorders: dyslexia, dyspraxia, dysphasia, dyscalculia, dysorthographia.
- Signs that students can recognize them.
- Concrete examples illustrating the difficulties encountered by children.
- Managing the emotions of DYS children
- Understanding the feelings of children in difficulty.
- Strategies for managing frustration and stress.
- How to make the class aware of the challenges of a DYS classmate.
- Educational adaptations and the school environment
- Presentation of tools and facilities to promote learning.
- Using new technologies to improve inclusion.
- Examples of activities adapted to each disorder.
- Strengthening links between schools, families and professionals
- How to inform families of their child’s difficulties.
- Integrate the work of speech therapists, occupational therapists and other professionals into the pedagogical project.
- Time for discussion and questions
- Sharing teachers’ experiences.
- Case studies and personalized advice.
2. Practical Workshops: Experiment and Apply
Duration: 3 hours
Price: €80/hour excl. tax (total €160 excl. tax, i.e. €192 incl. VAT)
These practical workshops enable teachers to put themselves in the shoes of DYS students and experience their difficulties, so as to adapt their teaching methods effectively.
Workshops include :
- Simulations of activities experienced by DYS children
- Experiment with everyday tasks in a DYS situation.
- Understand the sensory and cognitive impacts specific to each disorder.
- Setting the scene in a school context
- Case study and search for appropriate solutions.
- Strategies to facilitate learning and assessment.
- Introduction to new technologies
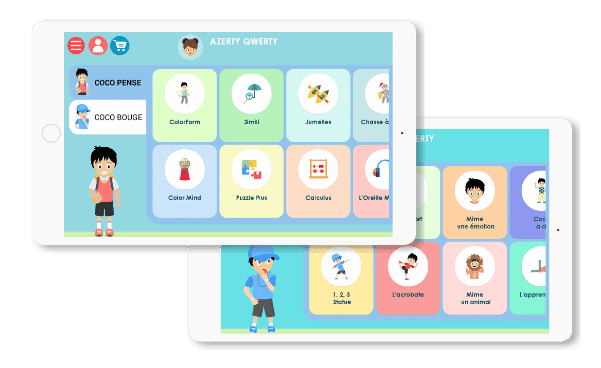
- Presentation and demonstration of the COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES application.
- Integrating digital tools for inclusive learning.
- Summary and discussion
- Workshop feedback.
- Discussion of concrete classroom applications.
Materials and media supplied
- Online materials: Access to a PDF presentation detailing the course.
- Materials for hands-on workshops: Teaching documents and visual aids.
- Access to tablets with the COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES application during workshops.
Some classroom practices to help DYS students
Space planning
The classroom environment plays a key role in the learning ability of DYS students. A structured, soothing environment reduces distractions and improves concentration.
- Place the student in a quiet area free from excessive distraction: DYS students are often sensitive to visual and auditory stimuli. It’s advisable to place them away from windows, doors and areas of frequent passage, to prevent them from being disturbed by outside noise or the movements of their peers.
- Creating an ergonomic workspace: comfortable, well-adapted seating is essential. Chairs that are too stiff or too high should be avoided, as they can cause postural fatigue and impair concentration.
- Offer visual aids to facilitate comprehension: DYS children assimilate information better when it is presented in different forms. The use of interactive boards, explanatory diagrams and illustrated displays helps to support explanations and structure learning.
- Limiting sources of stress: Some DYS students can be anxious about the unexpected. So it’s a good idea to post the daily class schedule and notify them in advance of any changes, to help them organize themselves mentally.
Adapted teaching strategies
The adoption of adapted teaching methods facilitates understanding and encourages the active participation of DYS students.
- Keep instructions short and clear: Instructions should be formulated concisely, with simple sentences and no double negatives. They should be repeated and rephrased if necessary. A concrete example can also help.
- Use color coding to structure information: Associating colors with certain categories of information helps DYS students to better organize their thoughts. For example, one color can be used for headings, another for definitions and yet another for examples.
- Offer interactive and varied exercises: Alternating between written, oral and visual activities helps to adapt teaching to different forms of intelligence and to the specific needs of DYS students. Paired or group exercises can also encourage self-help and promote learning.
- Split complex tasks: An exercise that is too long or too complicated can discourage a DYS student. We therefore recommend dividing tasks into several stages, and validating each stage before moving on to the next.
- Encourage manipulation and use of the body: For some dyspraxic children, learning through manipulation is more effective than purely theoretical learning. The use of movable letters, magnetic boards or kinaesthetic exercises can help them to memorize concepts better.
- Valuing success: DYS students sometimes have a low sense of competence. It is therefore essential to highlight their progress and encourage them with appropriate praise and positive reinforcement.
Use of new technologies
Digital tools offer innovative solutions to help DYS students compensate for their difficulties and actively engage in learning.
- Use adapted reading and writing software: Tools such as voice synthesizers or voice recognition software enable dyslexic and dysorthographic students to produce written work more fluently and efficiently.
- Use adapted fonts: Some fonts, such as OpenDyslexic, are specially designed to make reading easier for dyslexic students by accentuating the differences between letters.
- Integrate applications such as COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES: These interactive tools improve concentration and motor skills by alternating cognitive exercises with dynamic pauses. They also help regulate attention and limit mental fatigue.
- Encourage the use of tablets and digital pens: Handwriting can be a source of difficulty for some DYS students. Using tablets with handwriting recognition or simplified keyboards enables them to produce texts more quickly and legibly.
- Make lessons more accessible with audio and video support: Recording instructions or explanations in audio or video format can help DYS students to better assimilate information by enabling them to listen to them as many times as necessary.
Assessment and personalized follow-up
Assessment methods must be adapted to truly reflect the skills and knowledge of DYS students, without penalizing their specific difficulties.
- Allow more time for assessments: DYS students may need more time to read, understand and answer questions. Allowing extra time allows them to fully express their knowledge without rushing.
- Allowing alternative media such as oral instead of written: A dyslexic child may be able to explain verbally what he or she cannot write. Allowing oral assessments or diagrams can be a relevant solution.
- Set up adapted assessments: Instead of standardized assessments, you can adopt more flexible formats such as MCQs, mind maps or real-life situations.
- Establish regular reviews with the child and parents: Individual follow-up is essential to assess the effectiveness of the adaptations put in place, and adjust them if necessary. Regular meetings with families help coordinate efforts between school and home.
- Encourage self-assessment and positive reinforcement: It’s important to give DYS students the tools they need to monitor their own progress. The use of a logbook or self-assessment grid can help them become aware of their progress and boost their self-esteem.
By integrating these practices into their classrooms, teachers help to create a more inclusive and caring learning environment, enabling DYS students to progress at their own pace and in conditions adapted to their specific needs.
Why train with DYNSEO?
- An immersive, interactive approach: understanding DYS disorders in theory, but also experiencing them in real-life situations.
- Practical tools that can be put to immediate use in the classroom: teaching strategies, digital tools, adapted exercises.
- Recognized expertise in supporting DYS children: DYNSEO develops educational tools specifically adapted to children with learning disabilities.
- Post-training support: access to materials and resources to continue training and adapt your teaching.
How do I register?
Interested teachers and schools can contact us for more information on available sessions at contact@dynseo.com.
Invest in inclusive education and become an agent of change for DYS students!