There are sensory disabilities such as deafness or blindness. Motor disabilities as in hemiplegia. Finally, there are developmental disabilities such as autism, Down syndrome, ADHD or DYS disorders.
In this article we will have an excerpt from the webinar offered by DYNSEO on learning disabilities and developmental disorders.
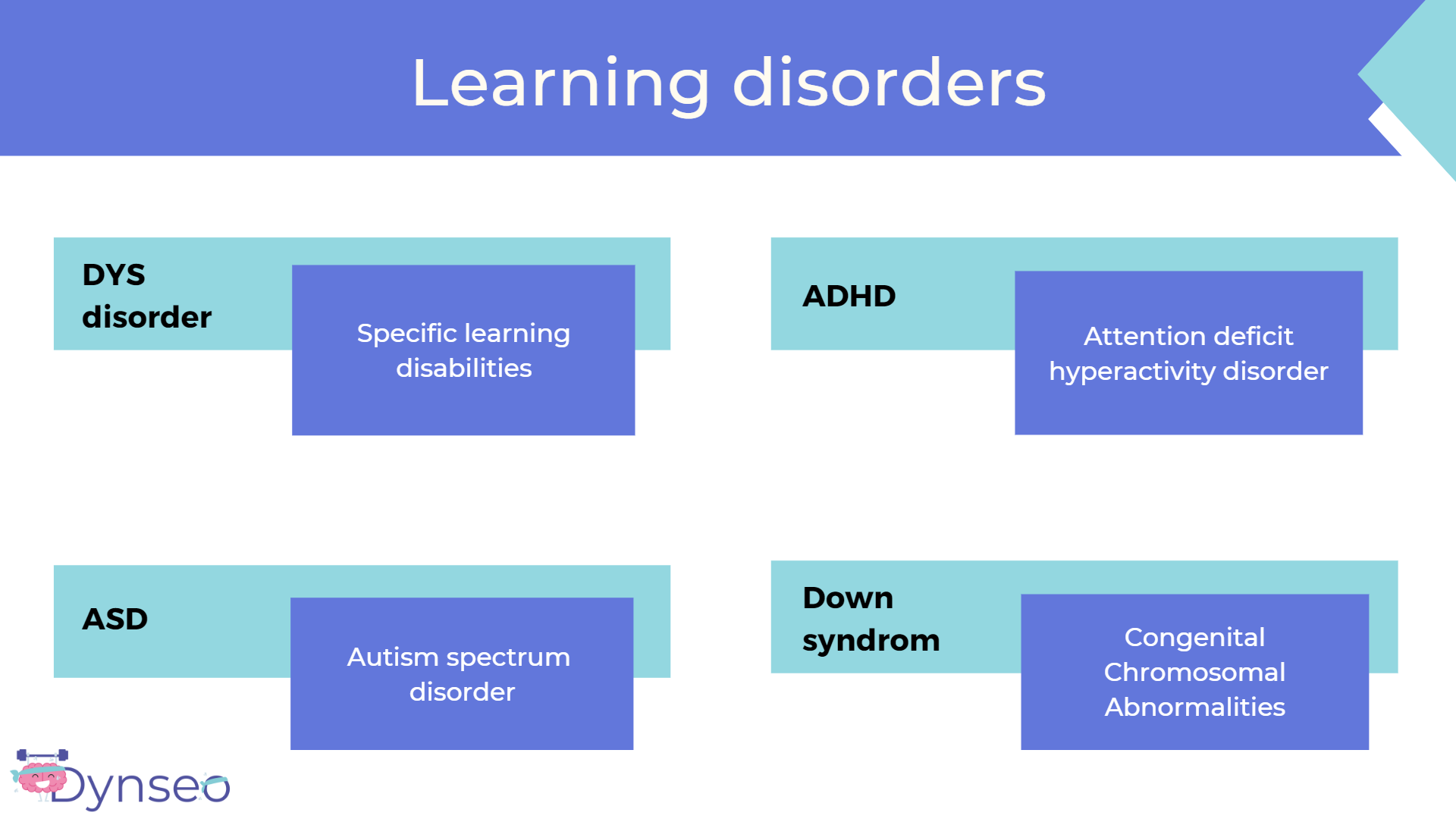
Learning disorder
DYS disorders are specific learning disabilities, such as dyslexia, dysorthographia, dyscalculia, dyspraxia and dysphasia.
ADHD children are children who have attention disorders that may or may not be associated with hyperactivity.
ASD is the autism spectrum disorder. As the term says, it’s a spectrum so it’s very broad and the child can have mild to severe symptoms, on different aspects of development.
Down syndrome is a genetic condition that causes cognitive problems. This is why children with Down syndrome have learning difficulties.
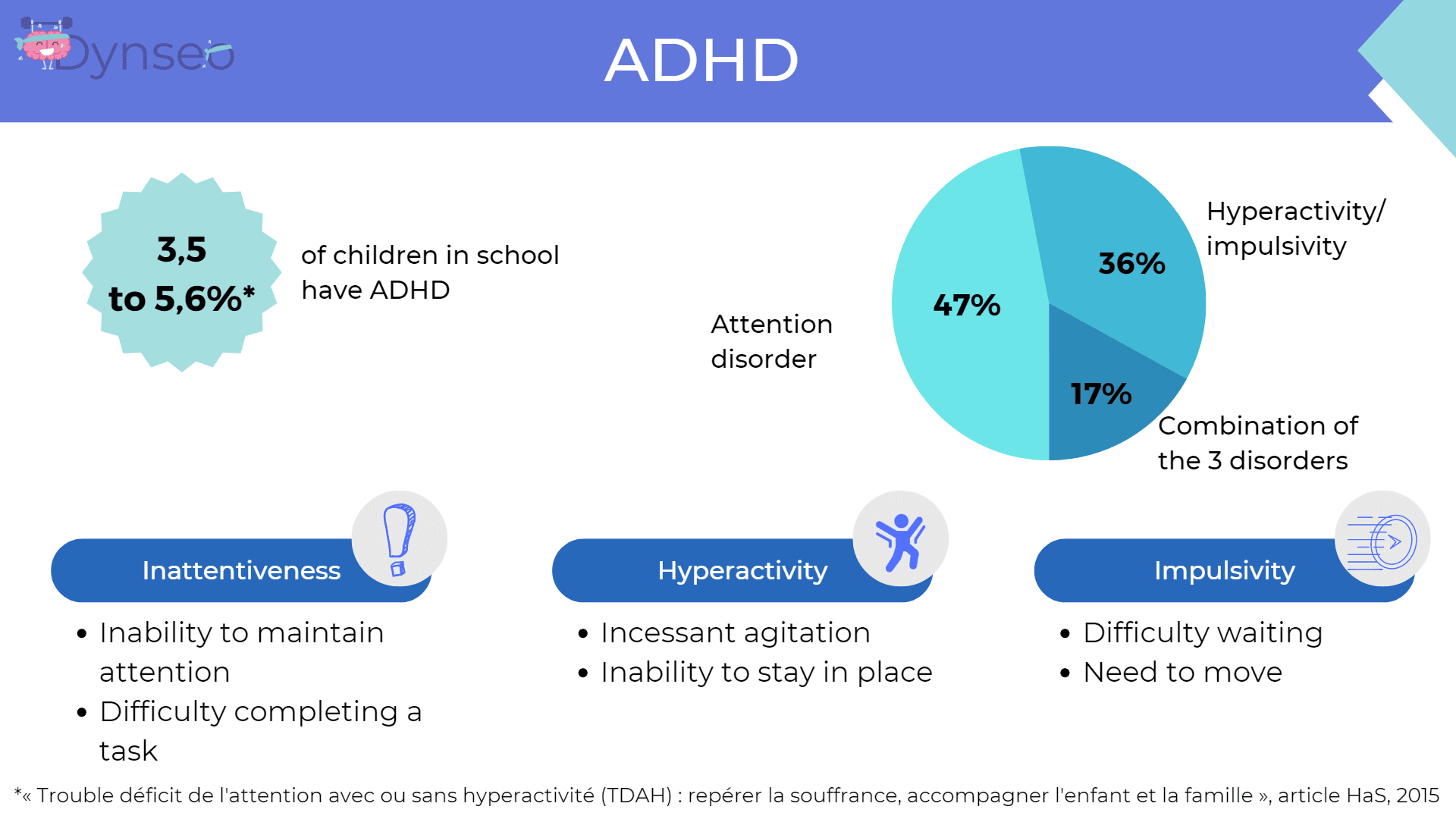
ADHD
Between 3.5% and 5.6% of children in school have ADHD. The majority of whom have an attention disorder (47%), followed by hyperactivity and impulsivity (36%).
In some cases, the three symptoms may be associated. In terms of attention, children are easily distracted. It is therefore important not to make them sit next to the window because otherwise they will look out. If the child is hyperactive, he or she will have difficulty sitting still. You can give the child tasks to get them moving in a controlled setting. For example, you can ask him to go and print some photocopies.
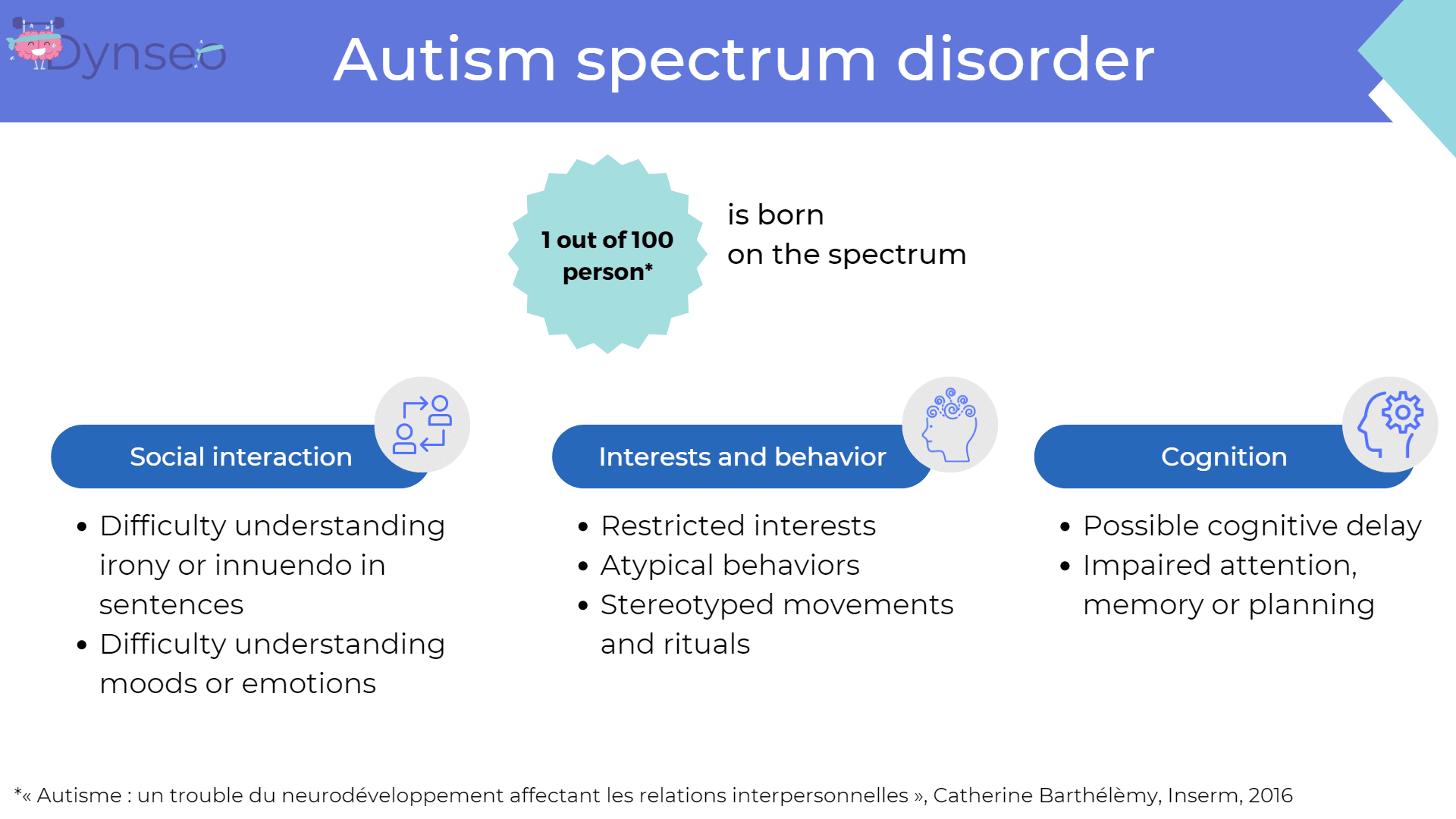
Autism spectrum disorders
1 in 100 children are born with an autism spectrum disorder. A child with autism may have difficulties in one or more areas, depending on the type of autism. For example, in Asperger’s Syndrome, the child has above average intelligence, but has great difficulty with relationships.
In general, children with autism have difficulty with social interactions. They do not understand irony or the emotions of others. So it’s important not to use a phrase like “you have your head in the clouds?”.
Interests are restricted and the child is only interested in that. There may also be stereotyped movements, i.e. repetitive movements that the child cannot control.
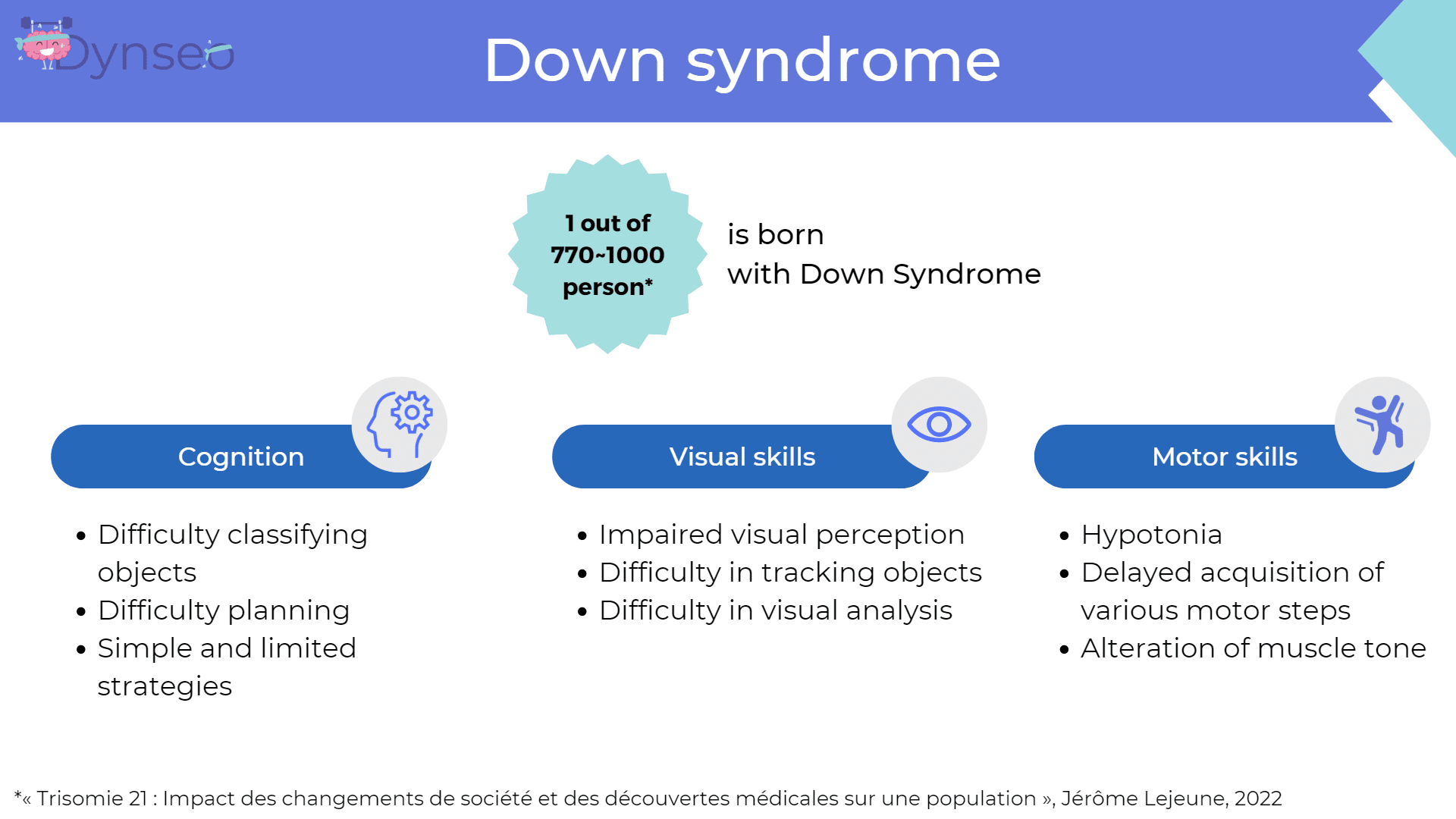
Down syndrome
Down syndrome, also known as Trisomy 21, is influenced by several factors such as genetics and the mother’s age.
Children with Down syndrome have cognitive problems. The difficulties are mainly in the classification of objects and in the creation and use of strategies.
Another difficulty is related to visual skills. Indeed, the child has an altered visual perception and it is more difficult for him to analyze or recognize objects. It is therefore important to propose exercises with well-contrasted colors.
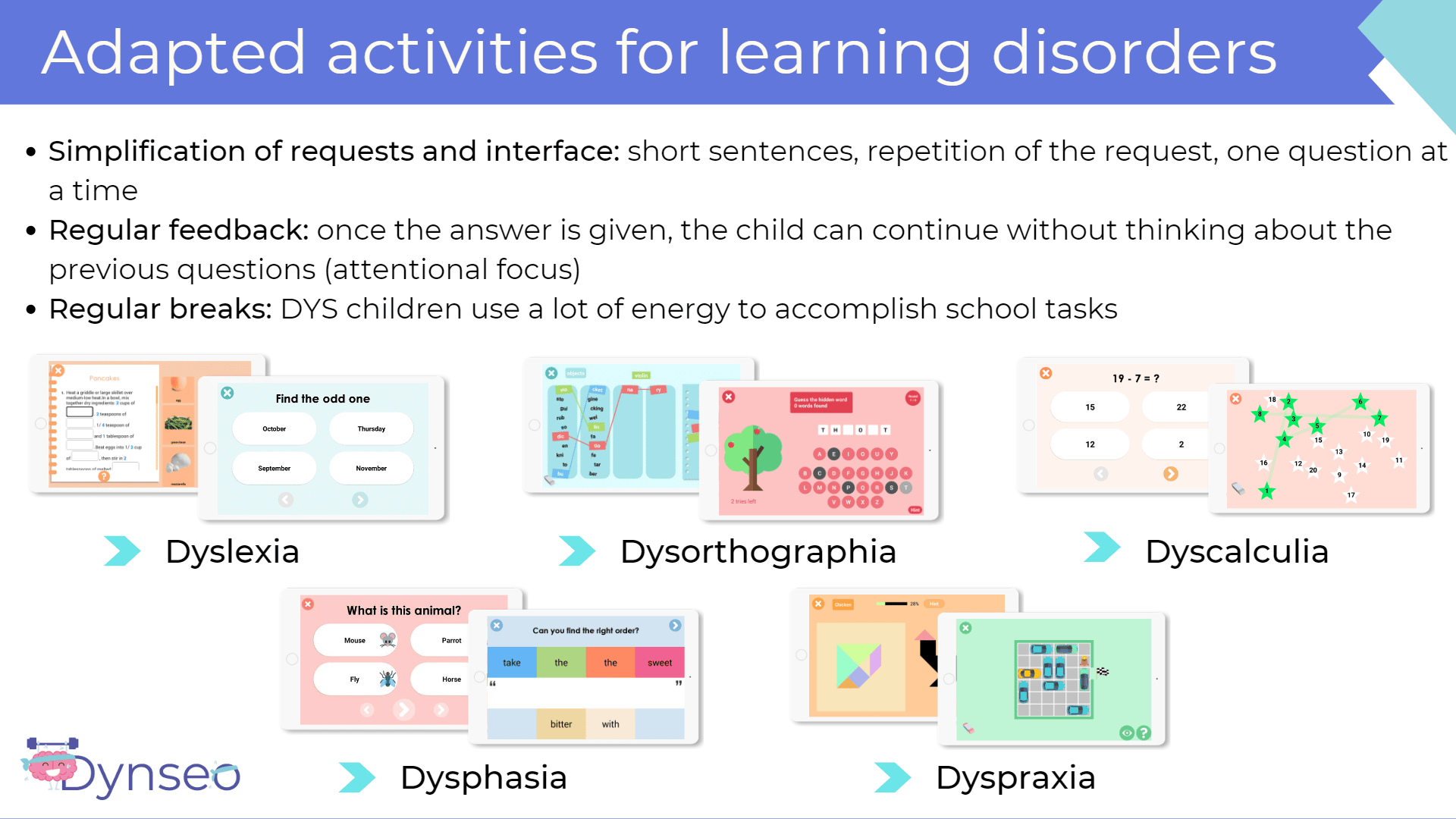
Learning disabilities in elementary school
At school it is important to adapt the activities to the needs of each child, in order to allow him/her to learn at his/her own pace. To do this, teachers can use technology, such as the tablet. Indeed, today there are many applications. A widely used application to accompany children with disabilities is COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES.
In this app there are more than 30 educational games for adapted activities. There are audio descriptions for children with reading disabilities, for example.
With COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES, you have acces to a wide range of activities for all children so that they are not excluded from the class. There are fill-in-the-blank texts, games on numerical order and sequencing, among other fun games.
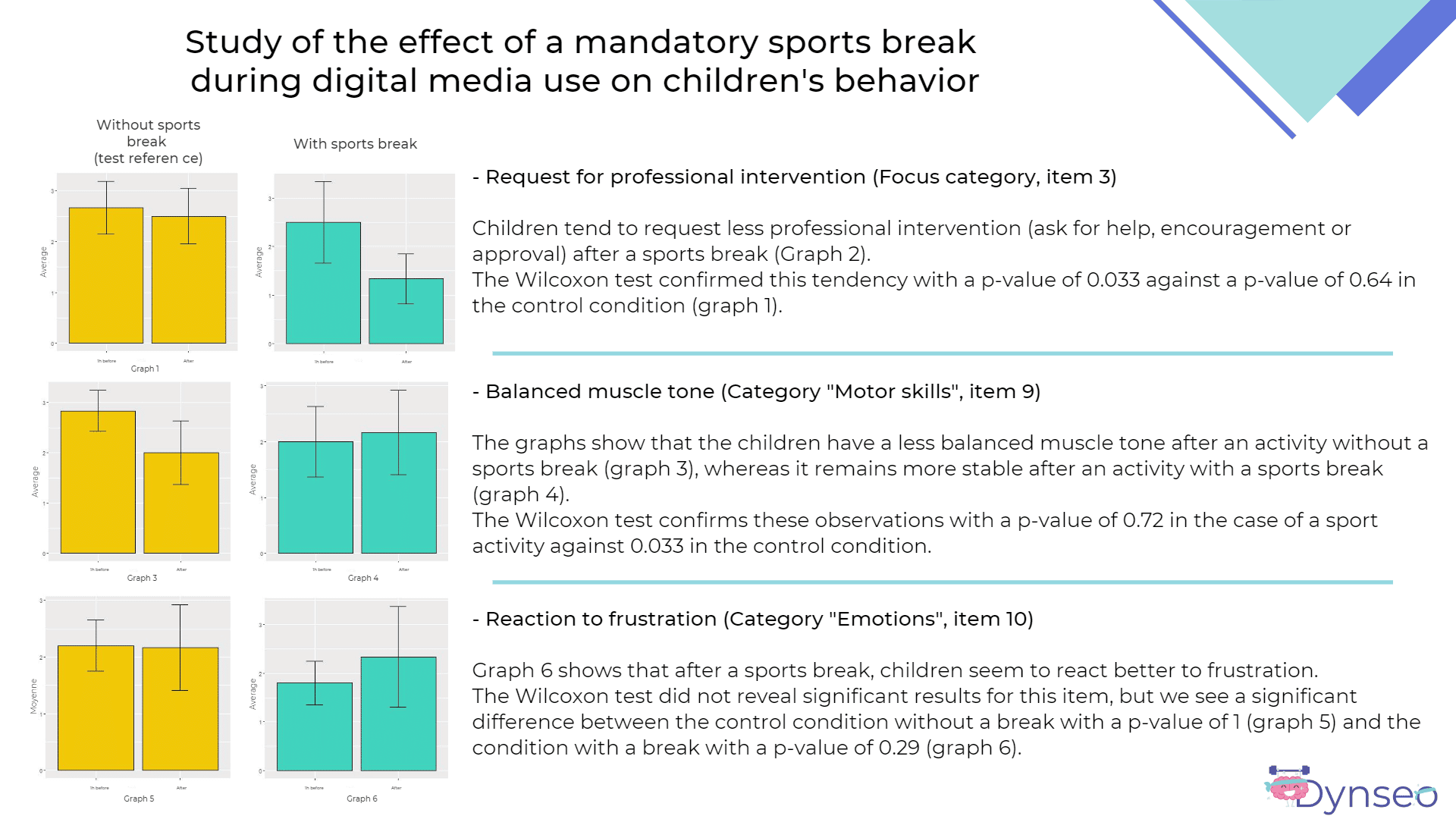
A sports break
In the COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES app, after 15 minutes of screen time the app stops and imposes a sports break. The child must therefore do activities that are more or less physical. There are also activities suitable for children with limited motor skills, such as the “mime an emotion” game.
This break is very important for the children because for them the activities require a lot of effort and can quickly tire them.
A survey showed that after a sports break, children asked less for professional intervention during activities, had a more balanced muscle tone and finally had a better reaction to frustration.
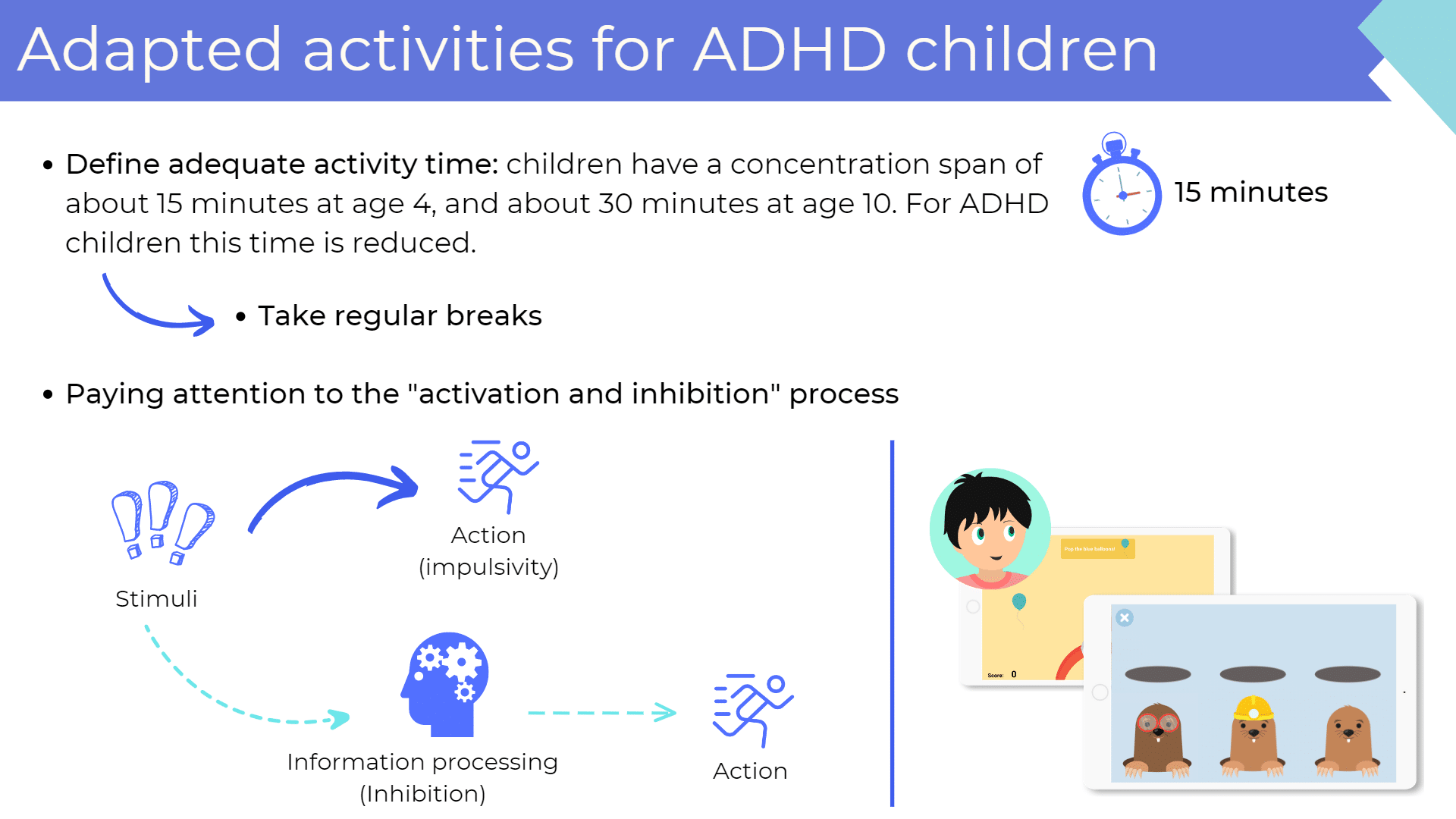
Learning disabilities in middle school
Children cannot be “cured” of developmental disabilities, but they can find tools to compensate. Also in middle school it is important to offer children a support.
One example is the CLINT app with over 30 games to work on cognitive functions while having fun.
For ADHD children it is important to work on inhibition. In the game “Moles Invasion”, the student must touch the normal mole once, the mole with the helmet twice and must not touch the mole with glasses.
Of course, in the CLINT app there are also literature, math and cultural games to work on general knowledge or history.

COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES: more than 30 educational games for children from 5 to 10 years old with a compulsory sports break after 15 minutes of screen time
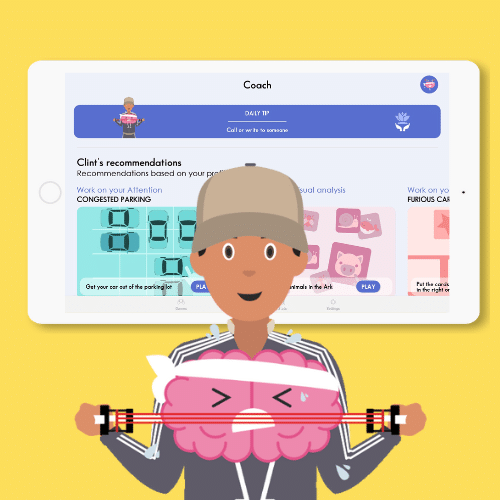
CLINT: 30+ cognitive and cultural games for middle school students to stimulate cognitive function and learning
Other articles that might interest you:
Supporting children with autism
Dynseo proposesSUPPORTING CHILDREN WITH AUTISM with COCO THINKS AND COCO MOVESDynseo and its team are very much...
Supporting DYS children with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES
Dynseo proposesDYS disorders with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVESOur educational and pedagogical games program COCO THINKS...
Language development
Children communicate from birth with movements, crying, looking at each other or with smiles. After only a few months,...
Supporting children with Down Syndrome with Coco
Dynseo proposesDOWN SYNDROME with COCODown syndrome is a non-hereditary chromosomal abnormality that leads to the...
Supporting people after a stroke
Dynseo proposesStroke with CLINT, your brain training coachThe Dynseo team is very involved in helping people who have...
Supporting someone with Alzheimer’s
In this guide, we will detail how SCARLETT can be used for supporting someone with Alzheimer's. SCARLETT is a...
10 myths about the human brain you didn’t know
The brain is an incredible muscle, however there are many things we do not know, and what we do know is not always...
Using Digital Tools to Support Students with Special Educational Needs
Special Educational Needs (SEN) encompass a wide range of learning difficulties and disabilities that can hinder a...
Down Syndrome and Communication: Facilitating Interaction with Visual and Interactive Supports
When we think about Down syndrome, we often recognize it as a genetic condition that affects physical and cognitive...
How to Track Progress in People with Down Syndrome Using Digital Tools
Down syndrome, a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, affects approximately 1 in every...