Mélanie Chabloz from the neuropsychology and neurorehabilitation department at the CHUV of Lausanne in Switzerland, tells us more about visual gnosias.
Visual gnosis is simply a term that defines the ability to recognize objects through vision.
What you need to know is that there are 2 major visual brain pathways:
- The “WHAT” channel, specialized in the visual identification of objects. It extracts visual information from the stimuli and processes it in order to recognize and assign meaning to it.
- The “OR” channel, which allows to locate objects in space.
When there is a brain lesion in one of these 2 pathways, it can lead to disorders that will affect either the recognition of objects or the localization of objects.
The disorders that will “interest” us, because they are related to our subject, are the disorders resulting from a lesion of the “WHAT” pathway, we call them visual agnosias.
What is visual agnosia?
Visual agnosias are defined as the inability to recognize people or objects when presented visually. In order to conclude that there is visual agnosia, recognition in other modalities must be preserved. For example, in the tactile modality, i.e. by touching the object, or in the auditory modality, by hearing the noise it makes.
Two types of visual agnosias should be noted:
- Associative visual agnosia, which is the inability to recognize what one perceives correctly; the perception is correct but meaningless. For example, you can copy a drawing, but you don’t recognize what you are copying.
- Aperceptive visual agnosia, which is the inability to recognize because of perceptual deficits, what one sees is no longer meaningful. For example, we are unable to copy a drawing.
So we should not neglect our visual gnosias, but how do we maintain them?
Nowadays nothing could be easier! There are tools to work on your brain in a playful way, Dynseo gives you the opportunity to do so, while having fun!
The brain is a muscle, it must be maintained and worked!
This interview with Mélanie Chabloz, helped us to enter the subject of visual gnosias.
Now we will look at the subject in more detail, see how to recognize visual agnosia, the causes and what to do if you are affected by these gnosias.
How to recognize visual agnosia?
Visual agnosia can be an effect of disease or trauma, and it can vary in severity.
When you have visual agnosia, you have difficulty recognizing objects or people. Often, these disorders can be associated with normal memory loss and are not noticed. However, it is very important to identify visual agnosia, as it is a symptom of something bigger.
If you have difficulty recognizing people or objects, it is important to go see your doctor for specific tests and to be taken care of by specialized professionals.
Causes of visual agnosias
In general, visual agnosia is due to a brain lesion. Visual agnosia can therefore be due to a stroke, a head injury, neurological disorders (such as Alzheimer’s), a brain tumor or a brain abscess.
In all of these situations, visual agnosia may be comorbid with other symptoms. The person must therefore be taken in charge by a professional to start a therapeutic project.
What to do when you have visual agnosia?
The treatment of agnosia is to treat the cause of the agnosia itself. It is therefore important to have a medical examination to define the cause. Once the cause of the agnosia is found, you can contact an occupational therapist, a speech therapist or a physical therapist.
The evolution of visual agnosia depends on several factors such as the cause, the severity of the symptoms and the general condition of the person.
The goal of therapy is to provide strategies for overcoming difficulties in daily life. In some cases, it is also possible to carry out a rehabilitation to recover part of the lost function. In this case, early intervention can make a difference and allow for a more favorable outcome.
Clint, you brain coach
In addition to sessions with health professionals, you can also continue your training at home. Sometimes, it is the professional himself who can advise you on which applications to use.
For example, some health professionals recommend the Joe application.
Joe offers over 30 games to work on cognitive functions such as attention, memory, language, logic and visual skills.
Each game has three difficulty levels so you can tailor the game to your skills and needs. In addition, you can track your progress over time to see your progress or to see your more fragile functions.

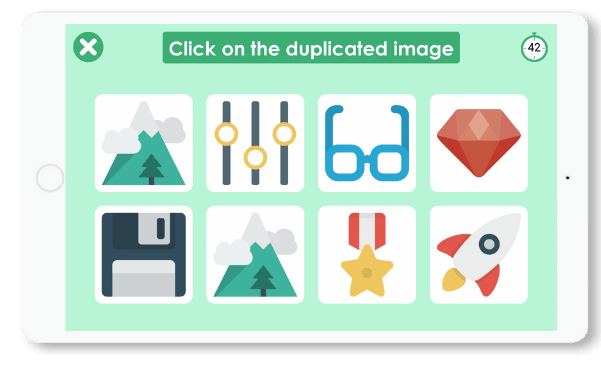
Simili
In this game, the person must find the duplicate image.
So the first step is for the person to look at all the images and recognize them. Then they have to find out which image is present twice.
This game is suitable for people with mild cognitive impairment since it requires complex skills.
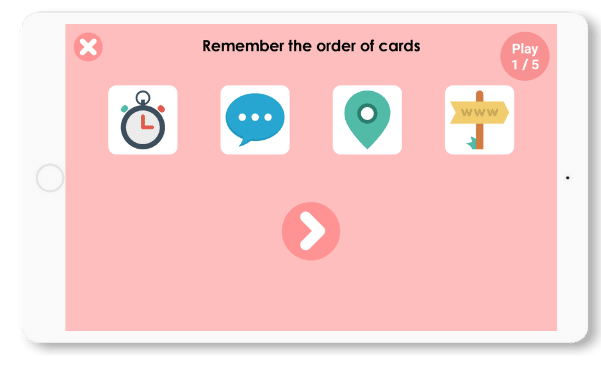
Furious Cards
In this game, the person must memorize the order of the cards.
Each card has a picture on it so the person has to recognize the pictures to memorize them. In this phase, the person can name the images to help memorize them.
When he has to put the cards back in order, he can use semantic memory, but to do so he must associate the right picture with the word.
Puzzle Plus
In this game, the person has to drag the pieces of the puzzle to reconstruct the hidden image.
The person works on the analysis of the image, in a general to detailed way.
Indeed, the person sees the global image before it is cut into several pieces. Then they must analyze the pieces to understand what part of the puzzle it represents.

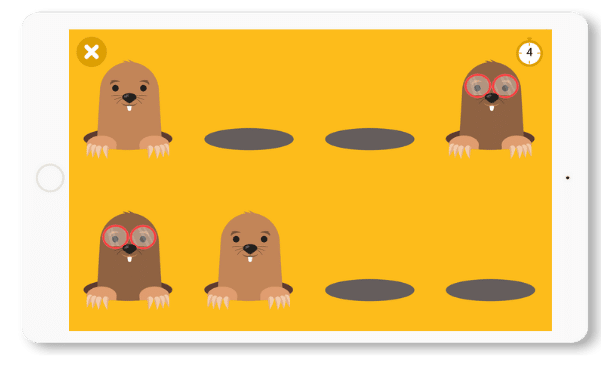
Moles Invasion
In this game, the person has to tap the moles that appear on the screen. The difficulty is that there are three different moles that require different action. The normal mole is to be tapped once, the mole with glasses is to be tapped twice and the mole with glasses is not to be tapped.
The person must therefore recognize the stimulus and adapt his or her movement to the image that appears.
Moreover, the moles will stay on the screen for a limited time so we also work on the response time.
Other types of agnosias
Generally, agnosias occur in only one perceptual sense. In this article, we analyzed visual agnosias, i.e. when the difficulty is with visible information. There are, however, other types of agnosias.
One example is auditory agnosia. In this case, the person may have difficulty recognizing everyday sounds or music. Or she may have difficulty understanding oral language.
Another type of agnosia is tactile agnosia. In this case, the person may have difficulty recognizing objects by palpation. The recognition disorder may be in the area of material, weight or shape.
There is also asomatognosia, which is a rare agnosia. This situation is characterized by a loss of recognition of part or all of the body. There may be difficulty in recognizing the body in general or only the fingers. In this case, we speak of digital agnosia.
Brain training programs
There are many ways to exercise your memory and cognitive functions. Daily practice of brain exercises reduces the risk of neurological disorders, as some programs act on all cognitive functions.
The CLINT brain training program was designed specifically for adults to keep theit brain healthy through fun and challenging brain exercises. It has over 30 cognitive games and targets concentration, focus, reflexes, language and many other cognitive functions.
Understanding the Impact of Visual Agnosia on Daily Life
Visual agnosia can significantly affect an individual’s ability to perform everyday tasks. The challenges posed by this condition can vary widely depending on the severity of the agnosia and the specific type experienced. Here are some common areas where individuals may struggle:
- Personal Care: Difficulty recognizing personal items such as clothing or grooming tools can hinder daily hygiene and dressing.
- Navigation: Individuals may have trouble recognizing familiar places or landmarks, making it challenging to navigate their environment.
- Social Interactions: The inability to recognize friends, family, or even acquaintances can lead to social withdrawal and feelings of isolation.
- Cooking and Meal Preparation: Recognizing ingredients or cooking tools can become problematic, impacting the ability to prepare meals safely.
Therapeutic Approaches for Visual Agnosia
Addressing visual agnosia typically involves a combination of therapeutic strategies tailored to the individual’s needs. Here are some common approaches:
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Tailored exercises and activities designed to improve visual recognition and processing skills.
- Occupational Therapy: Focuses on helping individuals adapt their environment and develop strategies to manage daily tasks despite their visual recognition challenges.
- Speech and Language Therapy: Assists in improving communication skills, especially if there are associated language difficulties.
- Assistive Technology: Utilizing apps and devices that can aid in recognizing objects and navigating environments can enhance independence.
Research and Advances in Visual Agnosia Treatment
Research into visual agnosia is ongoing, with many studies exploring innovative treatments and interventions. Some of the latest advancements include:
- Neuroplasticity Techniques: Exploring methods to harness the brain’s ability to reorganize itself and potentially recover lost functions.
- Virtual Reality Therapy: Utilizing VR technology to create immersive environments that stimulate visual recognition in a controlled setting.
- Brain Training Applications: Development of specialized apps aimed at improving cognitive functions related to visual processing.
- Genetic and Neurobiological Studies: Investigating the underlying genetic and biological factors that contribute to visual agnosia to develop targeted therapies.
Support Systems for Individuals with Visual Agnosia
Support from family, friends, and professionals is crucial for individuals with visual agnosia. Here are some ways to build a supportive network:
- Education: Informing family and friends about visual agnosia can foster understanding and patience.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others facing similar challenges.
- Professional Guidance: Regular consultations with healthcare professionals can help manage symptoms and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Community Resources: Accessing local resources such as rehabilitation centers or community programs designed for individuals with cognitive impairments can enhance quality of life.




