Parkinson’s disease, a complex neurodegenerative condition, manifests through a variety of physical symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and impaired movement. However, the impact of Parkinson’s extends far beyond the physical realm, deeply affecting the emotional and psychological well-being of patients and their families. The journey with Parkinson’s often entails confronting uncertainty, adapting to new limitations, and managing a myriad of emotions ranging from fear to frustration. In this context, the significance of emotional and psychological support cannot be overstated. It serves as a beacon of hope amidst the challenges, offering comfort, understanding, and practical strategies for coping with the multifaceted aspects of the disease.
By addressing the emotional needs of both patients and their families, this support not only alleviates feelings of isolation but also cultivates resilience and fosters a sense of empowerment. Recognizing the holistic nature of Parkinson’s care, integrating emotional and psychological support alongside medical interventions is essential for promoting overall well-being and enhancing quality of life for those affected by the condition.
Understanding Parkinson’s Disease
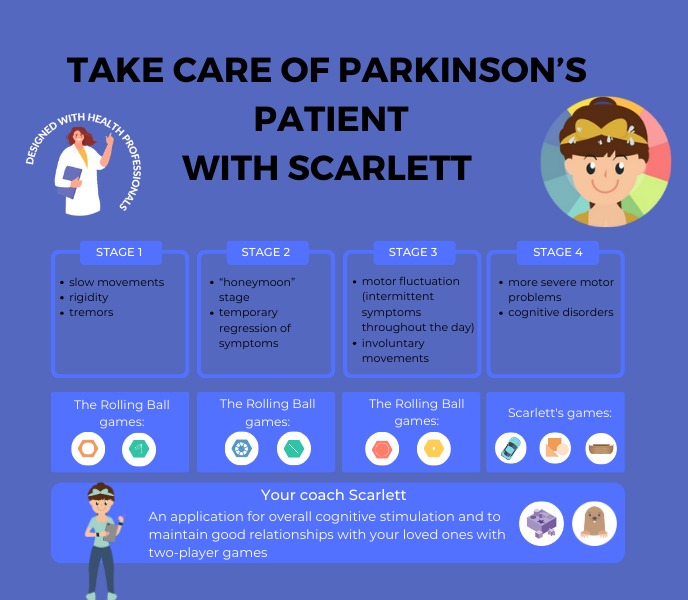
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by a range of motor and non-motor symptoms that progressively worsen over time. Motor symptoms include tremors, stiffness, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability, which significantly impair mobility and coordination. Non-motor symptoms encompass cognitive changes, mood disturbances such as depression and anxiety, sleep disturbances, and autonomic dysfunction. Beyond its physical manifestations, Parkinson’s profoundly impacts patients and their families emotionally, socially, and financially.
Patients often experience frustration, loss of independence, and decreased quality of life due to the limitations imposed by the disease. Families face challenges in providing care, coping with the emotional toll, and adjusting to changes in roles and responsibilities. Understanding these symptoms and their broader implications is crucial for providing comprehensive support and enhancing the well-being of individuals affected by Parkinson’s disease and their families.
Emotional Challenges Faced by Parkinson’s Patients
Parkinson’s disease brings forth a myriad of emotional challenges that significantly impact patients’ lives. Anxiety and depression are prevalent among individuals with Parkinson’s, often stemming from the uncertainties surrounding the progression of the disease and the accompanying lifestyle adjustments. The unpredictable nature of symptoms and the fear of losing control over one’s body contribute to heightened levels of anxiety. Additionally, feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and isolation can exacerbate depressive symptoms, affecting both the patient’s mental health and overall quality of life. Moreover, there’s a pervasive fear of the future and uncertainty about the disease’s trajectory, leading to apprehension about how symptoms will evolve and the potential impact on independence and relationships. Addressing these emotional challenges with empathy, support, and appropriate interventions is essential to help Parkinson’s patients navigate their journey with resilience and a sense of empowerment.
Importance of Emotional Support
Psychological Support Strategies
Psychological support strategies are essential components of comprehensive care for individuals living with Parkinson’s disease. Therapeutic interventions encompass a range of approaches aimed at addressing the psychological and emotional challenges associated with the condition. Counseling and psychotherapy provide patients with a safe space to explore their emotions, develop coping strategies, and navigate the complex dynamics of living with Parkinson’s. Additionally, support groups offer valuable opportunities for patients to connect with others facing similar experiences, share insights, and gain perspective on managing their condition. Alongside therapeutic interventions, medication management is another crucial aspect of psychological support.
Medications targeting symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive changes can help alleviate distress and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s. By integrating these psychological support strategies into Parkinson’s care plans, healthcare providers can effectively address the multifaceted needs of patients and enhance their emotional well-being and resilience.
Family Dynamics in Parkinson’s
Family dynamics play a significant role in the journey of Parkinson’s disease, both in providing essential support to patients and experiencing their emotional impacts. The role of family in patient support is multifaceted, encompassing practical assistance with daily tasks, emotional encouragement, and advocacy in healthcare settings. Family members often serve as caregivers, offering unwavering support and navigating the challenges alongside the patient. However, the emotional impact on family members should not be underestimated.
Witnessing a loved one cope with Parkinson’s can evoke feelings of sadness, stress, and helplessness. Family members may grapple with their fears about the future and adjustments to changing roles and responsibilities within the family unit. Acknowledging and addressing these emotional dynamics within the family context is crucial for fostering open communication, mutual understanding, and resilience in navigating the complexities of Parkinson’s disease together.
Communication Strategies
Coping Mechanisms for Patients
Coping mechanisms are essential tools for patients navigating the challenges of Parkinson’s disease, particularly in managing stress and promoting overall well-being. Stress reduction techniques play a crucial role in helping patients cope with the emotional and physical toll of the condition. Among these techniques, mindfulness and meditation offer powerful tools for cultivating present-moment awareness, reducing anxiety, and enhancing resilience in the face of adversity. Through mindfulness practices, patients can learn to observe their thoughts and sensations without judgment, fostering a sense of calm and inner peace.
Additionally, relaxation exercises such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualization techniques can help alleviate muscle tension, promote relaxation, and improve sleep quality. By incorporating these coping mechanisms into their daily routines, patients can enhance their ability to cope with stress, maintain emotional balance, and optimize their overall quality of life despite the challenges posed by Parkinson’s disease.
Educational Resources for Families
Understanding Parkinson’s progression
Understanding the progression of Parkinson’s disease is crucial for families to effectively support their loved ones and prepare for the future. Parkinson’s is a progressive condition, meaning symptoms typically worsen over time. By learning about the stages and patterns of progression, families can anticipate changes in symptoms and functional abilities, enabling them to make informed decisions about caregiving, treatment options, and long-term planning.
Educational resources provide families with insights into the various motor and non-motor symptoms that may emerge as the disease advances, empowering them to recognize signs of progression and seek appropriate medical and supportive interventions promptly. With a deeper understanding of Parkinson’s progression, families can proactively adapt their care strategies and advocate for their loved one’s evolving needs throughout the course of the disease.
Access to reliable information
Access to reliable information is essential for families navigating the complexities of Parkinson’s disease. Reliable sources of information, such as reputable medical websites, educational materials from Parkinson’s organizations, and literature endorsed by healthcare professionals, empower families with accurate, up-to-date knowledge about the condition, treatment options, and available support services. Access to reliable information helps families make informed decisions regarding their loved one’s care, treatment plans, and lifestyle adjustments.
It also equips them with the necessary tools to effectively communicate with healthcare providers, advocate for their loved one’s needs, and engage in shared decision-making processes. By promoting access to reliable information, healthcare professionals and Parkinson’s organizations play a pivotal role in supporting families as they navigate the challenges of living with Parkinson’s disease and strive to provide the best possible care and support for their loved ones.
Community and Social Support
Community and social support are invaluable resources for individuals and families affected by Parkinson’s disease. Building a network of support, both within the Parkinson’s community and beyond, provides a sense of belonging, understanding, and encouragement. Through support groups, online forums, and local community organizations, individuals can connect with others facing similar experiences, share insights, and offer mutual support and encouragement. These networks foster a sense of camaraderie and solidarity, alleviating feelings of isolation and loneliness often associated with chronic illness. Moreover, community engagement and involvement empower individuals to participate in advocacy efforts, raise awareness, and effect positive change within their communities.
By engaging with local resources, attending educational events, and volunteering, individuals and families can contribute to a more supportive and inclusive community while receiving the support and validation they need to navigate the challenges of Parkinson’s disease with resilience and optimism.
Professional Support Services
Professional support services play a critical role in the comprehensive care and management of Parkinson’s disease. The involvement of healthcare professionals, including neurologists, movement disorder specialists, and rehabilitation therapists, is essential in providing specialized medical care, monitoring disease progression, and optimizing treatment plans tailored to the individual needs of patients. Healthcare professionals offer expertise in managing motor and non-motor symptoms, prescribing appropriate medications, and coordinating multidisciplinary care teams to address the complex needs of Parkinson’s patients. Additionally, social workers and therapists play a vital role in addressing the psychosocial aspects of the disease, offering emotional support, counseling, and practical guidance to patients and their families.
Social workers assist with navigating healthcare systems, accessing community resources, and addressing financial and logistical challenges, while therapists provide cognitive-behavioral therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy to enhance patients’ overall well-being and quality of life. By collaborating with a diverse team of healthcare professionals, individuals living with Parkinson’s disease can receive comprehensive, holistic care that addresses their medical, emotional, and social needs effectively.
Promoting Resilience and Well-being
AND FOR FURTHER INFORMATION
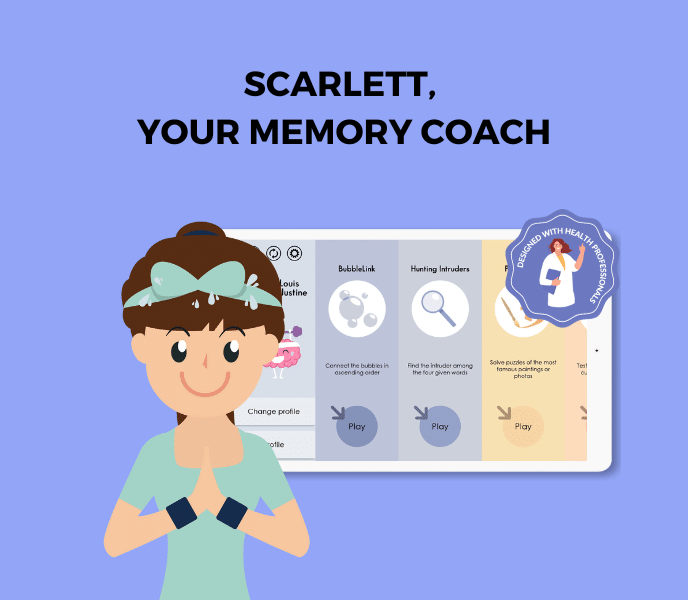
SCARLETT, EASY MEMORY GAMES FOR PARKINSON
SCARLETT is a user-friendly memory game program that offers a collection of simple yet engaging exercises, specifically designed to gently enhance memory skills. No timer, no score and no failure. Just the pleasure of playing. Try it for free for one week.

CLINT, A CHALLENGING BRAIN GAMES APP
For individuals seeking a more challenging experience, the CLINT program serves as a more demanding version, offering complex memory games that require greater cognitive effort, making it suitable for those in need of a more strenuous mental workout.

THE ROLLING BALL TO WORK ON FINE MOTOR SKILLS
The Rolling Ball app is an innovative tool designed to enhance fine motor skills through engaging and interactive challenges. By guiding a virtual ball through intricate mazes and obstacles, users can improve their precision, control, and hand-eye coordination.
Other articles that might interest you:
Supporting children with autism
Dynseo proposesSUPPORTING CHILDREN WITH AUTISM with COCO THINKS AND COCO MOVESDynseo and its team are very much...
Supporting DYS children with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES
Dynseo proposesDYS disorders with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVESOur educational and pedagogical games program COCO THINKS...
Language development
Children communicate from birth with movements, crying, looking at each other or with smiles. After only a few months,...
Supporting children with Down Syndrome with Coco
Dynseo proposesDOWN SYNDROME with COCODown syndrome is a non-hereditary chromosomal abnormality that leads to the...
Supporting people after a stroke
Dynseo proposesStroke with CLINT, your brain training coachThe Dynseo team is very involved in helping people who have...
Supporting someone with Alzheimer’s
In this guide, we will detail how SCARLETT can be used for supporting someone with Alzheimer's. SCARLETT is a...
10 myths about the human brain you didn’t know
The brain is an incredible muscle, however there are many things we do not know, and what we do know is not always...
Using Digital Tools to Support Students with Special Educational Needs
Special Educational Needs (SEN) encompass a wide range of learning difficulties and disabilities that can hinder a...
Down Syndrome and Communication: Facilitating Interaction with Visual and Interactive Supports
When we think about Down syndrome, we often recognize it as a genetic condition that affects physical and cognitive...
How to Track Progress in People with Down Syndrome Using Digital Tools
Down syndrome, a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, affects approximately 1 in every...