Bipolar disorder is a mood disorder that affects millions of people around the world. It is characterized by extreme mood swings, ranging from manic to depressive episodes. Treatments for bipolar disorder may include medication, therapy and lifestyle changes. However, a growing body of research suggests that brain training may also be beneficial for people with this disorder. In this article, we will explore the benefits of brain training on bipolar disorder, as well as the different forms of brain training that can be used to help manage the symptoms of this complex disorder.
What are the different types of bipolar disorder?
Manic episodes
They are a key feature of Type I bipolar disorder. They are also sometimes present in bipolar disorder type II. During a manic episode, people may have extremely high levels of energy and motivation, rapid thinking and grandiose ideas. This can lead them to make impulsive decisions, spend money excessively and behave recklessly. People experiencing a manic episode may also experience intense irritability, verbal and physical aggression, and feelings of invincibility.
The symptoms of a manic episode can be extremely severe and can lead to negative consequences, such as financial problems, relationship difficulties, work problems and even dangerous behaviour. Manic episodes can also cause sleep problems, weight loss, severe fatigue and decreased ability to perform daily tasks. Manic episodes can last for weeks or months, with periods of less intense symptoms between episodes. Treatments for manic episodes may include medication, therapy and lifestyle changes. Emotional regulation therapy and brain training can also be used to help manage the symptoms of manic episodes.
It is important to note that manic episodes can have serious consequences and that it is crucial to seek medical help if symptoms occur. People with bipolar disorder can benefit from treatments that can help them manage the symptoms of manic episodes and maintain a high quality of life.
Depressive episodes
Depressive episodes are another key feature of bipolar disorder. During a depressive episode, people may experience profound sadness, loss of interest in daily activities, fatigue, sleep problems and loss of appetite. People with bipolar disorder may also experience negative thoughts about themselves, low self-esteem, thoughts of suicide and an inability to concentrate. They can last for weeks or months, with periods of less intense symptoms between episodes. Depressive episodes can also have a negative impact on relationships, work and daily life in general.
Treatments for depressive episodes may include medication, therapy and lifestyle changes. Brain training can also be used to help manage the symptoms of depressive episodes. Emotional regulation techniques can also be useful in helping people with bipolar disorder better manage the symptoms of the depressive episode. It is important to note that depressive episodes can also have serious consequences and that it is crucial to seek medical help if symptoms occur. People with bipolar disorder can benefit from treatments that can help them manage the symptoms of depressive episodes and maintain a high quality of life.
What are the triggers of bipolar disorder?
Emotional and physical stress
It is one of the main environmental triggers of bipolar disorder. Life events such as the loss of a loved one, the loss of a job or an illness can trigger a manic or depressive episode in people with bipolar disorder. Major life changes such as marriage, the birth of a child, divorce or moving can also trigger episodes of bipolar disorder.

Changes in the pace of life
They may also play a role in triggering episodes of bipolar disorder. Sleep disruptions, such as transcontinental travel, irregular work schedules or lack of sleep, can trigger manic or depressive episodes in people with bipolar disorder.
Drug and alcohol use
Both of these can also trigger episodes of bipolar disorder in people with the disorder. People with bipolar disorder should avoid using psychoactive substances, as they can exacerbate symptoms and trigger manic or depressive episodes.
Genetic factors
They play a role in triggering episodes of bipolar disorder. People with a family history of bipolar disorder have a higher risk of developing the illness. However, it is important to note that bipolar disorder cannot be attributed to a single gene or genetic mutation.
What are the effects of bipolar disorder on the brain?
To understand the effects of bipolar disorder on the brain, it is important to first understand how the brain normally functions. The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells, called neurons, that communicate with each other through connections called synapses. Neurons communicate by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters, which bind to receptors on other neurons, triggering a chain reaction that allows communication between neurons.
Neurotransmitters
In bipolar disorder, the levels of certain neurotransmitters are altered, upsetting the chemical balance of the brain. The neurotransmitters most commonly affected in bipolar disorder are serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine. These neurotransmitters are involved in the regulation of mood, anxiety and behavior, among other functions.
During episodes of depression, serotonin and norepinephrine levels are often lower than normal. This can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness and fatigue. During manic episodes, dopamine levels are often higher than normal. This can lead to excessive excitement, impulsivity and insomnia.
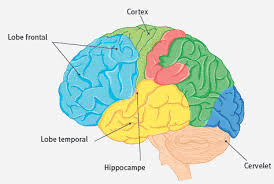
The hippocampus
It is a region of the brain that plays a key role in memory and learning. People with bipolar disorder often have a smaller than normal hippocampus, which can affect their ability to process and remember information.
The prefrontal cortex
Another important brain region involved in decision making, planning and emotional control. People with bipolar disorder often have abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex, which can lead to difficulties in regulating emotions and impulsive behaviors.
The different medications for bipolar disorder
Mood stabilizers
This includes lithium and valproate, which are designed to stabilize mood levels and prevent manic and depressive episodes. They may take several weeks to reach full effectiveness and require regular monitoring of renal and thyroid function, as well as blood lithium levels. Effects that may occur are: drowsiness, tremors, weight gain, hair loss and kidney problems.
Antipsychotics
For example, olanzapine and risperidone are used to treat the manic and psychotic symptoms of bipolar disorder. These medications can also be used in combination with mood stabilizers for more effective treatment. They can cause increased appetite, weight gain, drowsiness, restlessness and tremors.
Antidepressants
We have as medications, fluoxetine and venlafaxine, can be used to treat depressive episodes of bipolar disorder. However, they should be used with caution because they can trigger manic episodes in some people with bipolar disorder. They can cause sexual problems, insomnia and anxiety.
It is important to note that not all medications work the same way for everyone with bipolar disorder. It may be necessary to try several different medications to find the one that works best for each person. In addition, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and frequency of administration of medications to avoid unwanted side effects.
The benefits of brain training for people with bipolar disorder
It may be a promising alternative for the treatment of bipolar disorder. This form of therapy focuses on strengthening cognitive skills, such as memory, attention and mental flexibility. Cognitive training can help people with bipolar disorder better manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Improve cognitive functions
Training sessions often focus on specific tasks, such as memorizing word lists or problem solving. Patients work with a therapist to identify cognitive skills that need improvement and to develop a training plan tailored to their needs.
Preventing relapses in people
Those who underwent cognitive training showed a significant reduction in the number of episodes of mania and depression over time. This therapy can also help improve the quality of life of patients by allowing them to better manage their symptoms and function more effectively in their daily lives.
Few undesirable side effects
Unlike some medications, cognitive training does not have negative effects on weight, sleep or appetite. In addition, patients may participate in cognitive training in combination with other forms of treatment, such as
CLINT, a memory game program for people with bipolar disorder
Cognitive training is a promising alternative for the treatment of bipolar disorder. This form of therapy can help patients improve their cognitive skills, prevent relapse and improve their quality of life.
The JOE Brain Training program was designed specifically for adults to keep the brain healthy through fun and challenging brain exercises. It has over 30 cognitive games and targets concentration, focus, reflexes, language and many other cognitive functions.
Other articles that might interest you:
How Parents Can Contribute to Teacher Training
As we delve into the realm of education, it becomes increasingly clear that teacher training is not merely a...
Differentiated Instruction Approaches: Training and Practical Application
Differentiated instruction is a pedagogical approach that recognizes the diverse needs of students in a classroom. It...
Key Skills Teachers Need to Support Students with Special Needs
As we embark on our journey to support children with special needs, it is essential for us to cultivate a deep...










