Attention Deficit Disorder with or without Hyperactivity (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that can have a significant impact on a child’s life, including schooling. Indeed, symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity and hyperactivity can interfere with a student’s learning abilities and academic performance.
With this in mind, it is important to examine the impact of ADHD disorders on a student’s schooling in order to better understand the challenges they may face and determine appropriate supports and accommodations to help them succeed.
How can ADHD affect a student’s ability to concentrate in class?
Attention Deficit Disorder with or without Hyperactivity (ADHD) can have a significant impact on a student’s ability to focus in class and stay attentive during school tasks.
Attention
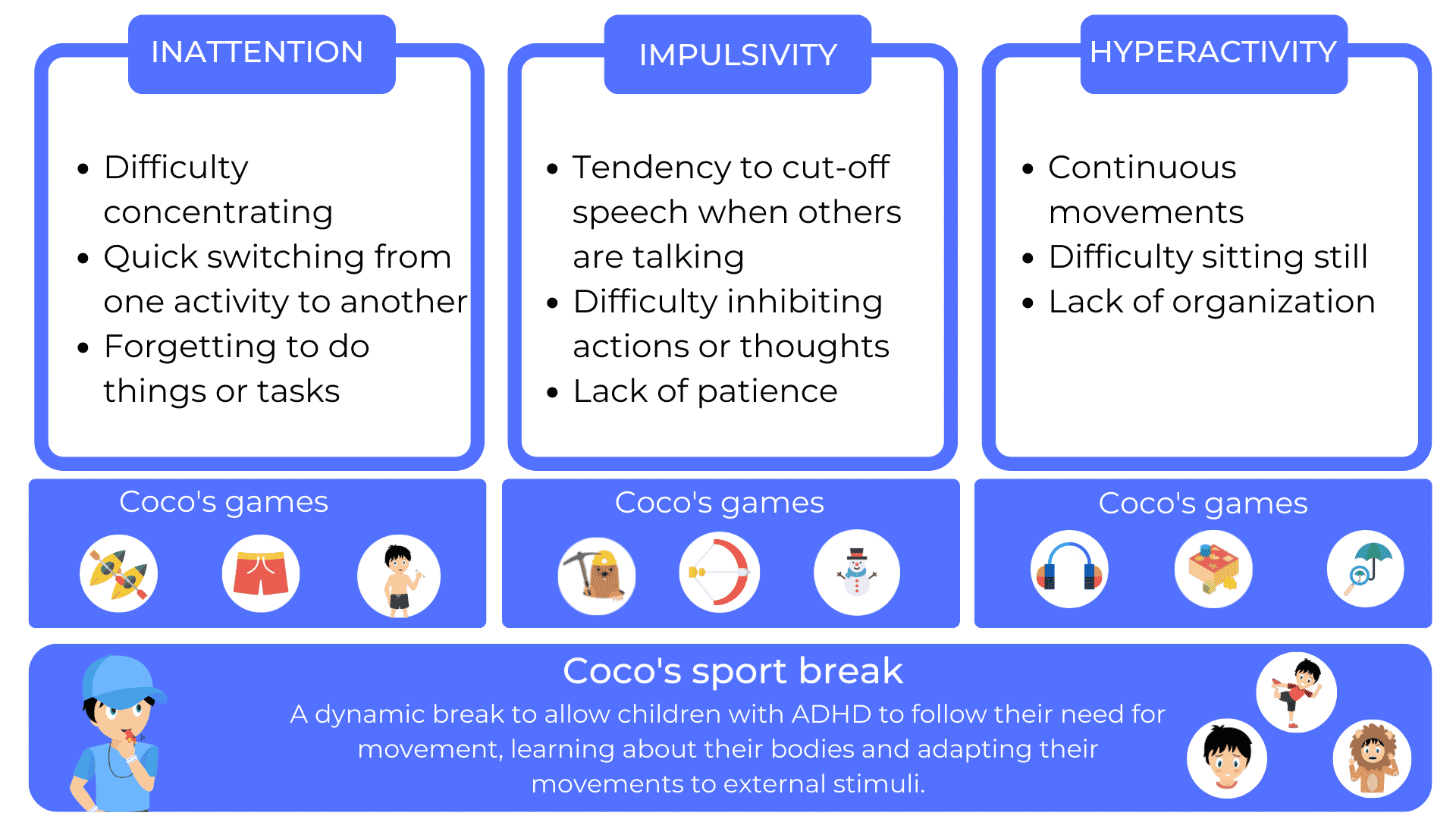
Children with ADHD often have difficulty maintaining their attention and can be easily distracted by external or internal stimuli, such as noises, movements or their own thoughts. As a result, they may have difficulty following lectures, taking notes, or concentrating on a task for an extended period of time.
These attention difficulties can negatively impact a student with ADHD’s academic success, as they may miss important information in class and have difficulty memorizing and recalling information for exams. In addition, students with ADHD may be behind in finishing tasks, as they may need more time to focus and organize their thoughts.
The activities
Students may also have difficulty engaging in activities that are not interesting to them, or not immediately rewarding. For example, they may find reading a book or doing math exercises boring, and may be tempted to distract themselves by doing something else.
It is important to note that the symptoms of ADHD can vary from child to child, and some students may have more difficulty than others in focusing and paying attention in class. However, with appropriate accommodations and supports, such as frequent breaks, shorter tasks, positive encouragement, and organizational strategies, students with ADHD can succeed in school and reach their academic potential.
Organizational and planning difficulties for a student with ADHD
Organizational and planning difficulties are common among students with ADHD and can make it difficult to manage their time and schoolwork. Children with ADHD may have difficulty planning their daily activities, organizing their time, and prioritizing tasks according to their importance. In addition, they may have difficulty keeping track of a calendar or schedule and may forget important deadlines, such as due dates.
Significant impact
These difficulties can have a significant impact on the academic success of a student with ADHD, as he or she may miss homework, or be late in completing school tasks. In addition, organization and planning are essential skills for future success, whether in pursuing higher education or in professional life.
Support
To help students with ADHD overcome these challenges, appropriate supports can be put in place. For example, teachers can help students develop action plans for school tasks by providing checklists or agendas to help them remember important deadlines.
Parents can also help by creating a calm and structured work environment at home, and by helping their child organize his or her work space. In addition, strategies such as segmenting tasks into shorter subtasks, prioritizing tasks based on their importance, and using memory techniques such as repetition and visualization can help students with ADHD improve their organization and planning.
Organization and planning are key skills that need to be taught and reinforced in all students, including those with ADHD. By putting appropriate supports in place and helping students develop these skills, they can succeed in school and prepare for a successful future.
Impulsivity and hyperactivity of an ADHD student in the classroom
Impulsivity and hyperactivity are common symptoms of ADHD that can disrupt the classroom environment and make it difficult for the student with ADHD to follow the teacher’s rules and expectations. Students with ADHD may be impulsive and act before they think, which may lead them to interrupt others, speak out of turn, or get up from their seats without permission. They may also be hyperactive, which may cause them to move frequently, squirm or get out of their seat repeatedly.
The behaviors
These behaviors can disrupt the classroom environment and make it difficult for the teacher to maintain a calm and structured learning environment. Frequent interruptions can interrupt classes and disrupt other students, which can affect the concentration and learning of all students. In addition, impulsive and hyperactive behaviors can make it difficult for the student with ADHD to follow teacher rules and expectations, which can lead to conflict and disciplinary problems.
For example, a student with ADHD may frequently interrupt class by asking off-topic questions or speaking without permission. This can disrupt the learning of other students and make it difficult for the teacher to complete the lesson in a timely manner. In addition, the student may have difficulty following instructions and meeting the teacher’s expectations, which may result in discipline problems such as warnings or suspensions.
Management strategy
To help students with ADHD overcome these challenges, it is important to provide appropriate behavior management strategies. Teachers can use clear and consistent rules to help students understand the expectations of the classroom environment and develop behavior regulation skills. They can also use positive rewards to encourage positive behaviors and help students focus on tasks.
In addition, parents can help by providing a supportive environment at home, helping their child develop emotional regulation strategies, and working with the teacher to implement appropriate supports.
By providing appropriate behavior management strategies and working collaboratively with parents and teachers, students with ADHD can overcome the challenges of impulsivity and hyperactivity and succeed in school.
Strategies for supporting a student with ADHD in the classroom
Recognition and management of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is crucial to helping students with the disorder succeed in school. Indeed, ADHD can have a negative impact on the student’s schooling, with difficulties in concentration, organization and planning, decreased academic performance, as well as disruptions in the classroom environment due to impulsivity and hyperactivity.
Managing a student with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in the classroom can be a challenge for teachers. Here are some strategies that can help manage a student with ADHD in the classroom:
Impose regular breaks
Therefore, it is important to recognize the signs of ADHD and make an early diagnosis. Appropriate interventions can then be put in place to help the student better manage his or her symptoms and succeed in school. These interventions may include instructional adjustments such as regular breaks for movement, clear and concise verbal instructions, and shorter academic tasks to better accommodate the student’s attentional difficulties.
Establish a ritual calendar with routines
For example, a visual calendar can be used to help the student plan and track tasks. Clear and predictable routines can also help students become more organized and better at managing their time. Students with ADHD often have difficulty focusing on tasks that do not interest them. To help them focus, it’s important to establish a clear, predictable routine that can help them feel secure and know what they need to do.
Create a distraction-free environment
Students with ADHD can be easily distracted by noise, movement and other environmental stimuli. It is therefore important to create a calm and distraction-free environment in the classroom.
Use visual aids
Students with ADHD may have difficulty following verbal instructions or remembering important information. Using visual aids such as pictures, diagrams or maps can help these students better understand and remember information.
Encourage active participation
Students with ADHD may need to move around and move to focus. Encouraging active participation in class, such as role-playing or using hands-on activities, can help these students stay engaged and focused.
Establish clear communication with parents
Communication with parents is essential to help manage a student with ADHD in the classroom. It is important to work collaboratively with parents to ensure that the student receives the support he or she needs at home and in the classroom.
Adapting assessments and tasks
Students with ADHD may have difficulty concentrating for long periods of time. It is important to adapt assessments and tasks to make them shorter and more manageable, while ensuring that they remain relevant and challenging for the student.

Use positive rewards and reinforcements
Students with ADHD can be easily discouraged by difficult or monotonous tasks. Using positive rewards and reinforcements, such as compliments or tangible rewards, can help maintain student motivation and reinforce desired behaviors.
It is important to note that each student with ADHD is unique, and it is important to tailor management strategies to the individual needs of the student.
Adhere to their medication regimens
Management of ADHD may include medical treatment if appropriate and recommended by a health care professional. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate, can help reduce symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity, as well as improve concentration and attention.
Each student with ADHD is unique and interventions must be tailored to meet individual needs. With proper recognition and management of ADHD, students with this disorder can be more successful in school and in their lives in general.
Adapted educational activities for ADHD students
There are educational games that can help a student with ADHD improve concentration, memory, planning and time management. Here are some examples of educational games that may be useful:
Memory games: Memory games such as Memory or Simon can help improve the student’s working memory.
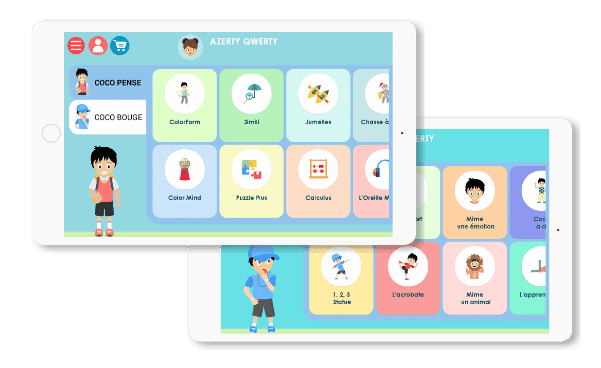
There is also the program COCO THINKS and COCO MOVESwhich for the 5-10 year olds offer more than 30 adapted educational games, working all the cognitive functions, but above all with a compulsory sports break every 15 minutes of play. The break is very beneficial for ADHD children.
- Construction games: Construction games such as Lego or K’NEX can help improve a student’s fine motor skills and concentration.
- Strategy games: Strategy games such as Monopoly, Risk or Chess can help improve a student’s planning, decision-making and time management skills.
- Word games: Word games such as Scrabble or Boggle can help improve a student’s working memory, concentration and creativity.
- Simulation games: Simulation games such as SimCity or RollerCoaster Tycoon can help improve a student’s planning, decision-making and time management skills.
Other articles that might interest you:
Supporting children with autism
Dynseo proposesSUPPORTING CHILDREN WITH AUTISM with COCO THINKS AND COCO MOVESDynseo and its team are very much...
Supporting DYS children with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES
Dynseo proposesDYS disorders with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVESOur educational and pedagogical games program COCO THINKS...
Language development
Children communicate from birth with movements, crying, looking at each other or with smiles. After only a few months,...
Supporting children with Down Syndrome with Coco
Dynseo proposesDOWN SYNDROME with COCODown syndrome is a non-hereditary chromosomal abnormality that leads to the...
Supporting people after a stroke
Dynseo proposesStroke with CLINT, your brain training coachThe Dynseo team is very involved in helping people who have...
Supporting someone with Alzheimer’s
In this guide, we will detail how SCARLETT can be used for supporting someone with Alzheimer's. SCARLETT is a...
10 myths about the human brain you didn’t know
The brain is an incredible muscle, however there are many things we do not know, and what we do know is not always...
Using Digital Tools to Support Students with Special Educational Needs
Special Educational Needs (SEN) encompass a wide range of learning difficulties and disabilities that can hinder a...
Down Syndrome and Communication: Facilitating Interaction with Visual and Interactive Supports
When we think about Down syndrome, we often recognize it as a genetic condition that affects physical and cognitive...
How to Track Progress in People with Down Syndrome Using Digital Tools
Down syndrome, a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, affects approximately 1 in every...