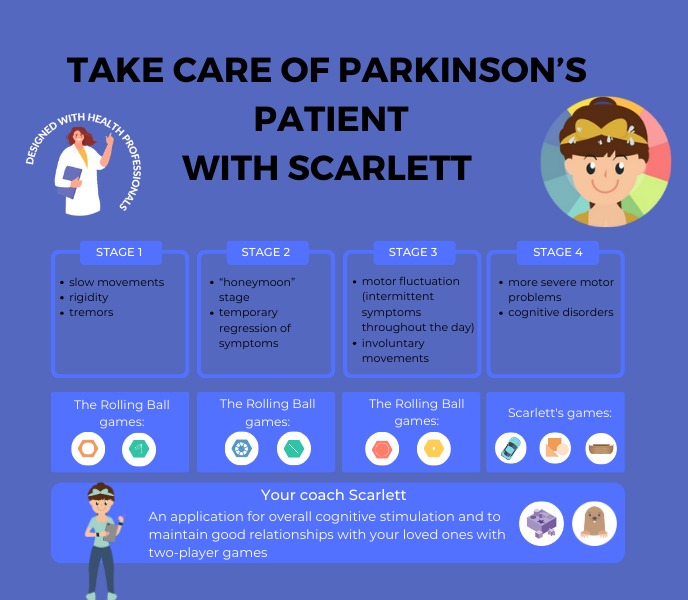
Occupational Therapy (OT) plays a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals grappling with Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinson’s, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, inflicts a range of motor and non-motor symptoms, significantly impairing daily functioning. OT encompasses a holistic approach aimed at promoting independence and well-being through meaningful engagement in daily activities. Particularly crucial in Parkinson’s management is the preservation and improvement of fine motor skills, essential for tasks like buttoning shirts, writing, and cooking.
Fine motor skills enable individuals to maintain autonomy and dignity in their daily routines, fostering a sense of control despite the challenges posed by Parkinson’s. By addressing these skills, OT interventions target the core difficulties faced by individuals with Parkinson’s, facilitating adaptation and compensatory strategies to overcome limitations. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the indispensable role of OT in empowering individuals with Parkinson’s to navigate the intricacies of everyday life with greater confidence and proficiency.
Understanding Occupational Therapy
Occupational Therapy (OT) encompasses a comprehensive approach to enhancing individuals’ ability to engage in meaningful daily activities, adapting environments, and promoting well-being across various contexts. Within the scope of OT, individuals receive tailored interventions aimed at improving physical, cognitive, and psychosocial functioning to facilitate independence and participation in daily life. In Parkinson’s care, OT objectives revolve around mitigating the impact of motor and non-motor symptoms on individuals’ functional abilities and quality of life.
Occupational therapists play a pivotal role in conducting assessments, developing personalized treatment plans, and implementing strategies to address fine motor deficits, cognitive impairments, and activities of daily living challenges. Through collaboration with individuals, families, and interdisciplinary teams, occupational therapists strive to optimize functional outcomes and empower individuals with Parkinson’s to live fulfilling and independent lives.
Tailored Intervention Strategies
Incorporating Occupational Therapy Techniques
Expanding on the incorporation of occupational therapy techniques into the management of Parkinson’s Disease reveals a comprehensive strategy aimed at enhancing the quality of life for individuals facing this condition. These techniques are designed not only to address the physical challenges associated with Parkinson’s but also to support independence and confidence in daily activities. Below, we further explore these strategies, grouped into three main categories: Handwriting Improvement, Coordination and Dexterity Training, and Adaptations for Activities of Daily Living (ADL).
Handwriting Improvement
Handwriting can become challenging for individuals with Parkinson’s due to decreased motor control. Techniques include:
- Tracing Activities: Utilizing tracing exercises to improve control and fluidity of hand movements, thereby enhancing handwriting precision.
- Grip Strengthening Exercises: Exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles in the hand and forearm can improve grip strength and stability for better handwriting control.
- Adaptive Writing Tools: Introduction to pens and pencils with adaptive grips or weighted options to facilitate easier and more comfortable writing.
Coordination and Dexterity Training
Fine motor skills are essential for many daily tasks, and occupational therapy focuses on exercises to enhance these capabilities:
- Pegboard Exercises: Using pegboards to practice precise hand movements and improve dexterity.
- Manipulation of Small Objects: Activities such as picking up, sorting, and placing small objects can help refine fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination.
- Hand-Eye Coordination Tasks: Engaging in tasks that require precise hand-eye coordination, such as catching or throwing small balls, to promote more fluid and controlled movements.
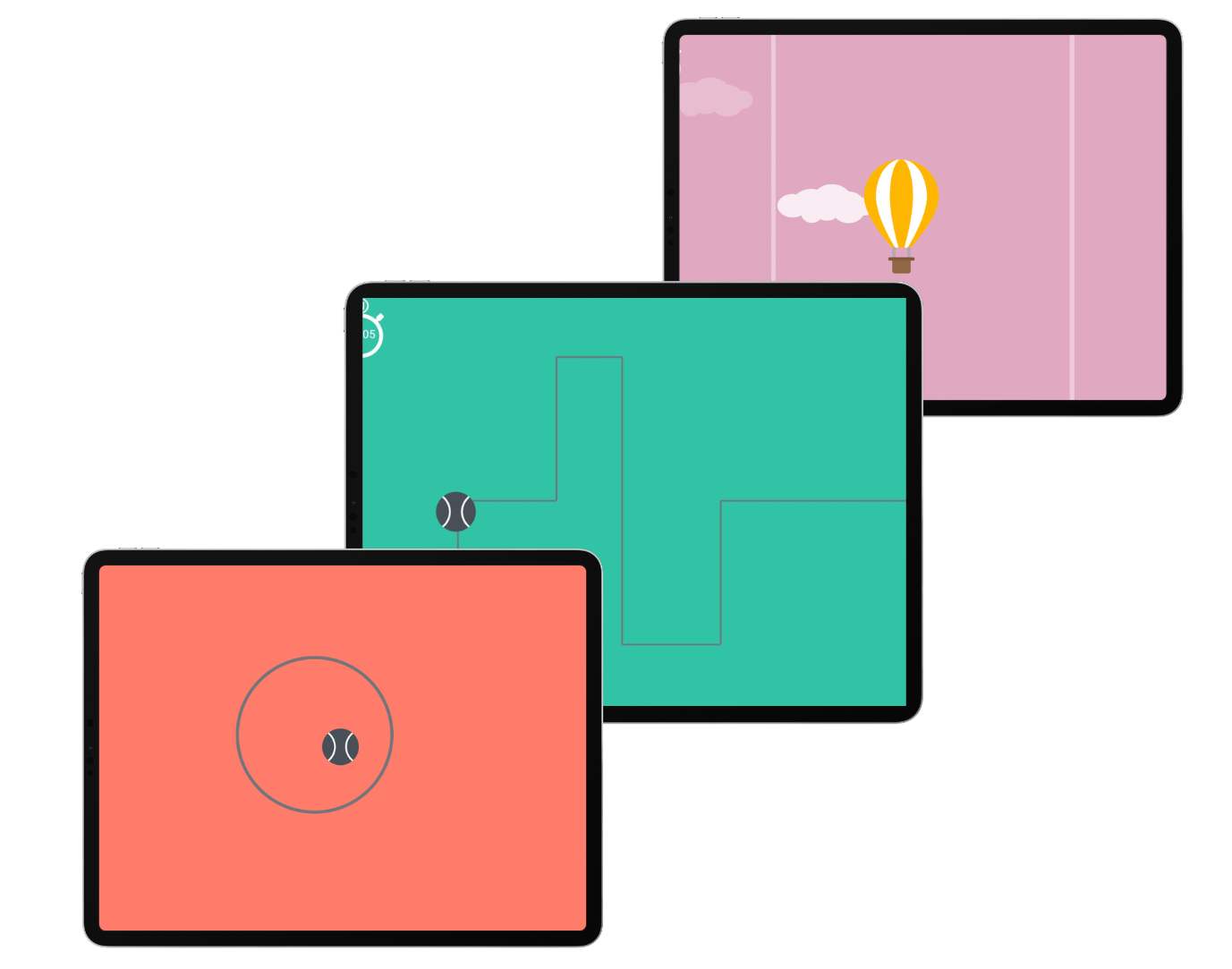
Adaptations for Activities of Daily Living (ADL)
Adapting the environment and routines is key to maintaining independence in daily living tasks:
- Home Environment Modifications: Adjusting the living space to make it safer and more functional, such as installing grab bars in the bathroom, using lever handles instead of knobs, and ensuring adequate lighting.
- Assistive Devices Introduction: Teaching the use of devices designed to aid in tasks like dressing (button hooks, zipper pulls), eating (weighted utensils, non-slip mats), and grooming (long-handled brushes or sponges) to facilitate independence.
- Compensatory Techniques for ADLs: Instruction on alternative methods to perform tasks such as dressing, grooming, and meal preparation to accommodate physical limitations, including strategies to reduce tremors’ impact on these activities.
By incorporating these occupational therapy techniques into the management plan for Parkinson’s Disease, therapists aim to address the unique challenges each individual faces. These targeted strategies enhance motor control, improve functional abilities, and enable individuals to navigate their daily lives with greater ease and confidence. Ultimately, the goal is to empower those with Parkinson’s to maintain their independence and improve their overall quality of life through personalized, skillful interventions.
Collaborative Approach with Healthcare Team
In managing Parkinson’s Disease, a collaborative approach with the healthcare team is paramount to addressing the complex needs of individuals comprehensively. Multidisciplinary care coordination involves the integration of various healthcare professionals, including neurologists, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, speech therapists, and social workers, to provide holistic care tailored to each patient’s unique requirements. Communication among specialists ensures seamless information exchange, enabling the team to synchronize treatment plans, monitor progress, and address emerging challenges promptly.
Central to this collaborative effort is patient-centered care planning, which prioritizes the individual’s preferences, goals, and values in decision-making processes. By fostering open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making, the collaborative approach empowers patients with Parkinson’s to actively participate in their care, fostering a supportive environment conducive to optimal health outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Assistive Devices and Technology
Assistive devices and technology play a crucial role in enhancing independence and functional abilities for individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Tools designed for fine motor skill improvement include specialized utensils, adaptive pens, and ergonomic keyboards, which help individuals maintain control and precision in tasks such as writing and typing. Adaptive equipment for daily activities encompasses a wide range of aids such as grab bars, dressing sticks, and modified kitchen utensils, facilitating independence in activities of daily living like bathing, dressing, and meal preparation.
Training in device usage and maintenance ensures individuals understand how to effectively utilize assistive technology, troubleshoot potential issues, and maintain equipment longevity. By integrating assistive devices and technology into daily routines, individuals with Parkinson’s can overcome physical limitations, maintain autonomy, and engage more confidently in meaningful activities, promoting overall well-being and quality of life.
Addressing Cognitive and Emotional Aspects
Addressing cognitive and emotional aspects is integral to comprehensive Parkinson’s Disease management, recognizing the multifaceted nature of the condition. Coping strategies for emotional well-being encompass psychoeducation, mindfulness practices, and cognitive-behavioral techniques aimed at managing stress, anxiety, and depression commonly experienced by individuals with Parkinson’s and their caregivers. Cognitive rehabilitation techniques focus on improving cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and executive functioning through structured exercises, cognitive training programs, and compensatory strategies.
Moreover, providing support for mental health challenges involves access to counseling services, support groups, and psychiatric interventions tailored to address mood disorders, adjustment issues, and psychological distress. By addressing cognitive and emotional aspects holistically, healthcare professionals can promote resilience, enhance coping skills, and foster emotional stability, contributing to improved overall quality of life for individuals living with Parkinson’s Disease.
Progress Monitoring and Adjustment
Progress monitoring and adjustment are essential components of effective Parkinson’s Disease management, ensuring interventions remain responsive to individuals’ evolving needs and goals. Periodic assessment and reassessment enable healthcare professionals to evaluate the effectiveness of current interventions, identify emerging challenges, and track changes in functional abilities over time. Goal setting and achievement tracking provide a framework for individuals to articulate their aspirations and measure progress towards desired outcomes, fostering motivation and engagement in the rehabilitation process. Moreover, modifying intervention plans as needed allows for flexibility in addressing new priorities, adjusting strategies, and incorporating feedback from patients and caregivers.
By embracing a dynamic and iterative approach to care, healthcare teams can optimize treatment outcomes, maximize functional independence, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals navigating the complexities of Parkinson’s Disease.
Education and Empowerment
Education and empowerment form the cornerstone of effective Parkinson’s Disease management, fostering informed decision-making and enhancing self-efficacy for both patients and caregivers. Patient and caregiver education initiatives provide valuable insights into the nature of Parkinson’s, its symptoms, progression, and available treatment options, empowering individuals to actively participate in their care journey. Teaching self-management skills equips individuals with practical strategies to navigate daily challenges, manage symptoms, and optimize overall well-being, promoting a sense of autonomy and control over their health outcomes.
Furthermore, building confidence and independence through tailored interventions and support networks enables individuals to cultivate resilience, adaptability, and a positive mindset in the face of adversity. By prioritizing education and empowerment, healthcare professionals empower individuals with Parkinson’s and their caregivers to navigate the complexities of the condition with resilience, dignity, and hope.
Community Engagement and Resources
Community engagement and resources play a vital role in providing individuals with Parkinson’s Disease and their caregivers with a network of support, information, and advocacy. Support groups and peer networks offer a safe space for individuals to share experiences, seek advice, and gain emotional support from others facing similar challenges. Accessing community services facilitates connections to resources such as home healthcare, transportation assistance, and respite care, enhancing overall quality of life and promoting independence.
Additionally, advocacy and awareness initiatives raise public consciousness about Parkinson’s Disease, promote research funding, and advocate for policy changes to improve access to healthcare services and support programs. By fostering a sense of belonging, facilitating access to essential services, and amplifying collective voices, community engagement empowers individuals with Parkinson’s and their caregivers to navigate their journey with resilience, dignity, and solidarity.
Future Directions and Research
Looking ahead, future directions and research in Parkinson’s Disease management present exciting opportunities for advancements in occupational therapy and innovative approaches to care. Emerging trends in occupational therapy include the integration of technology, such as telehealth and virtual reality, to deliver personalized interventions tailored to individual needs and preferences. Innovations in Parkinson’s management encompass promising developments in pharmaceuticals, neurosurgical procedures, and non-invasive interventions, aimed at improving symptom management, enhancing mobility, and preserving quality of life. Moreover, opportunities for collaboration and advancement abound, with interdisciplinary partnerships between healthcare professionals, researchers, industry leaders, and advocacy groups driving progress in treatment modalities, caregiver support programs, and public awareness campaigns.
By harnessing collective expertise, fostering collaboration, and embracing cutting-edge research, the future of Parkinson’s Disease management holds immense potential to transform care delivery, optimize outcomes, and improve the lives of individuals affected by the condition.
Occupational therapy stands as a cornerstone in the comprehensive management of Parkinson’s Disease, offering tailored interventions to address the diverse needs of individuals and promote independence in daily living. Through fine motor skill enhancement, adaptive strategies, and cognitive support, occupational therapists play a pivotal role in empowering patients to navigate the challenges of Parkinson’s with resilience and dignity. As we look to the future, continued engagement in research, innovation, and interdisciplinary collaboration holds the key to unlocking new avenues for improving treatment outcomes and enhancing quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s and their caregivers.
Let us remain steadfast in our commitment to advocating for patient-centered care, fostering a supportive community, and striving for excellence in our pursuit of enhancing the well-being and autonomy of those affected by Parkinson’s Disease. Together, we can make meaningful strides towards a brighter and more inclusive future for all.
AND FOR FURTHER INFORMATION
SCARLETT, EASY MEMORY GAMES FOR PARKINSON
SCARLETT is a user-friendly memory game program that offers a collection of simple yet engaging exercises, specifically designed to gently enhance memory skills. No timer, no score and no failure. Just the pleasure of playing. Try it for free for one week.

CLINT, A CHALLENGING BRAIN GAMES APP
For individuals seeking a more challenging experience, the CLINT program serves as a more demanding version, offering complex memory games that require greater cognitive effort, making it suitable for those in need of a more strenuous mental workout.

THE ROLLING BALL TO WORK ON FINE MOTOR SKILLS
The Rolling Ball app is an innovative tool designed to enhance fine motor skills through engaging and interactive challenges. By guiding a virtual ball through intricate mazes and obstacles, users can improve their precision, control, and hand-eye coordination.
Other articles that might interest you:
Supporting children with autism
Dynseo proposesSUPPORTING CHILDREN WITH AUTISM with COCO THINKS AND COCO MOVESDynseo and its team are very much...
Supporting DYS children with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES
Dynseo proposesDYS disorders with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVESOur educational and pedagogical games program COCO THINKS...
Language development
Children communicate from birth with movements, crying, looking at each other or with smiles. After only a few months,...
Supporting children with Down Syndrome with Coco
Dynseo proposesDOWN SYNDROME with COCODown syndrome is a non-hereditary chromosomal abnormality that leads to the...
Supporting people after a stroke
Dynseo proposesStroke with CLINT, your brain training coachThe Dynseo team is very involved in helping people who have...
Supporting someone with Alzheimer’s
In this guide, we will detail how SCARLETT can be used for supporting someone with Alzheimer's. SCARLETT is a...
10 myths about the human brain you didn’t know
The brain is an incredible muscle, however there are many things we do not know, and what we do know is not always...
Using Digital Tools to Support Students with Special Educational Needs
Special Educational Needs (SEN) encompass a wide range of learning difficulties and disabilities that can hinder a...
Down Syndrome and Communication: Facilitating Interaction with Visual and Interactive Supports
When we think about Down syndrome, we often recognize it as a genetic condition that affects physical and cognitive...
How to Track Progress in People with Down Syndrome Using Digital Tools
Down syndrome, a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, affects approximately 1 in every...