Understanding ADHD to better understand tantrums
The basics of ADHD
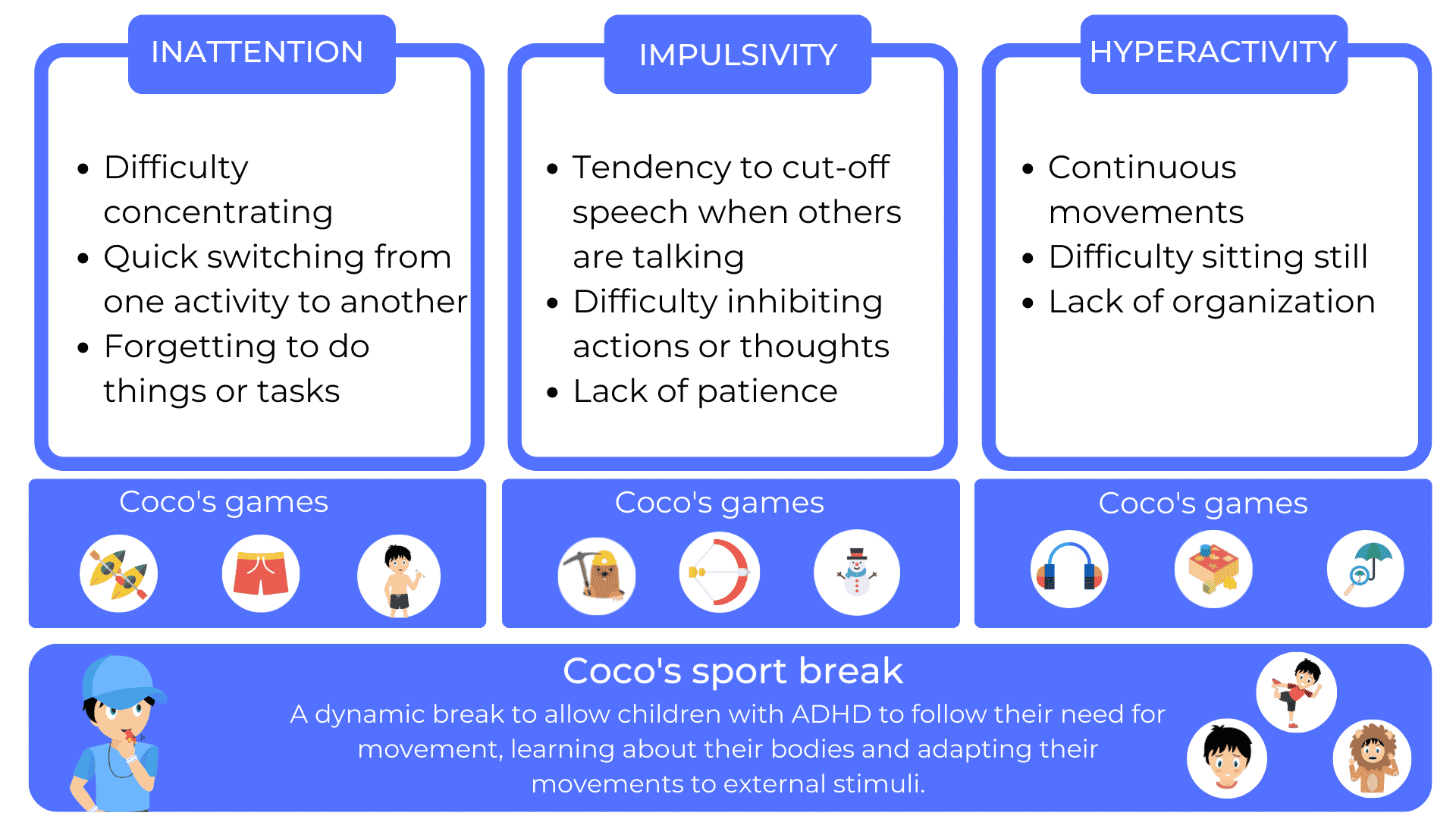
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects many children worldwide. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity. These symptoms can vary in intensity from child to child, making ADHD a complex disorder to understand and manage.
The influence of ADHD on emotions
ADHD is not limited to attention and hyperactivity challenges. It also has a significant impact on the emotions of affected children. One of the most striking characteristics is the difficulty in regulating emotions. ADHD children may experience stronger, more intense emotions than their peers, which can lead them to react more explosively to certain situations.
Examples of anger-related behaviors in ADHD children
To better understand how ADHD can influence anger in children, let’s look at some examples of commonly observed behaviors:
Increased impulsivity ADHD children often have difficulty controlling their impulses. They may react impulsively and act without thinking, which can lead them to express their anger suddenly and intensely.
Emotional sensitivity ADHD children may be more sensitive to emotional stimuli. A situation that might not provoke a reaction in other children can trigger a strong emotion in an ADHD child, leading to angry outbursts.
Frustration with difficulties ADHD children are often faced with challenges related to attention and concentration. When they have difficulty completing a task or following instructions, this can lead to frustration, which sometimes manifests itself in angry behavior.
By understanding these aspects of ADHD and how they can influence children’s emotions, we are better prepared to address anger management in these youngsters.
Anger triggers in ADHD children
Common tripping factors
Children with ADHD may react angrily to specific triggers. Understanding these triggers is essential to helping these children better manage their anger. Here are some common triggers:
Frustration with difficult tasks
When ADHD children are faced with tasks that require prolonged concentration or impulse management, they can quickly become frustrated. This frustration can turn into anger if left unchecked.
Transitions and changes of activity
Transitions between different activities or environments can be particularly difficult for ADHD children. Interruptions to their routine can provoke anxiety and anger.
Sensory stimuli
Some ADHD children are sensitive to sensory stimuli, such as loud noises, bright lights or unusual textures. These stimuli can trigger intense emotional reactions, including anger.
Warning signs of anger
Recognizing the warning signs of anger in ADHD children is essential to intervene in time and help them avoid tantrums. Here are some signs to look out for:
Agitation
Physical agitation, such as foot or hand tapping, may indicate that the ADHD child is beginning to feel frustrated or irritated.
Isolation or withdrawal
Some ADHD children tend to withdraw socially when they are angry. They may withdraw into themselves or avoid interaction.

Aggressive or provocative language
The child may start using aggressive or provocative language before moving on to more explosive behavior. It’s a sign that anger is rising.
The importance of communication
Open and respectful communication is crucial to helping an ADHD child manage anger. Parents, teachers and caregivers need to encourage children to express their emotions and report the warning signs of anger. Effective communication can help prevent crises and find solutions together.
By understanding the triggers of anger and paying attention to the warning signs in ADHD children, we can better support them in managing their emotions. In the next chapters, we’ll explore practical strategies to help these children develop anger management skills.
Anger Management Strategies for ADHD Children
Adapted Anger Management Techniques
Children with ADHD can benefit from anger management techniques specially adapted to their needs. Here are some effective strategies:
Deep breathing
Teaching children to practice deep breathing can help them calm down when they feel angry. These can be as simple as slow, deep breathing exercises to reduce agitation.
Identifying Emotions
Helping children to recognize and name their emotions is the first step towards anger management. This helps him better understand how he feels and why he gets angry.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation methods such as guided meditation, visualization or yoga can help ADHD children relax and manage anger proactively.
Distraction and Redirection Techniques
In addition to anger management techniques, ADHD children can benefit from distraction and redirection strategies:
Positive Distraction
Encouraging the child to turn to activities he or she is passionate about can help divert attention from anger. It could be reading, music, or any other hobby he enjoys.
Redirection to Soothing Activities
Suggesting calming activities such as drawing, building games or puzzles can help your child channel his or her energy and calm down.
Communication Strategies
Open and respectful communication is crucial to helping an ADHD child manage anger. Parents, teachers and caregivers need to encourage children to express their emotions and report the warning signs of anger. Here are some communication strategies:

Using Positive Language
Encourage the child to express frustration constructively, using words instead of physical anger. Teaching him to say what he feels can reduce tantrums.
Active Listening
Listening attentively when ADHD children express their emotions is essential. This strengthens the relationship and makes the child feel understood and supported.
Advance planning
Discussing anger management strategies with your child in advance can be beneficial. Teaching her to plan positive responses to stressful situations can help prevent anger.
Empathy and patience
The importance of empathy
Empathy plays a crucial role in anger management in children with ADHD. It enables adults to connect emotionally with children and understand their emotions. Here’s how empathy can help with anger management:

Understanding children’s emotions
By being empathetic, adults can better understand how children feel when they’re angry. This helps defuse the situation by showing the child that he or she is understood.
Strengthening relationships
Empathy strengthens the relationship between adult and child. When children feel listened to and supported, they are more inclined to accept help in managing their anger.
Cultivating patience
Patience is an essential quality when working with angry ADHD children. Here’s how it can help:
Giving the child time to calm down
Tantrums can be intense, but it’s important to give the child time to calm down without undue pressure. Patience allows the child to return to a calmer state of mind.

Avoid impulsive reactions
Reacting to a child’s anger with haste can make the situation worse. Patience allows adults to step back and respond thoughtfully.
Teaching empathy and patience
Modeling these behaviors
Adults can teach empathy and patience by modeling them themselves. When children see these behaviors in action, they are more likely to adopt them.
Activities to develop empathy
Introducing activities that foster empathy can be beneficial. For example, encouraging children to imagine how others feel can reinforce their empathy.
Learning to manage frustration
Teaching ADHD children to manage their own frustration can be an effective way of teaching them patience. This gives them the skills to deal more constructively with stressful situations.
Games and Activities to Help Reduce the Anger of an ADHD Child
When it comes to managing anger in a child with ADHD, it’s important to incorporate games and activities that can help channel this energy and promote better emotional control. Here are a few ideas for adapted games and activities:
Quiet Games
Board Games
Board games such as puzzles, card games or chess can help develop a child’s concentration and patience, while providing constructive entertainment.
Construction Games
Construction games such as LEGO or magnetic blocks allow children to channel their energy into creation, while improving their problem-solving skills.
Physical activities
Outdoor Sports and Games
Team sports or outdoor games such as soccer, cycling or basketball offer a healthy release of energy, reduce stress and promote coordination.
Yoga and Meditation
Child-friendly yoga and meditation can help improve concentration, reduce anxiety and promote better emotional control.

Creative Activities
Drawing and Painting
Artistic activities such as drawing and painting enable children to express themselves and release their emotions while developing their creativity.
Music
Learning a musical instrument or participating in musical activities can be soothing for the child, offering an emotional outlet.
Sensory Activities
Kinetic Sand
Kinetic sand or modeling clay can help soothe ADHD children by providing a relaxing sensory experience.
Sensory Swing
A sensory swing can provide soothing vestibular stimulation and help regulate a child’s emotions.

Relaxation Games
Quiet Stories
Calming stories or picture books with soothing themes can help relax children before bedtime or during tense moments.
Blowing games
Games that emphasize deep breathing, such as blowing bubbles or candles, can help calm children when they are angry.
The COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES program
The COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES program offers an innovative and effective approach to helping children with ADHD aged 5 to 10 to manage their emotions, including anger, while strengthening their concentration and self-control. Designed specifically to meet the needs of ADHD children, this program is based on a clever combination of educational games and physical activities, with a scheduled “sports break” every 15 minutes of screen time.
COCO THINKS engages children in educational games that stimulate thinking, improve problem-solving skills and encourage patience. These games are designed to help children develop essential cognitive skills, including planning, organization and time management, which are often challenges for ADHD children.
COCO MOVES, on the other hand, recognizes the importance of physical activity for emotional regulation. Regular sports breaks, every 15 minutes of screen time, release energy, reduce tension and improve concentration. Physical activities are adapted to the child’s needs and can include simple stretching exercises, yoga, or even short runs around the house.
One of the key benefits of COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES is that they encourage routine and structure in a child’s day, which is often beneficial for ADHD children. By integrating these activities into the child’s daily life, the program provides a predictable framework that can help reduce anxiety and promote better anger management. It also reinforces children’s understanding of the importance of breaks and physical activity for their emotional well-being.

I would like to share my experience with your program, as it has had an incredible impact on the life of my son, Lucas, who has ADHD. Before we discovered COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES, we were faced with considerable challenges in dealing with Lucas’ tantrums. The explosions of anger sometimes seemed insurmountable, and we often felt overwhelmed.
When I heard about your program, I was skeptical, but I was willing to try anything to help my son. As soon as we started using COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES, I noticed impressive changes in Lucas. The educational games were entertaining and stimulating, but above all, they helped her concentrate. Little by little, he began to manage his impulses better.
What really made the difference were the sports breaks planned by COCO MOVES. Lucas used to have trouble sitting for long periods, whether at school or at home. The sports breaks every 15 minutes were a revelation for us. Lucas now had a healthy outlet for his energy. He loved stretching, jumping up and down or even running around the garden for a few minutes. This seemed to soothe him, and he returned to his activities calmer and more focused.
By integrating COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES into Lucas’ daily routine, we’ve seen incredible progress. His tantrums became less frequent and less intense. He began to express his frustrations better verbally than through angry outbursts. Tense moments at home were gradually transformed into moments of calm and understanding.
I can’t thank you enough for creating this program. It has truly changed Lucas’ life and ours as a family. We now have the tools to help her manage her emotions and grow in confidence. Your program has brought a glimmer of hope into our lives, and we are infinitely grateful.
Thank you from the bottom of my heart,
The importance of professional support to help you manage the tantrums of an ADHD child
The role of healthcare professionals
When it comes to managing anger in a child with ADHD, healthcare professionals play an essential role. Here’s how they can help:
Precise diagnosis
Health professionals are qualified to make an accurate diagnosis of ADHD. This helps us to better understand the child’s specific anger management needs.
Individualized treatment plans
They are able to create individualized treatment plans that include therapeutic approaches, medication if necessary, and anger management strategies tailored to each child.
Support from psychologists and therapists
Cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT)
Psychologists and therapists trained in CBT can help ADHD children develop anger management skills by identifying and changing negative thinking and behavior patterns.

Family therapy
Family therapy can be beneficial in helping not only the ADHD child, but also his or her family to better understand and manage anger. It encourages communication and mutual support.
Support groups
Support groups for parents
Parents of ADHD children can benefit from support groups where they can share their experiences, get practical advice, and feel less alone in their journey.
Support groups for children
ADHD children can also benefit from support groups where they meet other children facing similar challenges. This gives them a space to share their emotions and learn peer-to-peer anger management strategies.
As a psychologist who has worked with children with ADHD for many years, I’d like to share an essential message with you. It’s perfectly normal to face challenges when your ADHD child expresses anger or intense emotions. You’re not alone in this, and you should never be ashamed to seek help.
Tantrums in ADHD children are often the result of frustration, impulsivity and difficulty in regulating their emotions. These challenges are real and impact not only the child, but the whole family. The good news is that there are trained professionals to help you.
I strongly encourage you to consider meeting with a psychologist who specializes in ADHD and behavioral disorders. We’re here to support you, listen to you and offer concrete strategies to help your child manage his or her anger more constructively.
Don’t be afraid to talk about your concerns. The first step to getting help is recognizing that you need it, and that doesn’t make you or your child a failure. On the contrary, it shows that you’re willing to do whatever it takes to make life better for your child and your family.
By working together, sharing your concerns, and seeking the expertise of a psychologist, you can discover solutions tailored to your unique situation. Your child deserves the tools to succeed, and you deserve the support you need as parents.
Don’t wait, take this step for the well-being of your child and your family. You’re not alone, and there’s help available for you.
Resources for finding professional support to deal with the temper tantrums of an ADHD child
Recommendations from the attending physician
The child’s doctor can recommend healthcare professionals who specialize in ADHD and anger management.
Dedicated associations and organizations
There are many associations and organizations dedicated to ADHD that provide information, resources and referrals to qualified professionals. Here are just a few examples:
- CHADD (Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder): CHADD is an American organization that provides information, resources and a support network for families affected by ADHD.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides resources on ADHD, including information on diagnosis, treatment, and management of ADHD in children,
-
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): NIMH offers information about scientific research on ADHD and available treatments.
-
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP): AAP provides clinical recommendations for the diagnosis and management of ADHD in children. )Understood.org: Understood.org is an online resource that offers information specifically designed for parents, teachers, and children with ADHD.
-
HealthyChildren.org: This website is managed by the American Academy of Pediatrics and provides articles and resources on ADHD for parents and caregivers.
-
ADDitude Magazine: ADDitude is an online publication dedicated to ADHD. They offer articles, tips, and personal stories from individuals living with ADHD.
-
WebMD: WebMD offers reliable medical information on ADHD, including articles, videos, and testimonials.
By seeking out the right professional support, parents and educators can give children with ADHD the tools and resources they need to better manage their anger. The combination of a caring approach, adapted strategies and professional support can have a significant impact on the lives of these children and those around them.
Discover the COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES program to help reduce the temper tantrums of an ADHD child.
The COCO THINK and COCO MOVES program offers a comprehensive set of tools for ADHD children, helping them to develop essential cognitive skills while incorporating sports breaks to reduce anger and improve concentration. This program demonstrates how education, play and physical activity can combine synergistically to offer valuable support to these children on their journey towards healthier emotional management.
Other articles that might interest you:
Supporting children with autism
Dynseo proposesSUPPORTING CHILDREN WITH AUTISM with COCO THINKS AND COCO MOVESDynseo and its team are very much...
Supporting DYS children with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES
Dynseo proposesDYS disorders with COCO THINKS and COCO MOVESOur educational and pedagogical games program COCO THINKS...
Language development
Children communicate from birth with movements, crying, looking at each other or with smiles. After only a few months,...
Supporting children with Down Syndrome with Coco
Dynseo proposesDOWN SYNDROME with COCODown syndrome is a non-hereditary chromosomal abnormality that leads to the...
Supporting people after a stroke
Dynseo proposesStroke with CLINT, your brain training coachThe Dynseo team is very involved in helping people who have...
Supporting someone with Alzheimer’s
In this guide, we will detail how SCARLETT can be used for supporting someone with Alzheimer's. SCARLETT is a...
10 myths about the human brain you didn’t know
The brain is an incredible muscle, however there are many things we do not know, and what we do know is not always...
Using Digital Tools to Support Students with Special Educational Needs
Special Educational Needs (SEN) encompass a wide range of learning difficulties and disabilities that can hinder a...
Down Syndrome and Communication: Facilitating Interaction with Visual and Interactive Supports
When we think about Down syndrome, we often recognize it as a genetic condition that affects physical and cognitive...
How to Track Progress in People with Down Syndrome Using Digital Tools
Down syndrome, a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, affects approximately 1 in every...