Work
its AUDITIVE GNOSIES


Preserving auditory gnosis
Reinforce the ability to identify, differentiate and interpret sounds

Reinforcing sound recognition
Associate sounds with specific objects, actions or events.

Applications in everyday life
Working on your attention with our games helps you to better perceive and understand sounds in the environment.

Auditory gnosia is the ability to perceive and understand spoken language. It’s a decoder that enables us to understand the person speaking to us.
What are auditory gnosias?
Auditory gnosia is therefore the ability to perceive sounds, elaborate them and give them meaning. This applies to both environmental sounds and language.
The first function of auditory gnosia is to distinguish between these two sounds. Our brain is then able to retrieve this sound from its memories, and give it meaning.
Our brain is also capable of giving different importance to the sounds it hears. For example, if we hear our first name, we’ll pay more attention. Or if we’re at home and hear the coffee pot whistling, we’ll go into the kitchen.
Auditory gnosis disorders
Auditory agnosia, on the other hand, is a disorder that results in a lack of understanding of spoken language and environmental sounds. The person is unable to decode the sounds he hears, without damaging his ear.
This type of disorder is generally caused by a lesion in the temporal lobe.
Depending on the symptoms, three types of auditory agnosia can be distinguished.
- Sound agnosia presents as an inability to identify sounds in the environment: we always hear the same sound, or confuse sounds with each other. However, sound agnosia does not impair speech comprehension.
- Verbal deafness or verbal agnosia affects the ability to recognize words, but does not affect the identification of environmental sounds.
- Phonagnosia no longer enables the subject to identify the voices of loved ones or well-known personalities.
The subject may also experience problems of expression, sometimes unable to decode his or her own words.
Exercises to train and improve auditory gnosis
You can train your auditory gnosis. You can listen to the sounds around you and try to identify as many as possible. Or you can listen to someone talking on TV, and clap your hands every time they say a specific word.
If you can practice with someone, take objects that make a noise when shaken (keys, a box of pasta, a newspaper, etc.). Turn your back to the person you’re with, and tell them to shake one of the objects, so you can recognize which object has been shaken.
Our games for working autobiographical memory
- Musical ear
- Colormind
- The Lost Poem
- Musical ear
- Colormind
- The Lost Poem

- Musical ear
- Colormind
- The Lost Poem
Auditory gnosias enable us to recognize all kinds of sound stimuli. Sounds are important information in the environment.
Here are the different types of information that can be obtained thanks to auditory gnosias :
1. Sound memorization
The environment is full of sounds and noises.
Auditory gnosias enable us to identify and recognize these sounds. This mechanism is very important, because we can find important information through sounds. For example, if we hear a car braking, we turn to see if it’s next to us.
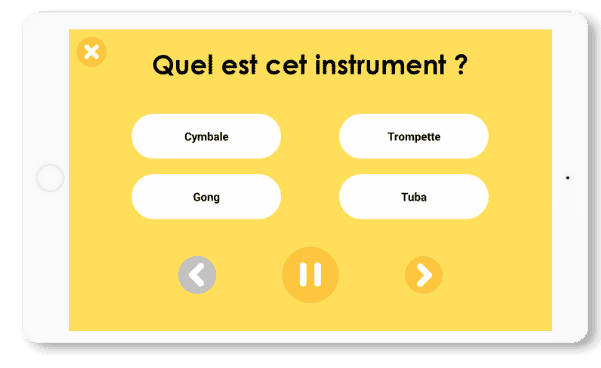
Musical ear
In this game, the player has to listen to sounds and recognize them. Different game modes allow the player to choose between recognizing a sound, an animal or an instrument.
With this exercise, we also work on auditory discrimination.
2. Word memorization
Auditory gnosias enable us to recognize the words we hear and give them meaning.
The first step is to recognize that a sound is actually a word, so we create a filter between environmental noise and language. We then have to recognize the word and look it up in our vocabulary to give it a meaning.
We’re always listening to what’s going on around us, and certain words catch our attention. For example, if someone calls your name, or if we hear about a film we want to see too.
3. Oral language comprehension
Language is a complex thing.
Several words are put together to form sentences, but depending on the words used and the context, the meaning of the sentence can change. Auditory gnosias enable us to understand spoken language in different forms.
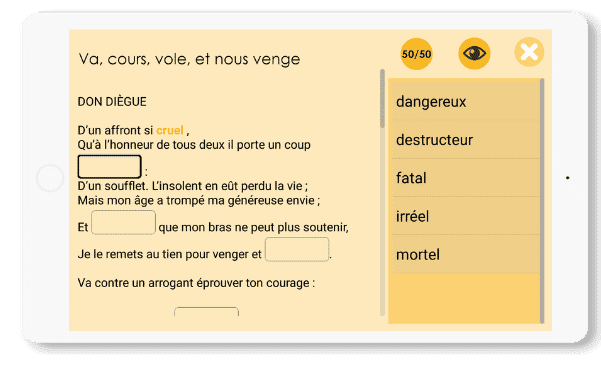
The Lost Poem
In this game, you listen to a poem and then find the missing words.
Listening to the poem, you need to understand the words and the meaning of the story. Then you have to remember the exact words, which means using semantic memory as well as context.
4. Immediate memorization of sound information
Our brain can store certain sound information in order to accomplish a task.
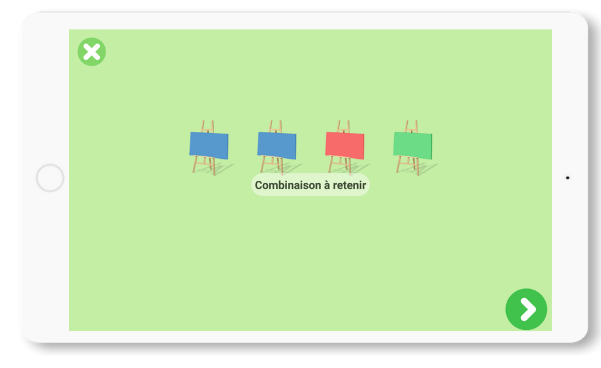
Colormind
In this game, you have to remember the proposed sequence.
Colored objects will appear on the screen, each color associated with a different sound.
We can therefore try to pay attention to the sound and remember the sequence of sounds rather than the colors.
Auditory gnosias are one of the cognitive functions needed to gather information and interact with the environment around us and with others.
Want to improve your auditory gnosis?
Our games have the following 3 impacts:
-
Stimulating auditory gnosis in everyday life: Our games are designed to train sound and noise recognition. For example, “The Musical Ear” game helps you distinguish different sounds and associate them with objects or actions, reinforcing your ability to identify and interpret sounds in your environment.
-
Reinforce sound recognition: Games encourage the ability to quickly identify sounds, as in “ColorMind”, where each color is associated with a different sound to be memorized.
-
Applications in everyday life: Working on your auditory gnosis with our games helps you to recognize sounds in a variety of situations, such as understanding complex conversations, distinguishing sound alerts or reacting to environmental noise in everyday life.
Discover our attention training programs with our coaches!
COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES
A version for children aged 5 to 10

CLINT
A preventive version for seniors

SCARLETT
An easy and adapted version for seniors

Follow a training program for 4 weeks
ATTENTION PROGRAM
For 4 weeks, follow our program to work on attention by playing our specially selected games for 15 minutes a day.
MEMORY PROGRAM
For 4 weeks, follow our program to work the memory by playing our specially selected games for 15 minutes a day.
LANGUAGE PROGRAM
For 4 weeks, follow our program to work on language by playing our specially selected games for 15 minutes a day.
PLANNING PROGRAM
For 4 weeks, follow our program to work on your planning by playing our specially selected games for 15 minutes a day.
PERCEPTION PROGRAM
During 4 weeks follow our program to work on perception by playing our specially selected games for 15 minutes a day.
Complementary exercises at home to work on your autobiographical memory
Identifying different sounds
-
Recognize the sounds of nature: Listen to recordings of natural sounds (rain, wind, birds) and try to identify them. This improves your ability to distinguish sounds in a natural environment.
-
Play a game of “mystery sounds”: Record different sounds from your environment (kitchen, street, forest) and try to recognize them. This stimulates the ability to identify sounds in a varied context.
Improving frequency perception
-
-
Distinguish between low and high-pitched sounds: Listen to a series of sounds ranging from low to high pitched, and try to classify them in order of frequency. This reinforces the ability to perceive and distinguish sounds by pitch.
-
Use sound frequency applications: Download an application that generates different sounds at different frequencies and practice recognizing them. This improves your auditory discrimination.
-
Developing speech comprehension
-
-
Listen to complex conversations: Listen to multi-person conversations, then try to summarize what was said. This helps you to better understand verbal exchanges in a noisy environment.
-
Follow verbal instructions: Ask someone to give you instructions to follow (for example, to prepare a recipe) while you concentrate solely on hearing. This develops the ability to understand and follow verbal information.
-
Improve auditory memory
-
Memorize a list of sounds: Listen to a series of sounds (e.g. bells, horns, laughter) and try to remember them after a while. This improves short-term auditory memory.
- Repeat phrases you’ve heard: Listen to a phrase or series of words and repeat them aloud immediately afterwards. This stimulates auditory memory and attention.
Identify sounds in noisy environments
-
-
-
Listen to sounds in context: Record background noise (e.g. a busy street) and try to distinguish the different sounds (cars, voices, sirens). This helps train auditory attention and sound discrimination in noisy environments.
-
Follow moving sounds: Follow a moving sound (e.g. a passing vehicle) and try to locate its position at different times. This develops directional perception of sounds.
-
-
Exercising selective auditory attention
-
-
Listen to a conversation in a noisy place: In a cafe or other noisy place, concentrate on one of several conversations. This enhances your ability to isolate a specific sound in a complex environment.
-
Follow a particular sound among others: Play a game where several sounds are emitted at the same time, but you have to concentrate on just one. This improves selective attention.
-
Practice voice recognition
-
-
Identify familiar voices: Listen to recordings of people speaking and try to recognize who is speaking without seeing their face. This improves your ability to identify voices in different contexts.
-
Associating voices with emotions: Listen to a conversation and try to identify participants’ emotions solely through the tone of their voice (joy, anger, sadness). This develops auditory recognition of emotional states.
-
Improve your understanding of music
-
-
-
-
Identify musical instruments: Listen to a musical composition and try to recognize the instruments used. This helps refine auditory discrimination and improve the ability to identify musical sounds.
-
Follow the rhythm of a song: Listen to a song and try to follow the rhythm by clapping or tapping your feet. This develops rhythm perception and auditory coordination.
-
-
-
Practicing sound discrimination
-
-
-
Compare similar sounds: Listen to two sounds that sound similar (for example, bells and chimes) and try to differentiate the subtleties between them. This improves your ability to distinguish between similar sounds.
-
Categorize sounds: Listen to a range of sounds (e.g. nature sounds, musical instruments, industrial noises) and categorize them. This helps you hone your ability to differentiate between types of sound.
-
-