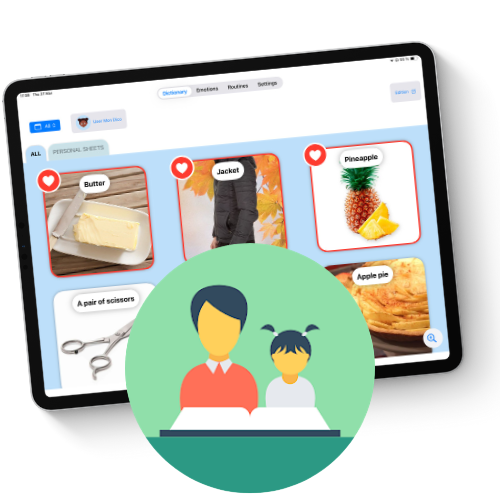
Boost your brain
with DYNSEO
Cognitive games and training programs designed with healthcare professionals, adapted to every need and every age — children, adults, and seniors.



Our commitments
Why choose DYNSEO?
Innovative & Fun
Games and training programs that stimulate your brain while having fun.
Personalized Programs
Games and training programs adapted to your level with more than 30 activities per application.
Designed with Professionals
Developed with neurologists, speech therapists, and psychologists.
For PROs & Families
Solutions for healthcare professionals as well as private customers.
No Internet Needed
Play offline, anywhere, anytime. Ideal for seniors and children.
Our players' favorites
Hover to discover each program!

COCO THINKS & COCO MOVES
Hover over me!COCO THINKS & COCO MOVES
The educational coach COCO offers your children both educational and physical games. Every 15 minutes of screen time, a physical activity break is required. Smart screen time, without the need for internet.

COCO THINKS & COCO MOVES
The educational coach COCO offers your children both educational and physical games. Every 15 minutes of screen time, a physical activity break is required.

CLINT, YOUR BRAIN COACH
Hover over me!CLINT, YOUR BRAIN COACH
With your brain coach CLINT, train your mind with logic and strategy games, as well as games focused on culture, geography, and literature.

CLINT, YOUR BRAIN COACH
Train your brain with logic, strategy, culture, and geography games. Choose which cognitive functions to stimulate.

SCARLETT, YOUR MEMORY COACH
Hover over me!SCARLETT, MEMORY COACH
Your coach SCARLETT offers you over 30 easy and adapted memory games on tablet. No timer or score – the most important thing is to enjoy playing.

SCARLETT, YOUR MEMORY COACH
Over 30 easy and adapted memory games. No timer or score, the most important thing is to enjoy playing. No internet needed!
AI Coach Assist
Want to play with someone? The AI Coach accompanies each player by voice: it chats, suggests adapted games, and launches them automatically.
A warm vocal companion, always available, making each session more lively and engaging.

AI Coach Assist
Online




Our offers with tablet
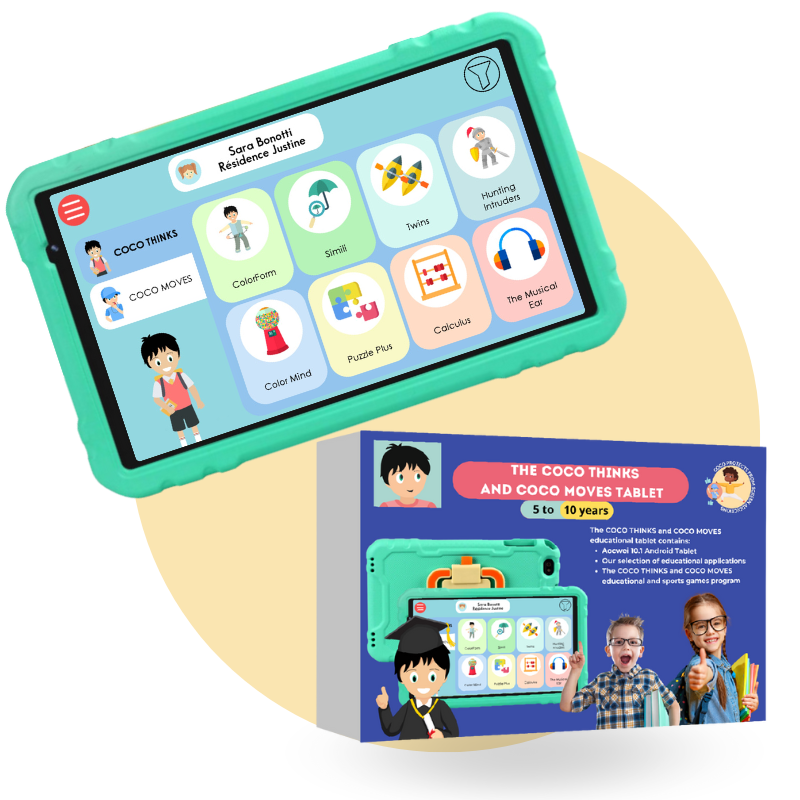

EDUCATIONAL TABLET COCO
Hover over me!EDUCATIONAL TABLET COCO
Offer smart screen time with the COCO THINKS and COCO MOVES tablet, designed for children aged 5 to 10: over 30 educational games and physical activity breaks every 15 minutes. Lifetime warranty!
$ 160

EDUCATIONAL TABLET COCO
Over 30 educational games and physical activity breaks every 15 minutes. Lifetime warranty, it's the only screen that truly gets them moving!
$ 160

SCARLETT TABLET
Hover over me!SCARLETT TABLET
The SCARLETT tablet is seniors' favorite gaming tablet for gently stimulating memory, with over 30 cognitive games developed with healthcare professionals. Delivered ready to use, with no need for internet, on a large screen Samsung tablet.

SCARLETT TABLET
Gently stimulate memory with over 30 cognitive games. Delivered ready to use, without internet, on a large screen Samsung tablet.

HOME ASSISTANCE
TOOLBOX
Hover over me!
HOME ASSISTANCE TOOLBOX
Supports professionals (SAAD, SSIAD, ESA…) with cognitive stimulation games that work without Wi-Fi, helping to build connections, value seniors, and restore their self-confidence. Designed with healthcare professionals.

HOME ASSISTANCE
TOOLBOX
Cognitive stimulation games without Wi-Fi for home assistance professionals. Build connections and restore seniors' confidence.
Our other apps to boost your brain
Thousands of professionals
won over by our innovations
Discover our dedicated solutions for the medical, educational, and home care sectors.
Health professionals
Tools designed with speech therapists, psychologists, and occupational therapists for cognitive rehabilitation.
Schools & Education
Educational programs for special education, adapted learning, and inclusive classrooms.
Home assistance
Support for SAAD, SSIAD, and ESA professionals with turnkey stimulation tools.
Establishments
Solutions for nursing homes, day care centers, rehabilitation centers, and senior living residences.
For each specific need,
its customized solution!
Autism, DYS, ADHD, stroke, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s… We have a solution for every need.
1 Million+
of smiles generated!!!
With a professional, at home, at school, in hospital, with a loved one, in peace and quiet, in a group… Playing is good for your health. So smile with us!












They trust us